I remember the first time I walked into a bustling warehouse; the hum of forklifts, the chatter of workers coordinating shipments, and the sheer energy of the place was overwhelming. It was then that I realized just how vital logistics is in our everyday lives. Whether it's the coffee we sip in the morning or the gadgets we use daily, logistics ensures that products reach us efficiently and effectively.
Understanding the Essence of Logistics
Introduction
Logistics Overview
System Approach for Info Flow
Coordination
Conclusion
At its core, logistics is more than just moving goods from point A to point B. It's a complex system that coordinates various activities, ensuring that materials flow smoothly from suppliers to customers. This coordination isn't just about transportation; it encompasses inventory management, warehousing, order processing, and more.
The System Approach to Information Flow
One of the key elements in logistics is the system approach to information flow. This approach views the entire supply chain as an interconnected system where information is just as crucial as the physical movement of goods. By effectively managing information, companies can make better decisions, reduce delays, and improve customer satisfaction.
Optimizing Logistics Management Balancing Stock And Service Levels
Collaborative Logistics Strategies For Supply Chain Efficiency
When I worked with a small retail company, we faced challenges with our order processing. Orders were often delayed because we didn't have a streamlined system. Implementing a system approach, we began registering, checking, and editing orders meticulously. This not only reduced errors but also improved our delivery times.
Steps in the System Approach:
1- Order Registration: Collecting essential information about the order and customer.
2- Order Checking: Verifying the accuracy of the order details.
3- Order Editing: Making necessary adjustments to ensure everything is correct.
4- Order Processing: Coordinating the actual movement of materials to fulfill the order.
Underlined emphasis: Order Processing is where the magic happens; it's the culmination of all prior steps.
The Importance of Coordination
In logistics, coordination is like the glue that holds everything together. Without it, even the most efficient systems can fall apart. When different departments—like procurement, warehousing, and transportation—work in silos, it leads to delays, errors, and increased costs.
I recall a time when a lack of coordination led to a significant issue. Our procurement team ordered materials without informing the warehouse. When the shipment arrived, there was no space, leading to additional storage costs. This taught us the importance of interdepartmental communication and coordination.
The Interdependence of Logistics Activities
Every activity in logistics is interdependent. For instance, timely transportation depends on accurate order processing, which in turn relies on effective information flow. Recognizing these dependencies helps businesses optimize their operations.
Strategies for Effective Coordination
To enhance coordination, companies can adopt several strategies:
Logistics Management is an organized system for the flow of information and coordination of resources.
Regular Meetings: Holding frequent meetings between departments to discuss ongoing projects.
Integrated Systems: Using software that allows different departments to access and update information in real-time.
Clear Communication Channels: Establishing protocols for information sharing.
Training Programs: Educating employees about the roles and challenges of other departments.
Collaborative Platforms: Implementing tools that facilitate collaboration and information sharing.
The Role of Technology
Technology plays a significant role in modern logistics. With advancements like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT), companies can monitor shipments in real-time, predict delays, and optimize routes.
For example, using GPS tracking, a logistics manager can see where a shipment is at any moment. If there's an unexpected delay, they can inform the customer promptly, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Technology in Logistics:
Improved Efficiency: Automation reduces manual errors.
Cost Reduction: Optimized routes and processes save money.
Better Decision Making: Access to real-time data aids in making informed choices.
Enhanced Transparency: Customers can track their orders, improving trust.
Italicized note: Technology isn't just a tool; it's a catalyst for transformation in logistics.
Ethical Dilemmas in Logistics
While technology and strategies improve logistics, they also bring about ethical dilemmas in supply chain management. Questions arise around labor practices, environmental impact, and data privacy.
During interviews for logistics positions, candidates are often asked about ethical dilemmas in supply chain management interview questions. They might be asked how they would handle situations like:
Choosing between cost reduction and fair labor practices.
Prioritizing speed over environmental concerns.
Handling sensitive customer data.
It's crucial for logistics professionals to navigate these dilemmas thoughtfully, balancing business goals with ethical considerations.
Underlined insight: Making ethical choices isn't always easy, but it's essential for long-term success.
Real-World Examples
Case Study: Efficient Logistics at ABC Corp
ABC Corp, a leading electronics manufacturer, revamped its logistics by adopting a system approach. They integrated their information flow, ensuring that all departments had access to up-to-date data.
Results:
30% Reduction in delivery times.
20% Cost Savings due to optimized routes.
Increased Customer Satisfaction from timely deliveries.
Personal Experience with Coordination Challenges
In my previous role, I was part of a team responsible for launching a new product. Despite meticulous planning, we faced delays because our suppliers weren't informed about the change in manufacturing schedules. This oversight highlighted the critical role of coordination in logistics.
The Human Element in Logistics
Behind every successful logistics operation are dedicated individuals working tirelessly. From the warehouse workers ensuring items are correctly picked and packed to the drivers navigating through traffic to deliver goods on time, each person's role is crucial.
Personal Anecdote:
While volunteering for a disaster relief organization, I witnessed how critical logistics is in crisis situations. Coordination was vital to ensure supplies reached affected areas promptly. We had to manage interdependent activities, such as sourcing supplies, coordinating transportation, and liaising with local authorities. The experience taught me that logistics isn't just a business function; it's also about making a real difference in people's lives.
Challenges in Logistics Coordination
Despite its importance, coordination in logistics faces several challenges:
Communication Barriers: Differences in language and time zones can hinder effective communication.
Technology Gaps: Not all partners may have access to the same technology, leading to information silos.
Cultural Differences: Varying business practices can cause misunderstandings.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating different legal requirements across regions adds complexity.
Addressing the Challenges:
1- Implementing Universal Communication Tools: Utilize platforms that support multiple languages and real-time communication.
2- Standardizing Processes: Establish common procedures and protocols.
3- Training and Development: Invest in cross-cultural training for employees.
4- Staying Informed: Keep up-to-date with international regulations and compliance requirements.
5- Building Strong Relationships: Foster trust with partners and suppliers.
Italicized wisdom: Overcoming challenges requires patience, persistence, and proactive strategies.
The Impact of Globalization
With globalization, supply chains have become more complex. Companies source materials from various parts of the world, making logistics coordination even more critical. An efficient logistics process ensures that despite the distances, products reach customers effectively.
For instance, a smartphone may have components from multiple countries. Coordinating the production and delivery of these components requires meticulous planning and execution.
Sustainability in Logistics
Today, there's a growing emphasis on sustainability. Companies are re-evaluating their logistics operations to reduce their environmental footprint.
Sustainable Practices Include:
Optimizing Routes: Reducing fuel consumption by planning efficient delivery routes.
Utilizing Alternative Energy: Using electric vehicles or other green energy sources.
Reducing Packaging Waste: Implementing eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Reverse Logistics: Managing the return and recycling of products.
Underlined fact: Sustainability isn't just good for the planet; it's good for business.
Ethical Considerations
As mentioned earlier, logistics professionals often face ethical dilemmas. Balancing cost efficiency with ethical practices is a challenge.
Common Ethical Dilemmas:
Labor Practices: Ensuring fair wages and working conditions in all parts of the supply chain.
Environmental Impact: Deciding between faster delivery options that may have a higher carbon footprint versus slower, more sustainable methods.
Data Privacy: Protecting customer and partner data in an era where information flow is critical.
It's essential for professionals to not only be aware of these dilemmas but to prioritize ethical decision-making. This is not just beneficial for the company's reputation but also for long-term sustainability.
Preparing for Ethical Questions in Interviews
For those pursuing careers in logistics and supply chain management, being prepared to answer questions about ethical dilemmas is crucial.
Example Interview Question:
"Can you describe a time when you faced an ethical dilemma in supply chain management and how you resolved it?"
Answer Strategy:
Reflect on Past Experiences: Think of real situations where you had to make tough decisions.
Highlight Your Decision-Making Process: Explain how you weighed the pros and cons.
Emphasize Ethical Considerations: Show that you prioritize ethics over short-term gains.
Discuss the Outcome: Share the results of your decision.
Italicized tip: Be honest and sincere; interviewers appreciate authenticity.
The Role of Leadership in Logistics
Strong leadership is vital in ensuring effective logistics operations. Leaders set the tone for coordination, communication, and ethical practices.
Leadership Qualities Important in Logistics:
Strategic Thinking: Ability to see the big picture and plan accordingly.
Excellent Communication: Facilitating clear and open communication channels.
Adaptability: Being flexible in response to unforeseen challenges.
Empathy: Understanding the needs of team members and stakeholders.
Integrity: Upholding ethical standards in all decisions.
I once worked under a manager who, during peak seasons, would personally assist in the warehouse. His hands-on approach not only boosted team morale but also improved overall efficiency.
Education and Training
To excel in logistics, continuous learning is essential. With evolving technologies and practices, staying updated is crucial.
Recommended Areas of Study:
Supply Chain Management: Understanding the end-to-end process.
Information Systems: Learning about software and tools used in logistics.
Project Management: Developing skills to manage complex projects.
Ethics and Compliance: Being aware of legal and ethical standards.
Sustainability Practices: Learning how to implement eco-friendly solutions.
Underlined reminder: Education doesn't stop at graduation; it's a lifelong journey.
Bullet Points: Tips for Effective Logistics Management
Implement Real-Time Tracking: Use GPS and RFID technology.
Foster Interdepartmental Collaboration: Encourage teams to work together.
Regularly Review Processes: Identify areas for improvement.
Invest in Employee Training: Equip staff with the necessary skills.
Prioritize Customer Feedback: Use it to enhance services.
Adopt Sustainable Practices: Reduce environmental impact.
Stay Updated with Technology: Embrace new tools and systems.
Numbered List: Steps to Improve Coordination
1- Assess Current Processes: Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
2- Set Clear Objectives: Define what you aim to achieve.
3- Choose the Right Tools: Select software and technologies that fit your needs.
4- Train Your Team: Ensure everyone knows how to use new systems.
5- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly check progress and make necessary adjustments.
6- Encourage Feedback: Listen to suggestions from team members.
7- Celebrate Successes: Acknowledge and reward effective coordination.
Italicized encouragement: Small steps lead to significant improvements over time.
The Future of Logistics
As we look ahead, logistics will continue to evolve. Embracing new technologies and strategies will be essential. However, the fundamental principles of effective information flow and coordination will remain constants.
Emerging Trends:
Sustainable Logistics: Focusing on environmentally friendly practices.
Blockchain Technology: Enhancing transparency and security in the supply chain.
Robotics and Automation: Increasing efficiency in warehouses and transportation.
Data Analytics: Leveraging big data to make predictive decisions.
Artificial Intelligence: Using AI for demand forecasting and route optimization.
Underlined emphasis: The future is not just about moving goods faster; it's about moving smarter.
Conclusion
Logistics is the heartbeat of any business that deals with physical products. By adopting a system approach to information flow and emphasizing coordination, companies can achieve efficient and effective movement of materials. Whether it's through embracing technology or refining communication strategies, the goal remains the same: delivering value to the customer.
In my journey, I've seen firsthand how a well-coordinated logistics system can transform a business. It's not just about moving goods; it's about creating a seamless experience for everyone involved. As we navigate the complexities of the modern supply chain, let's remember the importance of coordination, the power of information, and the impact of our choices.
References
Ballou, R. H. (2004). Business Logistics/Supply Chain Management. Pearson Education.
Bowersox, D. J., Closs, D. J., & Cooper, M. B. (2013). Supply Chain Logistics Management. McGraw-Hill.
Chopra, S., & Meindl, P. (2016). Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation. Pearson.
Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & Supply Chain Management. Financial Times Press.
Rushton, A., Croucher, P., & Baker, P. (2014). The Handbook of Logistics and Distribution Management. Kogan Page Publishers.
Simchi-Levi, D., Kaminsky, P., & Simchi-Levi, E. (2007). Designing and Managing the Supply Chain. McGraw-Hill.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of using a system approach for information flow and coordination in logistics management?
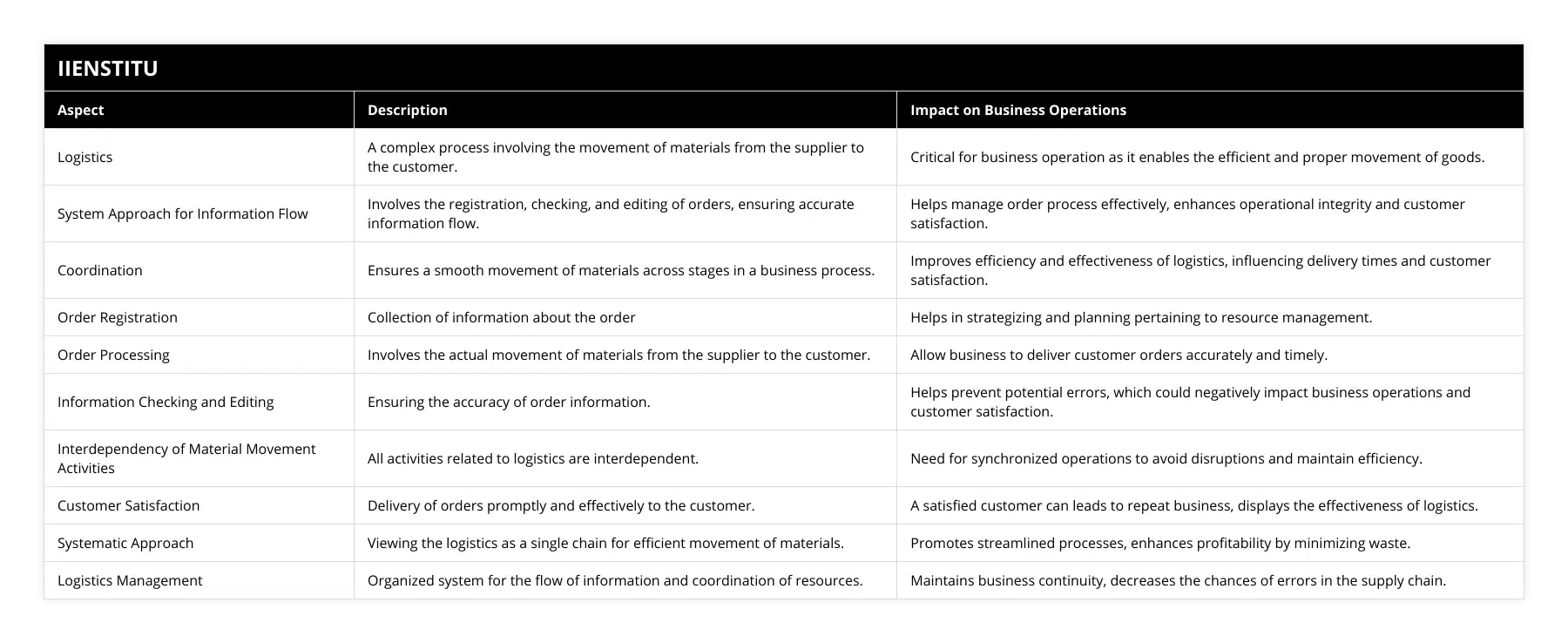
Logistics management is a complex process involving coordinating resources, personnel, and materials to ensure the efficient delivery of goods and services. A system approach to information flow and coordination can significantly benefit logistics management.
The advantages of using a system approach for information flow and coordination in logistics management include increased efficiency, improved communication, better decision-making, and enhanced customer service.
Efficiency is improved when a systematic approach is used for information flow and coordination. The system can reduce the time and resources needed to carry out tasks by streamlining the process. It can also reduce the paperwork for tracking and managing materials and personnel. Additionally, a systematic approach can help to reduce mistakes and errors, resulting in a more efficient and accurate process.
A system approach can also improve communication between personnel, vendors, customers, and other stakeholders. By making information more accessible to all parties, decision-making can be improved. With a system approach, stakeholders can see the latest information in real-time, enabling them to act quickly and make better decisions.
A system approach can also enhance customer service. By providing customers with timely and accurate information, they can make better decisions and be more satisfied with their experience. Additionally, customers can be kept up to date on order status and delivery details, allowing them to plan accordingly.
In conclusion, a system approach for information flow and coordination can significantly benefit logistics management. It can increase efficiency, improve communication, enhance decision-making, and improve customer service. By utilizing this approach, organizations can ensure better management of resources, personnel, and materials, resulting in the more efficient and effective delivery of goods and services.
How can a system approach for information flow and coordination improve the efficiency of logistics operations?
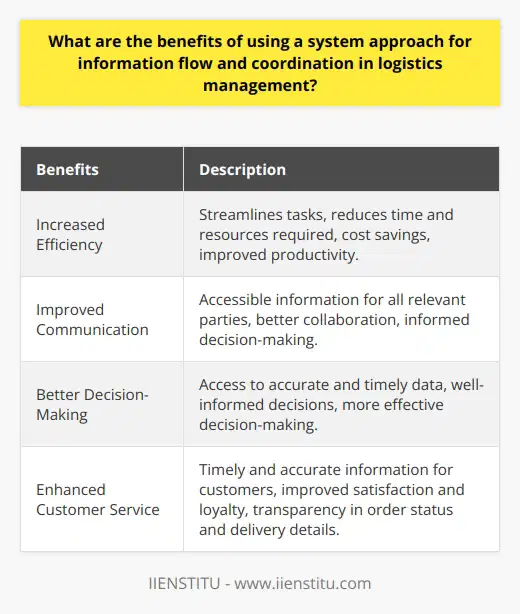
Logistics is an essential part of any business, and its efficiency can significantly impact a company’s performance. Thus, it is essential to consider how a system approach for information flow and coordination can improve the efficiency of logistics operations.
To start, a system approach for information flow and coordination requires a unified data source that all stakeholders can access. This data source must be up-to-date and reliable so all stakeholders can access the same information. Additionally, a secure platform should be implemented to ensure that the data is protected from unauthorized access.
The next step is ensuring the data is properly organized and structured. This can be done through Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, which allow for data integration from different sources. This integration can enable stakeholders to access the data quickly and accurately.
In addition to data integration, a system approach for information flow and coordination should include automated processes. Automation can help reduce the time spent on manual tasks, such as data entry or report generation. Automation can also help to reduce the number of errors that occur due to manual processes.
Finally, a system approach for information flow and coordination should also focus on communication. The goal is to ensure that stakeholders can communicate clearly and effectively so that problems can be identified and resolved quickly. This can be accomplished by implementing a communication platform, such as a chatbot or a customer relationship management (CRM) system.
To conclude, a system approach for information flow and coordination can improve the efficiency of logistics operations. Companies can improve their logistics operations and increase efficiency by implementing a unified source of data, integrating data from different sources, automating processes, and focusing on communication.
What strategies can be employed to ensure effective coordination between different stakeholders in logistics management?
Logistics management involves coordinating many stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, carriers, warehouses, and third-party logistics providers. Effective coordination between these stakeholders is essential for successful logistics operations.
A key strategy for ensuring effective coordination between stakeholders is developing and implementing clear communication protocols. This can be done by setting up regular meetings between the stakeholders and establishing a communication process that is easy to follow. For example, having a designated contact person for each stakeholder and clearly defining roles and responsibilities can help ensure that all stakeholders are aware of their responsibilities and that communication flows smoothly.
Another important strategy is ensuring all stakeholders have access to the same information. Stakeholders can easily access and share data such as inventory levels, shipment status, and delivery times by having a centralized information system, such as an enterprise resource planning system. This ensures that all stakeholders have access to the same information, enabling them to make more informed decisions and coordinate their activities more efficiently.
In addition, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the objectives and goals of the logistics management operation. All stakeholders should know the objectives and the strategies necessary to achieve them. This ensures that everyone is working towards the same goals and that coordination between the stakeholders is more effective.
Finally, it is essential to establish an effective feedback mechanism for stakeholders. This allows them to provide feedback on their experiences and can help identify any issues or opportunities for improvement.
In conclusion, effective coordination between stakeholders in logistics management is essential for successful logistics operations. By following the strategies outlined above, organizations can ensure that all stakeholders are aware of their responsibilities, have access to the same information, understand the objectives and goals of the operation, and provide feedback on their experiences. This will ultimately lead to improved stakeholder coordination and more successful logistics operations.
What is the role of information flow in achieving effective logistics management?
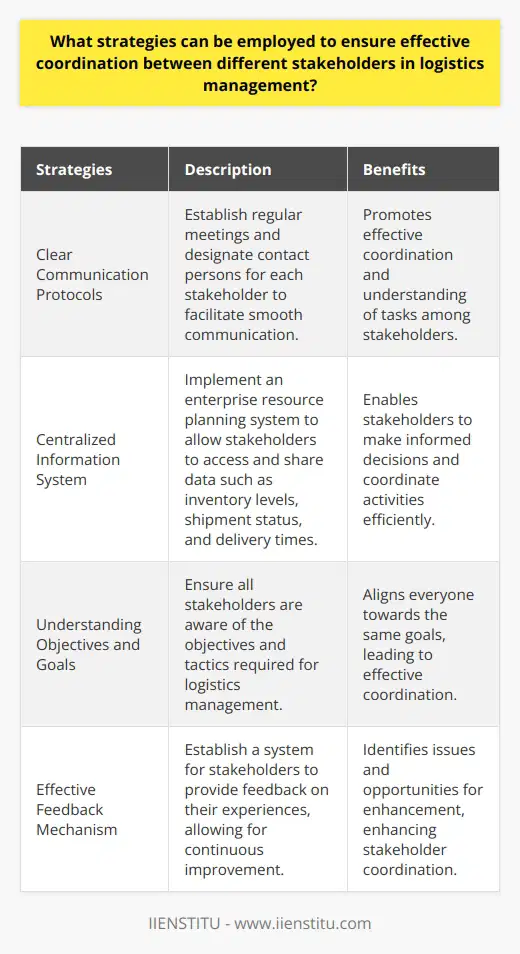
Role of Information Flow
In essence, effective logistics management relies heavily on the proper flow of information throughout the supply chain. This flow entails the seamless transfer of data between various stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, transporters, and buyers. Accurate and timely information sharing provides a solid foundation for sound decision-making processes and ensures all elements of the supply chain work in harmony.
Enhancing Coordination and Integration
Information flow fosters better coordination and integration among different parties involved in supply chain operations. By having access to real-time data on inventory levels, supply, and demand, relevant stakeholders can synchronize their actions to adapt to changes, optimize resource utilization, and minimize potential disruptions.
Optimizing Transport and Delivery
In the context of logistics management, information flow is crucial for streamlining transport and delivery processes. Through the exchange of information on cargo status, shipment schedules, and delivery routes, transportation efficiency can be improved, resulting in reduced shipping costs and delivery timelines.
Facilitating Inventory Management
Robust data exchange supports efficient inventory management by providing insights into current stock levels, historical usage patterns, and projected demand trends. As a result, businesses can fine-tune their inventory procurement and replenishment strategies, ensuring the availability of the right products in the right quantities, thus preventing stockouts and overstock situations.
Improving Customer Satisfaction
Lastly, effective information flow contributes to enhanced customer satisfaction by enabling supply chain visibility and allowing businesses to provide accurate order status updates, timely deliveries, and personalized services. This transparency and open communication ultimately foster trust and loyalty between the company and its customers.
In conclusion, information flow plays a critical role in achieving effective logistics management by enhancing coordination among supply chain partners, optimizing transport and delivery operations, facilitating efficient inventory management, and improving overall customer satisfaction. Implementing advanced technologies and robust communication practices can help ensure the seamless flow of information, ultimately driving supply chain excellence.
How can a system approach in logistics management contribute to the overall sustainability of a supply chain?
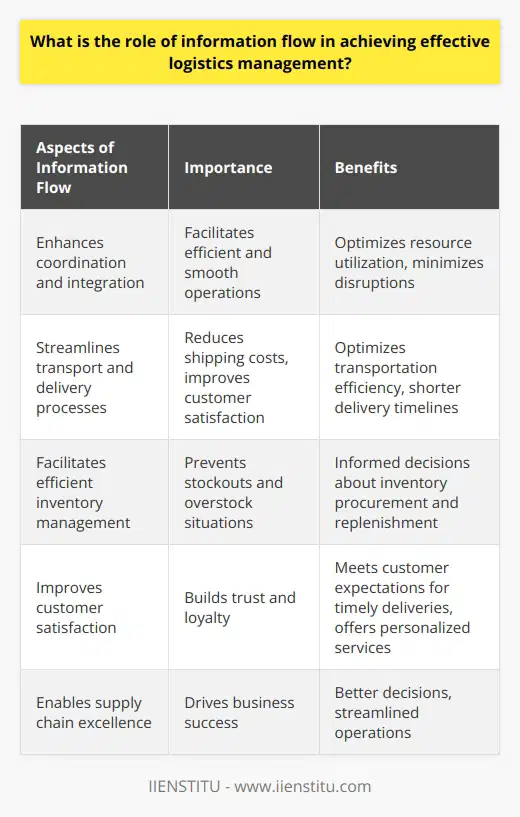
System Approach in Logistics Management
A system approach in logistics management provides a holistic perspective to the supply chain, considering all the interconnected components and processes as a single entity. By adopting this approach, organizations can effectively identify areas of improvement and potential bottlenecks, leading to enhanced sustainability throughout the entire supply chain.
Efficient Resource Utilization
Through the system approach, organizations can optimize the use of resources such as energy, materials, and labor. By identifying areas where resources are underutilized or wasted, it becomes possible to implement strategies that reduce the overall consumption of resources, thus promoting sustainability.
Reduced Transport Emissions
Another benefit of employing a system approach in logistics management is the reduction of transport-related emissions. By analyzing the entire supply chain, organizations can devise transportation strategies that effectively minimize the distance traveled by goods and the associated environmental impact. This can lead to a decrease in harmful greenhouse gas emissions and reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
Collaborative Supply Chain Relationships
A system approach also encourages collaboration among stakeholders within the supply chain. Establishing strong relationships between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors fosters communication and information sharing, which can lead to joint efforts in enhancing sustainability. This collaboration can result in the creation of innovative solutions for reducing waste and improving resource efficiency across the supply chain.
Increased Flexibility and Adaptability
By considering the entire supply chain as a single system, organizations can improve the flexibility and adaptability of their logistics operations. This approach allows for the development of contingency plans that ensure the supply chain can continue to function efficiently and sustainably in the face of unexpected disruptions. Such resilience is crucial in a rapidly changing global marketplace.
Supplier Assessment and Development
Lastly, a system approach in logistics management allows organizations to evaluate the sustainability performance of suppliers and support their development in this area. Engaging in supplier development initiatives is crucial for promoting the overall sustainability of the supply chain, as it ensures that suppliers adhere to environmental and social standards.
In conclusion, adopting a system approach in logistics management can significantly contribute to the overall sustainability of the supply chain. Through the efficient utilization of resources, reduced transport emissions, collaborative relationships, increased flexibility, and supplier assessment, organizations can enhance sustainability and ensure their operations are environmentally and socially responsible.
What are the key factors to consider when implementing a logistics system approach for optimizing information flow and coordination?
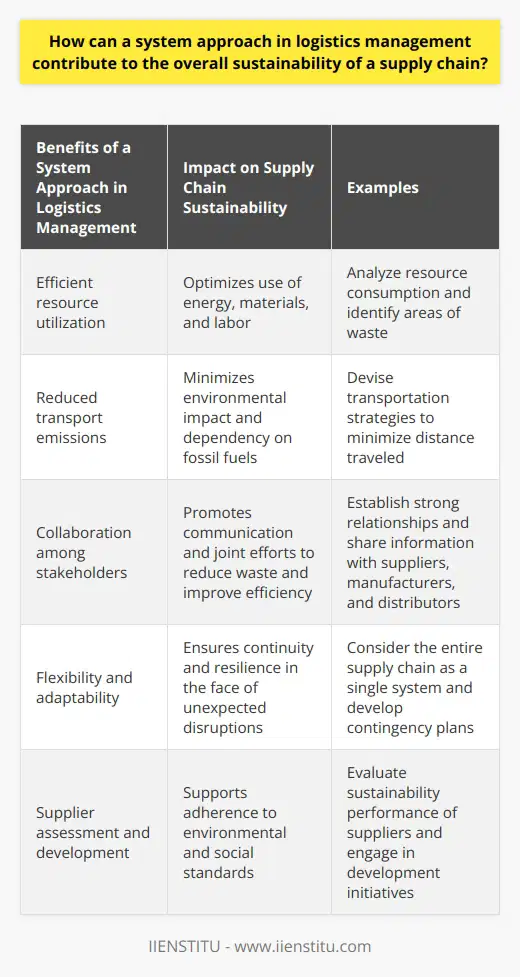
Logistics System Approach: Key Factors
Effective Coordination and Communication
Efficient information flow and coordination are crucial in implementing a logistics system approach. Robust communication channels help stakeholders ensure well-orchestrated operations and prevent the gap of misinterpretation between different stages in the supply chain. This way, organizations can react promptly to any unforeseen events, minimizing downtime and performance inefficiencies.
Integration of Technologies
Incorporating cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) can greatly enhance a logistics system approach. These innovations are invaluable for reducing manual intervention, improving reporting accuracy, and fostering data-driven decision-making to accelerate overall performance - seamlessly linking transport, warehousing, and order fulfillment activities.
Vendor and Partnership Management
Effective vendor and partnership management play a crucial role in implementing a logistics system approach. Businesses must establish strong relationships with all relevant entities in the supply chain network. Cooperation, trust, and synchronization are vital components for information exchange, risk distribution, and optimal operational performance.
Customizing Logistics Strategies
Understanding the specific needs of a business is critical to establishing a well-organized logistics system approach. Customizing strategies accordingly enables organizations to address their unique challenges in different stages of the supply chain - such as procurement, transportation, warehousing, and delivery. Tailored strategies also enable real-time adjustments and quick decision-making processes in reaction to shifting market trends.
Continuous Improvement and Learning
Fostering continuous improvement and learning within your organization's logistics operations is vital for optimizing information flow and coordination. Adopting best practices, monitoring performance indicators, and facilitating ongoing development allows for better compliance with emerging regulations, greater cost savings, and enhanced efficiencies in supply chain management.
In conclusion, implementing a logistics system approach for optimizing information flow and coordination involves a combination of effective communication, integration of advanced technologies, sound vendor and partnership management, customization of strategies, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Adopting these considerations will assist organizations in optimizing their supply chain processes to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
What is the role of a systems approach in identifying bottlenecks and improving efficiency in logistics management?
Role of Systems Approach in Identifying Bottlenecks
A systems approach plays a crucial role in logistics management by providing a comprehensive framework to analyze bottlenecks and inefficiencies within the entire supply chain. By examining the interdependencies between different elements of the logistics network, the systems approach enables supply chain professionals to pinpoint the root causes of inefficiencies and develop appropriate strategies to optimize performance.
Holistic Analysis of Supply Chain
The systems approach involves a holistic analysis of the supply chain, accounting for the interactions between various components, such as transportation, storage, and order processing. This comprehensive view allows practitioners to detect not only the immediate sources of bottlenecks but also the indirect factors contributing to suboptimal performance. Consequently, logistics managers can make informed decisions to improve operational efficiency by addressing critical points across the chain.
Continuous Improvement through Feedback Loops
Incorporating feedback loops into the systems approach facilitates continuous improvement in logistics management. By regularly monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and collecting data on the entire supply chain, managers can make data-driven decisions to enhance efficiency. Furthermore, the feedback loops allow potential bottlenecks to be identified in advance, helping managers to proactively adjust operations before these inefficiencies impact overall performance.
Coordination and Collaboration
The systems approach promotes coordination and collaboration among various stakeholders in the logistics process, increasing the effectiveness of the supply chain. By considering the perspectives of suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers, the approach fosters cross-functional communication, which facilitates the identification of bottlenecks and the implementation of mutually beneficial improvements. This collaborative mindset is crucial to achieving efficiency gains in logistics management.
Adoption of Technology and Innovation
The systems approach encourages the adoption of advanced technologies and innovation to improve logistics management. By integrating the latest advancements—such as artificial intelligence, automation, and blockchain—into the logistics process, organizations can enhance visibility, increase agility, and optimize resource utilization. This modernization, driven by a system-wide outlook, helps overcome bottlenecks and increase efficiency in the complex and dynamic logistics landscape.
In summary, the systems approach offers a comprehensive, proactive, and collaborative framework for identifying bottlenecks and improving efficiency in logistics management. By analyzing the entire supply chain and its interdependencies, incorporating feedback loops for continuous improvement, fostering collaboration among stakeholders, and embracing technology and innovation, the systems approach emerges as a vital tool for enhancing logistical performance.

How does the effective management of logistics information systems contribute to risk mitigation and decision-making processes?
Roles of Logistics Information Systems in Risk Mitigation
Effective management of logistics information systems (LIS) plays a crucial role in mitigating risks associated with supply chain operations. LIS provide real-time visibility of inventory levels, product locations, and transportation routes, allowing decision-makers to identify bottlenecks, forecast demand, and allocate resources optimally.
Data-driven Decision-making Processes
Through data analytics capabilities, LIS enable managers to make informed decisions based on historical and current data trends. By analyzing patterns in customer orders, transit times, and supplier reliability, decision-makers can design strategies that minimize the risk of stockouts, delays, and supplier failures.
Improved Transparency and Accountability
An efficient LIS supports transparency and accountability within supply chain networks. By tracking the movement of goods and documenting transactions, LIS facilitates the identification of errors, fraud, or inefficiencies. This information empowers managers to address these issues quickly, thus mitigating risks and improving overall supply chain performance.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
LIS facilitate seamless communication and collaboration among stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, carriers, and customers. This interconnectedness enables faster and more accurate decision-making processes, as organizations can easily share critical information, anticipate potential challenges, and develop coordinated responses to mitigate risks.
Proactive Risk Management Strategies
The predictive analysis feature of LIS allows organizations to anticipate risks and develop proactive strategies to manage them. For example, by analyzing weather patterns and transportation schedules, businesses can prepare contingency plans in case of disruptions caused by natural disasters or unforeseen delays. By staying ahead of potential risks, organizations can prevent catastrophic failures and maintain smooth operations.
In conclusion, the effective management of logistics information systems contributes significantly to risk mitigation and decision-making processes in supply chain management. By leveraging data-driven insights, improving transparency, facilitating communication, and enabling proactive risk management strategies, businesses can optimize their operations and minimize the likelihood of disruptions.
In the context of supply chain resilience, how can a logistics system approach facilitate better communication and collaboration among various stakeholders?
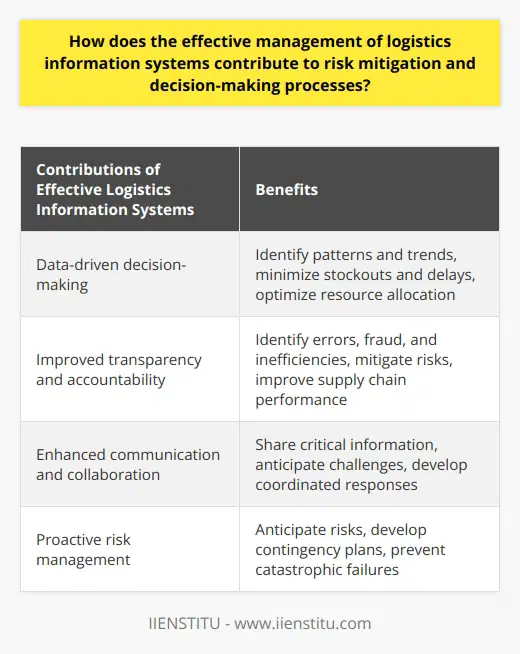
**Logistics System Approach in Supply Chain Resilience**
A logistics system approach can enhance supply chain resilience by facilitating seamless communication and collaboration among various stakeholders. This strategy involves integration, information sharing, and involvement from all parties involved in the supply chain.
**Integration of Stakeholders**
Integrating different stakeholders in the supply chain helps promote smooth coordination across various channels during operations. This integration allows for efficient collaboration, resulting in a more resilient supply chain. It enables organizations to better manage risks, anticipate disruptions, and respond to unforeseen events.
**Information Sharing and Transparency**
Real-time information sharing and transparency among supply chain stakeholders play an essential role in reinforcing resilience. Timely data exchange ensures the early identification of potential risks, allowing stakeholders to implement appropriate mitigation strategies. Streamlined communication further allows for efficient collaboration and decision-making, ultimately leading to a more resilient logistics network.
**Active Stakeholder Involvement**
Encouraging active involvement of all supply chain stakeholders ensures a comprehensive understanding of the logistics network. By engaging and involving all relevant parties, logistical challenges can be addressed effectively, enhancing the supply chain's overall resilience. Active stakeholder collaboration fosters a sense of collective responsibility, improving the system's ability to withstand and recover from disruptions.
In conclusion, a logistics system approach is vital for establishing strong communication and collaboration among supply chain stakeholders, ultimately contributing to increased resilience. Integrating stakeholders, fostering information sharing, transparency, and encouraging active involvement across the supply chain help organizations better manage risks, anticipate disruptions, and ensure efficient operations.
What is the role of a system approach in managing the complexity and uncertainty inherent in logistics management?
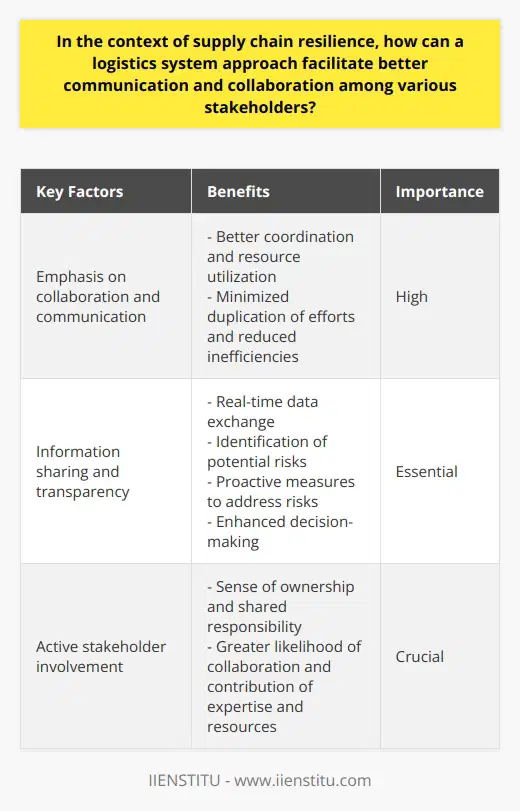
Role of a System Approach in Logistics Management
Understanding Complexities
A system approach plays a crucial role in managing the complexity and uncertainty inherent in logistics management by holistically considering the various interrelated components. It helps in understanding the intricacies and dependencies of different elements, including transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and information systems.
Handling Uncertainties
The system approach assists in dealing with uncertainties by identifying potential risks, analyzing their impact, and developing robust contingency plans. Through scenario planning and simulations, organizations can anticipate potential disruptions and devise strategies for swift recovery and adaptation.
Optimizing Resources
One of the key benefits of adopting a system approach is the effective utilization of resources. By considering the logistics network as a whole, decision-makers can optimize the allocation of resources, such as vehicles, storage facilities, and workforce, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
Improving Coordination
The system approach fosters better coordination and communication between various stakeholders, such as suppliers, carriers, and customers. By aligning their goals and operations, organizations can facilitate seamless information exchange, allowing for improved planning and execution across the supply chain.
Promoting Collaboration
The role of a system approach in managing complexity and uncertainty also extends to promoting collaboration across different departments, functions, and organizations. This collaborative approach helps in addressing challenges, sharing knowledge, and pooling resources, resulting in improved logistics performance.
Enhancing Flexibility
Lastly, the system approach aids in enhancing the flexibility and adaptability of logistics operations. By integrating various elements and continuously monitoring their performance, organizations can swiftly respond to any changes in market demands, ensuring a smoother supply chain process.
In conclusion, a system approach is instrumental in navigating the complexities and uncertainties prevalent in logistics management. The holistic perspective, coordination, collaboration, optimization of resources, and enhanced flexibility provided by this approach contribute to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of logistics operations.
How can a system approach help in the design and implementation of logistics management information systems to support data-driven decision-making?
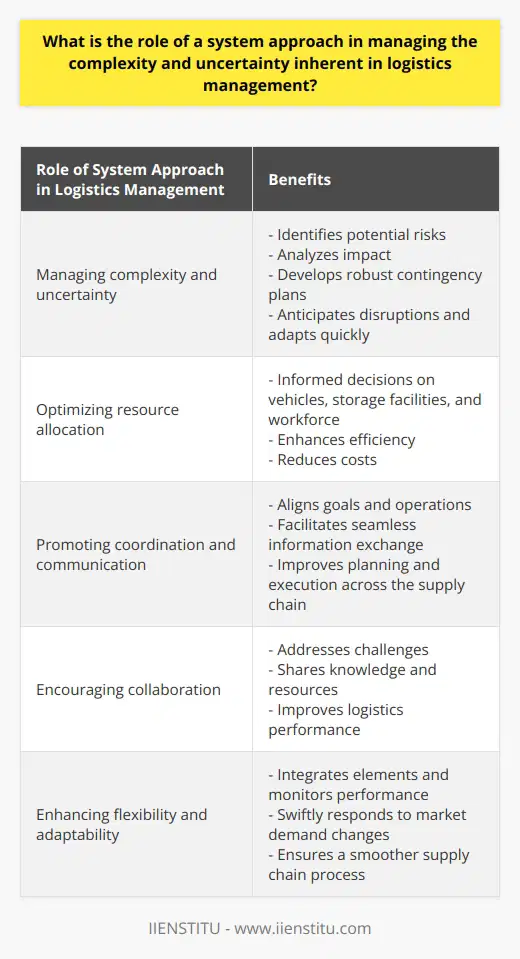
System Approach in Design and Implementation
A system approach to designing and implementing logistics management information systems can effectively support data-driven decision-making by encompassing all relevant factors and providing comprehensive insights. By considering the entire system of logistics, this approach enables the identification of interdependencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for optimization.
Integration of Functionalities
Logistics management information systems that utilize a system approach often feature the integration of multiple functionalities, such as inventory management, transportation management, and order management. This holistic approach ensures that all processes are seamlessly coordinated, resulting in more accurate data and facilitating well-informed decisions. Additionally, this cohesive perspective reduces the risk of information silos and fosters a more efficient allocation of resources.
Continuous Feedback Loop
The system approach also emphasizes the importance of a continuous feedback loop, which guides the development and refinement of the logistics management information system. By regularly evaluating the system's performance, adjustments can be made in real-time to improve its effectiveness in supporting data-driven decision-making. This dynamic process reduces the lag time between identifying issues and implementing solutions, ensuring that the system remains agile and responsive to the changing needs of the organization.
Adoption of Advanced Technologies
Another advantage of the system approach is its emphasis on adopting advanced technologies that can enhance the accuracy and reliability of data. By leveraging tools like the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, and machine learning, logistics management information systems can provide real-time insights, predictive analytics, and intelligent decision support. These technological innovations facilitate more nuanced and actionable information, empowering decision-makers with the necessary tools to make data-driven decisions.
Collaborative Decision-Making
Lastly, the system approach fosters a collaborative decision-making environment within an organization. By providing a unified view of the logistics processes and data, stakeholders can effectively communicate, align on objectives, and make informed decisions. This collaborative framework not only improves the efficiency of decision-making but also promotes a culture of data-driven thinking within the organization.
In conclusion, a system approach to the design and implementation of logistics management information systems greatly enhances the organization's ability to make informed data-driven decisions. By considering the entire system, integrating functionalities, advocating a continuous feedback loop, adopting advanced technologies, and encouraging collaborative decision-making, this approach ultimately leads to a more efficient and effective logistics management process.
What are the main challenges in integrating a system approach to support effective information flow in the logistics system, and how can they be addressed?
Challenges in System Integration
One of the main challenges in integrating a system approach to support effective information flow in the logistics system is the lack of standardization and interoperability among various information systems. Different systems may have their own data formats, communication protocols, and interfaces, which create barriers to the seamless exchange of information. This issue can be addressed by adopting common data standards, such as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), and ensuring that new systems comply with these standards.
Compatibility and Legacy Systems
Another challenge is the significant presence of legacy systems in the logistics sector. These systems, which are often outdated and not designed for integration, can hinder the effective flow of information. Updating or replacing legacy systems with modern, compatible systems can resolve this issue. Additionally, employing middleware and application programming interfaces (APIs) can help facilitate communication between legacy systems and newer technologies.
Human Factors and Organizational Resistance
The integration of a system approach may also face resistance from employees or organizational cultures that are resistant to change. To address this challenge, change management practices should be implemented, such as engaging stakeholders, communicating the benefits of the new system, and providing training on its use. This will help ensure a smooth transition and acceptance of the integrated approach.
Security and Data Privacy
Security and data privacy concerns also pose challenges in an integrated logistics system. Unauthorized access to sensitive information, data breaches, and cyberattacks are potential issues that must be addressed to ensure the integrity and safety of the information flow. Adopting industry-standard security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and secure communication protocols, can help mitigate these risks.
Cost and Resource Constraints
Lastly, cost and resource constraints are often cited as challenges by organizations seeking to integrate their logistics systems. Developing, implementing, and maintaining an integrated system can require substantial financial investments and skilled personnel. To address this challenge, organizations should conduct a cost-benefit analysis to assess the potential return on investment and explore alternative financing options. Additionally, building in-house expertise or partnering with external providers can help to address resource constraints.
In conclusion, there are several challenges in integrating a system approach to support effective information flow in the logistics system, such as standardization, legacy systems, human factors, security concerns, and cost constraints. By addressing these challenges through appropriate strategies and practices, organizations can improve their logistics system's overall efficiency and performance.

What is the role of information flow in facilitating the 7 R approach of the modern understanding of logistics?
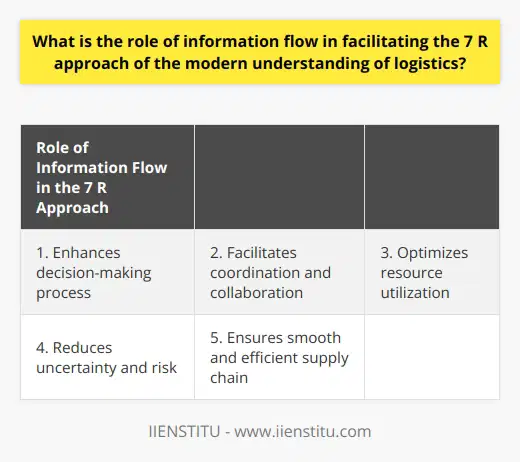
Role of Information Flow in the 7 R Approach
Efficient information flow is crucial in facilitating the modern understanding of logistics, which is centered around the 7 R approach. This approach emphasizes the importance of managing logistics to ensure the right product, at the right time, in the right quantity, and at the right price, reaches the right customer while maintaining the right condition and using the most efficient resources.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Effective information flow plays a central role in the decision-making process within logistics management. Accurate and timely data allows logistics managers to make well-informed decisions regarding product handling, transport, and storage. This helps in achieving the primary objectives of the 7 R approach, ensuring a smooth and efficient supply chain.
Enhancing Coordination and Collaboration
Information flow enhances coordination and collaboration between different stakeholders in the supply chain. Sharing information regarding demand, production schedules, and inventory levels helps stakeholders better understand each other's needs and capabilities. This fosters a collaborative environment, leading to more efficient usage of resources and ultimately, the achievement of the 7 R objectives.
Optimizing Resource Utilization
Logistics managers rely on information flow to optimize the use of available resources. Access to real-time data regarding inventory levels, transportation options, and customer demand allows managers to allocate resources efficiently. This not only reduces operational costs but also contributes to the integral aspects of the 7 R approach, such as delivering products in the right condition and at the right price.
Reducing Uncertainty and Risk
Effective information flow helps reduce uncertainty and risk in the logistics process. Managers can use data to foresee potential disruptions, such as unpredictable demand fluctuations or transportation issues, and develop strategies to address them. Consequently, this proactive approach contributes to the successful implementation of the 7 R approach by equipping organizations with the necessary tools to tackle challenges in a dynamic and unpredictable environment.
In conclusion, the role of information flow in facilitating the 7 R approach of the modern understanding of logistics cannot be understated. A robust and efficient information flow system not only enhances decision-making processes and coordination among supply chain stakeholders but also optimizes resource utilization and mitigates risks associated with uncertainty. As a result, organizations that effectively manage information flow are better positioned to achieve the objectives laid out by the 7 R approach, ensuring success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
How does a system approach in logistics management assist in the effective implementation and management of the 5 logistics management information systems?
System Approach in Logistics Management
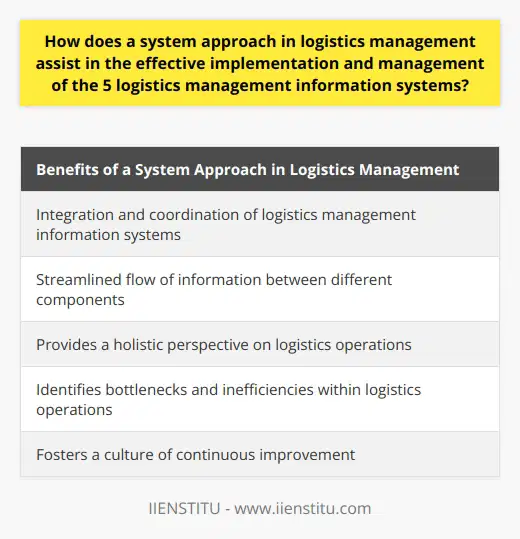
A system approach in logistics management contributes significantly to the effective implementation and handling of the five logistics management information systems. By offering a comprehensive perspective, it improves the overall efficiency of logistics operations.
Integration and Coordination
This method enables integration and coordination of information in logistics management information systems (LMIS) such as warehouse management systems, transportation management systems, order management systems, inventory control systems, and material requirements planning systems.
Streamlined Information Flow
A system approach ensures streamlined flow of information between various components involved in the logistics process, leading to successful decision-making and reducing the chances of miscommunication or delays in the logistics cycle.
Holistic Perspective
By taking into account all the interconnected factors, a systemic method allows managers to focus not only on individual elements but also on the relationships between them. Consequently, the organization benefits from enhanced efficiency and agility in logistics processes.
Identifying Bottlenecks
Through comprehensive analysis, it becomes easier to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in logistics operations. This timely identification of weak spots allows management to implement corrective measures and improve the overall efficiency of the logistics systems.
Continuous Improvement
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, a system approach encourages the organization to constantly reevaluate the logistics process, identify opportunities for growth and enhancement, and adapt to changing market conditions.
In conclusion, a system approach in logistics management is instrumental in the effective implementation and management of the five logistics management information systems. This holistic approach enables integration and coordination of LMIS components, facilitates streamlined information flow, provides a comprehensive perspective, identifies bottlenecks, and fosters continuous improvement. As a result, organizations can significantly enhance their logistics efficiency and adaptability to dynamic market conditions.
In the context of the system approach in logistics management, what are the key elements and considerations for ensuring efficient information flow and coordination among various stakeholders?
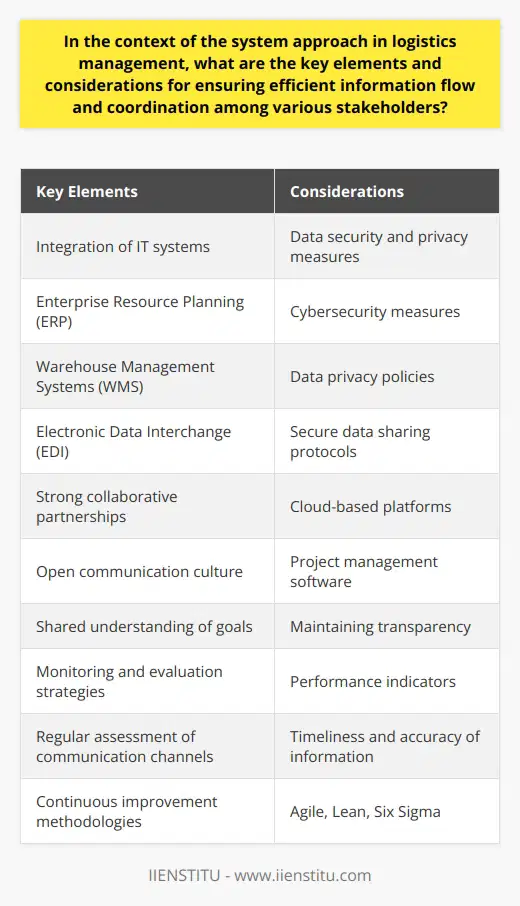
Key Elements of Efficient Information Flow
To ensure efficient information flow and coordination among various stakeholders in logistics management, it is essential to consider a system approach that encompasses several key elements. One such element is the integration of information technology (IT) systems. This enables seamless communication between all parties involved, from suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to customers. Implementing technologies such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) can facilitate the exchange of real-time, accurate information which enhances decision-making processes.
Data Security and Privacy Measures
In the age of digital transformation, data security and privacy are paramount. Organizations must take proactive steps to safeguard sensitive information, including implementing robust cybersecurity measures and establishing clear data privacy policies. Secure data sharing protocols should be in place, with adequate access controls to prevent unauthorized use or leakage of information. Training employees on data security procedures and conducting regular audits of information systems are essential steps towards ensuring the integrity of information flow.
Strong Collaborative Partnerships
Another key consideration in promoting information flow and coordination is fostering strong collaborative partnerships between stakeholders. This entails creating a culture of open communication and a shared understanding of goals, objectives, and expectations. By nurturing these relationships, stakeholders can effectively solve challenges, address potential bottlenecks, and optimize logistics processes. Collaboration tools such as cloud-based platforms and project management software can aid in maintaining transparency, accountability, and coordination among stakeholders.
Monitoring and Evaluation Strategies
Monitoring and evaluation strategies are essential for the ongoing improvement of information flow and coordination. Implementing performance indicators and regularly assessing the effectiveness of communication channels can help identify opportunities for improvement. This includes monitoring the timeliness, accuracy, and reliability of information exchanged among stakeholders. Strengthening feedback loops and integrating continuous improvement methodologies such as Agile, Lean, and Six Sigma can assist organizations in refining their information flow processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the key elements and considerations for ensuring efficient information flow and coordination in logistics management include the integration of IT systems, data security and privacy measures, strong collaborative partnerships, and monitoring and evaluation strategies. By addressing these aspects, organizations can foster an effective system approach in logistics management that promotes seamless communication, decision-making, and overall performance.