A credit facility is a financing arrangement where a supplier extends credit to a buyer, allowing them to purchase goods or services without immediate payment. This type of financing has become increasingly popular in recent years, particularly in the business-to-business (B2B) sector. As someone who has worked in the finance industry for over a decade, I have seen firsthand the benefits that credit facilities can offer to both suppliers and buyers.
One of the primary advantages of a credit facility is that it allows buyers to purchase goods or services without having to pay upfront. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses that have limited cash flow or are looking to conserve their working capital. By deferring payment, buyers can better manage their finances and invest in other areas of their business.
Introduction
Overview of Credit Facility
Benefits of Credit Facility
Industry Trends in Credit Facility
Conclusion
For suppliers, offering a credit facility can be an effective way to attract new customers and build long-term relationships. By providing flexible payment terms, suppliers can differentiate themselves from competitors and create a loyal customer base. As the old saying goes, "a rising tide lifts all boats." By helping their customers succeed, suppliers can ultimately benefit from increased sales and revenue.
However, offering a credit facility is not without its risks. Suppliers must carefully assess the creditworthiness of potential buyers before extending credit. This typically involves a thorough review of the buyer's financial statements, credit history, and other relevant information. As the famous investor Warren Buffett once said, "It's better to be approximately right than precisely wrong." In other words, it's better to err on the side of caution when extending credit than to risk significant losses down the road.
To mitigate these risks, many suppliers require buyers to provide some form of collateral or security before extending credit. This could include a personal guarantee, a lien on the buyer's assets, or a letter of credit from a bank. By securing the credit facility with collateral, suppliers can reduce their exposure to potential defaults and ensure that they are repaid in the event that the buyer is unable to meet their obligations.
System Approach To Logistics Management For Packaging Handling
Optimizing Logistics Management Production Distribution Decisions
Another way that suppliers can manage the risks associated with credit facilities is by setting clear terms and conditions upfront. This should include details such as the credit limit, interest rate, repayment schedule, and any fees or penalties for late payments. By clearly communicating these terms to buyers, suppliers can avoid misunderstandings and disputes down the road.
In addition to the benefits and risks associated with credit facilities, there are also several industry trends that are worth noting. One of the most significant trends in recent years has been the increasing use of technology in the credit facility process. Many suppliers are now using software platforms to automate the credit application and approval process, as well as to manage ongoing credit relationships with buyers.
These platforms can help to streamline the credit facility process and reduce the administrative burden on suppliers. For example, some platforms use machine learning algorithms to analyze a buyer's financial data and assess their creditworthiness in real-time. This can help suppliers make faster and more accurate credit decisions, while also reducing the risk of fraud or errors.
Another trend in the credit facility space is the use of alternative credit scoring methods. Traditional credit scoring models, such as those used by banks and credit bureaus, can be limited in their ability to assess the creditworthiness of certain types of buyers, such as small businesses or startups with limited credit history.
To address this issue, some suppliers are turning to alternative credit scoring methods that take into account a wider range of data points. For example, some platforms analyze a buyer's social media activity, online reviews, and other digital footprints to assess their creditworthiness. While these methods are still relatively new, they have the potential to expand access to credit for underserved markets and help suppliers make more informed credit decisions.
Optimizing credit facilities and staying abreast of industry trends are essential components of successful logistics management.
Despite these trends, it's important to note that credit facilities are not a one-size-fits-all solution. The specific terms and conditions of a credit facility will vary depending on the needs and risk profile of both the supplier and the buyer. As with any financial arrangement, it's important for both parties to carefully consider their options and seek professional advice before entering into a credit facility agreement.
For buyers, some key considerations when evaluating a credit facility include:
1- The interest rate and fees associated with the facility
2- The repayment terms and schedule
3- Any collateral or security requirements
4- The flexibility of the credit limit and the ability to adjust it over time
5- The reputation and track record of the supplier offering the facility
For suppliers, some key considerations when offering a credit facility include:
1- The creditworthiness and financial stability of the buyer
2- The potential risks and rewards associated with extending credit
3- The terms and conditions of the credit facility agreement
4- The internal processes and resources needed to manage the credit facility over time
5- The alignment of the credit facility with the supplier's overall business strategy and goals
Ultimately, the decision to enter into a credit facility agreement should be based on a careful analysis of the costs, benefits, and risks involved. By doing their due diligence and seeking expert advice, both suppliers and buyers can make informed decisions that support their long-term financial health and success.
In conclusion, credit facilities can be a valuable tool for both suppliers and buyers in today's fast-paced and competitive business environment. By providing flexible payment terms and access to working capital, credit facilities can help businesses grow and thrive. However, it's important for both parties to carefully consider the risks and rewards associated with credit facilities and to enter into these arrangements with a clear understanding of the terms and conditions involved.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, it's likely that we will see further innovation and disruption in the credit facility space. From the increasing use of technology and alternative credit scoring methods to the emergence of new financing models and platforms, there are many exciting developments on the horizon. As always, those who are able to stay ahead of the curve and adapt to these changes will be best positioned for success in the years to come.
References:
1- Miller, R. L., & VanHoose, D. D. (2017). Fundamentals of Financial Markets and Institutions. Cambridge University Press.
2- Ross, S. A., Westerfield, R. W., & Jordan, B. D. (2018). Fundamentals of Corporate Finance. McGraw-Hill Education.
3- Brealey, R. A., Myers, S. C., & Allen, F. (2016). Principles of Corporate Finance. McGraw-Hill Education.
4- Tirole, J. (2010). The Theory of Corporate Finance. Princeton University Press.
5- Damodaran, A. (2012). Investment Valuation: Tools and Techniques for Determining the Value of Any Asset. John Wiley & Sons.
Frequently Asked Questions
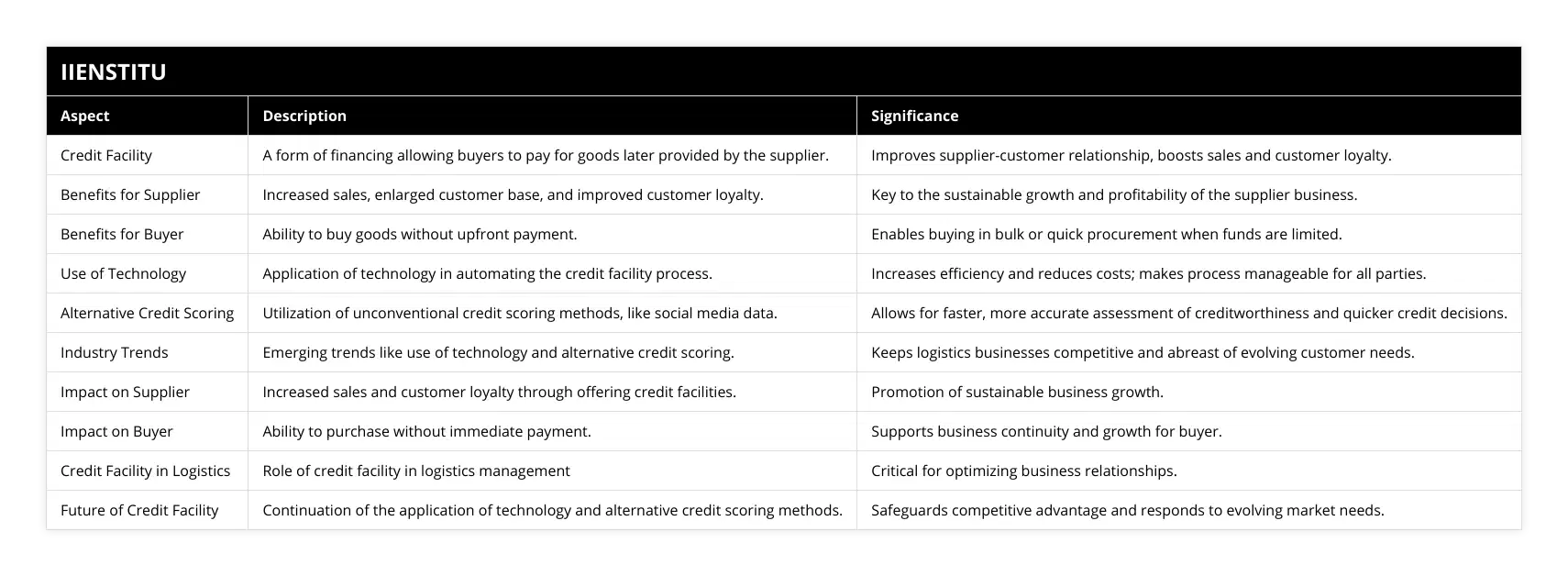
What are the key benefits of using a credit facility in logistics management?
Logistics management is a vital component of the supply chain and is often the difference between success and failure. Using a credit facility in logistics management can provide several key benefits, including improved cash flow, reduced inventory costs, and improved customer service.
Cash flow is one of the primary benefits of using a credit facility in logistics management. By providing access to additional funds, a credit facility can help to level out cash flow fluctuations, allowing companies to take advantage of opportunities that may otherwise be missed. This can help ensure that companies have the necessary funds to purchase supplies and inventory when needed without waiting for customer payment.
Using a credit facility can also help to reduce inventory costs. By providing access to additional funds, a credit facility can enable the purchase of inventory in bulk, allowing companies to take advantage of lower prices and discounts. Additionally, companies can use a credit facility to finance the purchase of new equipment or technology, allowing them to take advantage of technological advances that can help to streamline their operations and increase efficiency.
Finally, using a credit facility can also help to improve customer service. A credit facility can help companies reduce delivery times and provide better customer service by providing access to additional funds. This can help to ensure that customers receive the items they need promptly, resulting in increased customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, using a credit facility in logistics management can provide several key benefits. A credit facility can help level out cash flow fluctuations, reduce inventory costs, and improve customer service by providing access to additional funds. As such, using a credit facility can help companies take advantage of all the opportunities available to them in the supply chain.
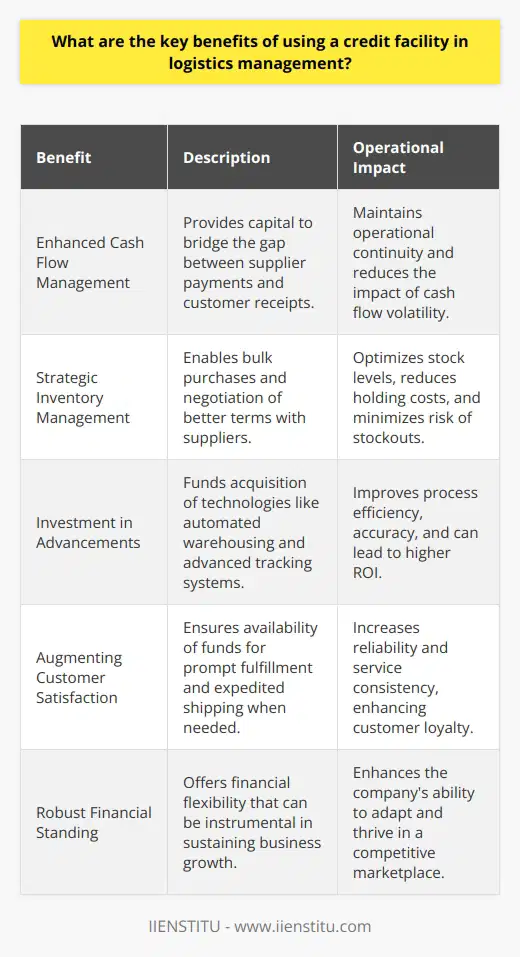
How has the use of credit facilities in logistics management evolved over time?
The use of credit facilities in logistics management has evolved significantly over the years. As global trade has become increasingly complex, businesses have had to adapt their strategies to keep up with the changing market trends. Credit facilities have become an increasingly important component of logistics management, allowing companies to manage their cash flow and mitigate risks associated with financial transactions.
In the past, the use of credit facilities in logistics management was primarily limited to cash advances, which were used to finance short-term needs such as paying vendors or covering transportation costs. These advances were often made personally, with the lending institution evaluating the borrower's creditworthiness and charging interest on the loan. While this approach may have worked for some businesses, it was often too risky for others and could lead to significant losses if the borrower defaulted on the loan.
Today, the use of credit facilities in logistics management has become much more sophisticated. Businesses now have access to a wide range of financing options, including factoring and invoice financing, which allow them to access working capital without taking on too much risk. These options also give businesses more flexibility in managing their cash flow, as they can access funds quickly, meet tight deadlines or take advantage of market opportunities.
In addition to traditional financing options, businesses now have access to various non-traditional financing solutions, such as supply chain finance. Supply chain finance allows businesses to access working capital by leveraging the creditworthiness of their suppliers or customers. This approach is beneficial for companies dealing with long payment cycles, as they can access funds quickly while mitigating the risk associated with long-term loans.
Overall, the use of credit facilities in logistics management has evolved significantly over the years. With the increasing complexity of global trade and the availability of a wide range of financing options, businesses are better equipped to handle their cash flow and mitigate risks associated with financial transactions. By taking advantage of these options, companies can ensure that their logistics operations run smoothly and efficiently.
What are the current trends in the use of credit facilities in logistics management?
Logistics management has always been an essential factor in any business. The need for efficient and cost-effective transportation and delivery of goods is necessary for any organization to remain competitive in the marketplace. However, in recent years, the use of credit facilities has become increasingly popular in logistics management. This article will discuss the current trends in using credit facilities in logistics management.
The use of credit facilities in logistics management has become increasingly important as businesses have become more global and transportation costs have increased. Companies can use credit facilities to finance transportation costs, allowing them to remain competitive worldwide. Additionally, credit facilities can provide businesses with access to a greater variety of transportation services, allowing them to optimize their logistics management.
One of the most popular trends in the use of credit facilities in logistics management is the use of third-party financing. Third-party financing allows businesses to purchase transportation services from a third-party provider instead of financing the cost of the transportation themselves. This can benefit companies as they can access a greater variety of transportation services and often get a better rate than they would by financing the vehicle themselves. Additionally, third-party financing can help businesses manage their cash flow, as they can access funds when needed and not have to worry about financing the cost of the transportation themselves.
Another popular trend in using credit facilities in logistics management is the use of “pay-as-you-go” financing. This financing allows businesses to access funds when needed and pay them back as they use them. This can benefit companies as it will enable them to manage their cash flow more effectively and provide them with access to a greater variety of transportation services. Additionally, pay-as-you-go financing can help businesses manage their costs more effectively, as they can access funds when needed and not worry about financing the cost of the transportation themselves.
Finally, businesses are also beginning to use “credit cards” in logistics management. Credit cards are a convenient and efficient way to access funds when they need them. Additionally, credit cards can provide businesses with access to a greater variety of transportation services, allowing them to optimize their logistics management.
In conclusion, using credit facilities in logistics management is becoming increasingly popular. Businesses are using third-party financing, pay-as-you-go financing, and credit cards to finance their transportation costs and to access a greater variety of transportation services. This can help businesses remain competitive in the global marketplace and can help them manage their costs more effectively.
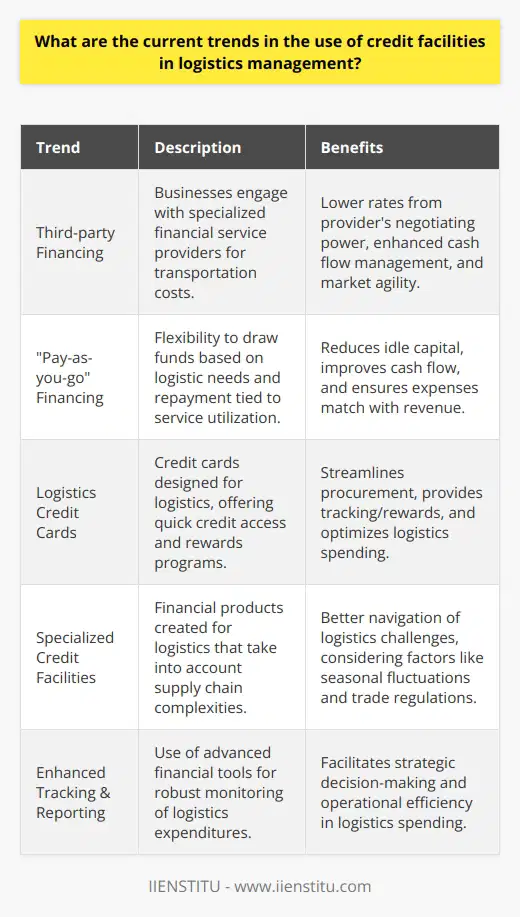
What are the major trends in logistics for 2023?
Major Trends in 2023
Technology Integration
Logistics in 2023 will see increased integration of technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), automation, and artificial intelligence (AI). IoT devices will enhance real-time tracking and monitoring of goods, while AI-based algorithms enable smart route optimization and predictive analytics.
Sustainable Solutions
Eco-friendly practices will become a more significant focus for the logistics sector. Companies will aim to reduce carbon emissions by using green transportation options and optimizing routes. Emphasis on circular economy principles will lead to increased use of recyclable packaging materials and waste reduction strategies.
Urban Logistics
Rapid urbanization will reshape logistics, as companies adjust to support growing urban populations. This trend will demand innovative last-mile delivery solutions, such as the utilization of electric vehicles, drones, and autonomous delivery robots. Additionally, the establishment of urban fulfillment centers will reduce delivery times and congestion.
Supply Chain Resilience
In response to global disruptions like pandemics and natural disasters, logistics providers will prioritize building robust, flexible supply chains. Companies will diversify sourcing, implement advanced risk management strategies, and collaborate with partners to mitigate disruptions. Real-time visibility and data-driven decision-making will be essential for supply chain resilience.
Collaborative Networks
In 2023, companies will increasingly rely on collaborative networks to optimize their logistics operations. By sharing resources and expertise, businesses can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and drive innovation. Partnering with technology providers, governments, and educational institutions will be key to addressing complex logistics challenges.
Workforce Development
The logistics industry will adopt new approaches in talent management and workforce development. Digital upskilling initiatives and technical training programs will be crucial to ensure employees can capitalize on the new technologies transforming the sector. Embracing diversity and inclusion strategies will also help meet the demand for skilled labor.
E-commerce Expansion
The growth of e-commerce will continue to impact logistics profoundly. To meet the evolving needs of online consumers, logistics providers must offer flexible, fast, and convenient delivery options. In addition, companies will need to enhance their returns management processes and invest in robust, scalable warehouse management systems.
In conclusion, the major trends in logistics for 2023 will center around technology integration, sustainability, urban logistics, supply chain resilience, collaborative networks, workforce development, and e-commerce expansion. Adapting to these trends and driving innovation will be vital for companies to maintain a competitive advantage within the rapidly evolving logistics landscape.
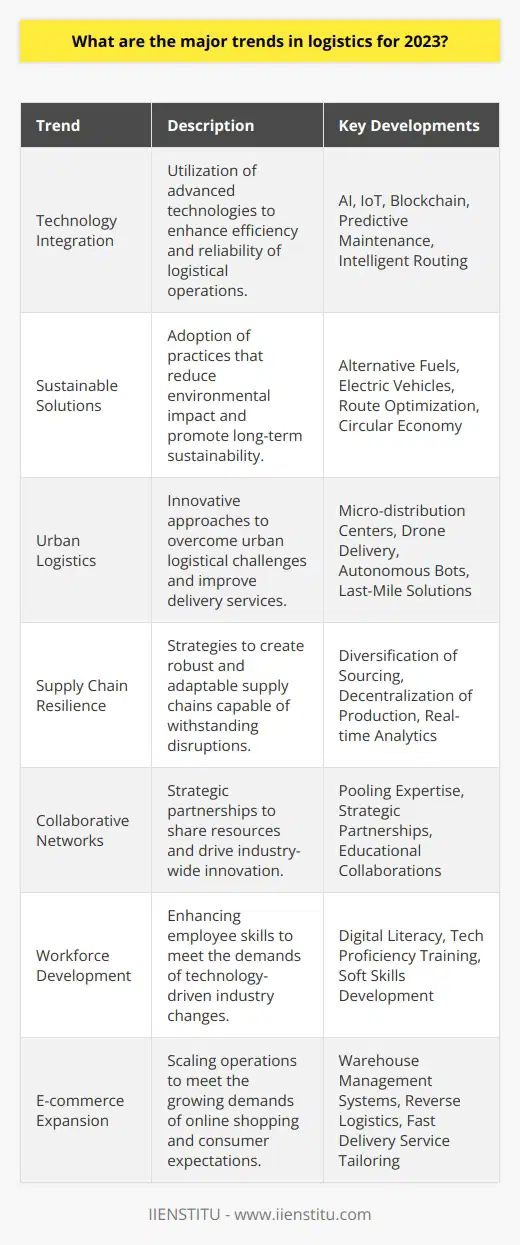
What are the four key components of logistics management?
Logistics Management Components
The effectiveness of logistics management lies in its four key components: transportation, warehousing and storage, inventory management, and order fulfillment. A well-designed logistics plan must successfully coordinate and integrate these essential elements to optimize the supply chain and meet customer expectations.
Transportation Management
Transportation is a critical aspect of logistics management. It involves selecting the most efficient and cost-effective modes of transportation to move goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption. This component encompasses strategic route planning, carrier selection, freight negotiation, and performance tracking to ensure the timely delivery of products at a reasonable cost.
Warehousing and Storage
Effective warehousing and storage strategies are crucial for maintaining inventory levels and meeting customer demands. This component includes the allocation of storage space, layout design, material handling equipment, and warehouse management systems to maximize storage efficiency, reduce stock discrepancies, and minimize operational costs.
Inventory Management
Inventory management entails maintaining appropriate stock levels to prevent stockouts or overstock situations. This requires accurately forecasting demand, implementing efficient replenishment techniques, and continuously monitoring inventory levels. An effective inventory management system reduces lead times, minimizes excess inventory, and prevents potential stock obsolescence, which ultimately leads to improved customer satisfaction.
Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is the final component of logistics management. It entails the seamless execution of all processes involved in fulfilling customers' orders, including order processing, picking, packing, shipping, and tracking. It is critical to establish accurate and efficient order fulfillment strategies to reduce errors, minimize shipping delays, and enhance overall customer experience.
In conclusion, transportation, warehousing and storage, inventory management, and order fulfillment are the four key components that constitute successful logistics management. By optimizing each element, businesses can streamline their supply chain, reducing costs, and enhancing their overall operational efficiency, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction.
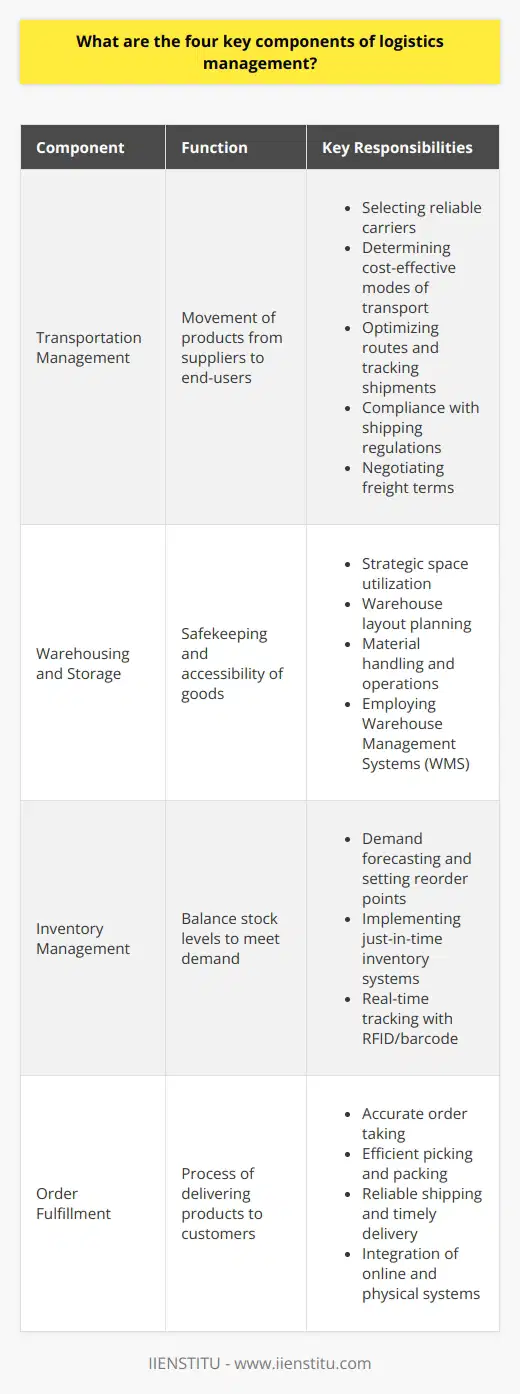
What are the primary factors influencing market logistics decisions?
Market logistics decisions are primarily influenced by four key factors: customer service requirements, transportation options, warehousing, and inventory management. It is essential to analyze these interconnected elements in order to optimize logistics operations, drive efficiency, and ultimately meet customer demands.
Customer Service Requirements
The heart of any logistics strategy lies in understanding and responding to customer service requirements. Factors such as delivery lead time, order accuracy, and product availability play a significant role in determining customer satisfaction. Effective market logistics decisions should focus on meeting these requirements while maintaining cost efficiency.
Transportation Options
Another critical factor in market logistics decisions is transportation. Companies must evaluate various options like road, rail, air, or sea, considering factors such as cost, transit time, and environmental impact. Decisions should weigh the trade-offs between speed and cost-effectiveness, taking into account customer expectations for on-time delivery and the value of the goods being transported.
Warehousing
Warehousing decisions are also an integral aspect of market logistics planning. The choice of warehouse location, size, and design can have a significant impact on the overall efficiency of a logistics network. Companies must consider factors such as proximity to suppliers, customers, and transportation hubs, as well as the need for specialized equipment or storage conditions, when making warehousing decisions.
Inventory Management
Lastly, effective inventory management plays a crucial role in market logistics. Balancing the need to provide sufficient stock to meet customer demands with the desire to minimize costs associated with holding inventory is essential. Decisions regarding optimal inventory levels, reorder points, and safety stock determine the efficacy of logistics operations.
In conclusion, market logistics decisions are influenced by a complex interplay of customer service requirements, transportation options, warehousing, and inventory management. Companies must carefully analyze these factors in order to optimize their logistics operations and ultimately provide a seamless and efficient experience for their customers.
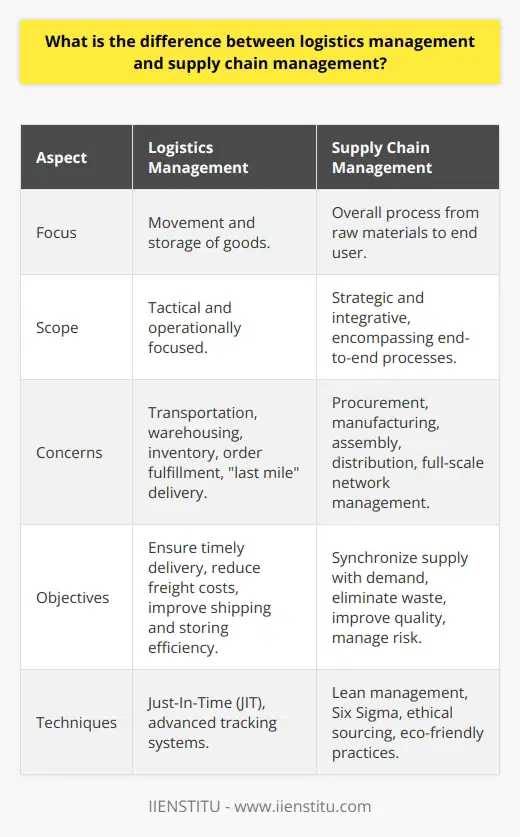
What is the difference between logistics management and supply chain management?
Defining Logistics Management
Logistics management is an essential component of the broader supply chain management discipline, focusing on planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient flow and storage of goods, services, and relevant information between the point of origin and the point of consumption. Its main intent is to optimize the process by ensuring that products reach their end consumers in a cost-effective and timely manner. Logistics management is integral for companies that aim to meet customer needs, retain market competitiveness, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Explaining Supply Chain Management
Meanwhile, supply chain management encompasses a wider scope of activities and involves overseeing the entire chain of product flow, from raw materials procurement to the distribution of finished goods to end consumers. It includes managing multiple aspects such as sourcing, production, transportation, warehousing, and inventory control. Supply chain management brings together various entities such as suppliers, manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and customers, to collaborate and optimize the complete supply chain. The primary objective is to achieve a seamless and efficient value chain by minimizing costs, reducing lead times, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Comparing Logistics and Supply Chain Management
The core difference between logistics management and supply chain management lies in their scope and focus. While logistics management concentrates on the movement and storage of goods and related information, supply chain management is more comprehensive and extends to include other elements such as suppliers, producers, and customers. Logistics management can be considered a subfunction within the broader supply chain management framework.
Interdependence and Importance
It is crucial to understand that logistics management and supply chain management are closely related and interdependent activities. Both disciplines aim to deliver value to end customers by improving overall efficiency and effectiveness, while also minimizing costs. A well-functioning logistics management system supports supply chain management strategies and ensures successful execution. Consequently, businesses need to employ robust logistics management practices within their supply chain management efforts to maintain a competitive edge and achieve sustainable growth.
In conclusion, logistics management and supply chain management are distinct, yet interconnected disciplines that serve to enhance a company's operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Strategies and practices that integrate both areas of expertise are crucial for organizations seeking to thrive in today's competitive global marketplace.
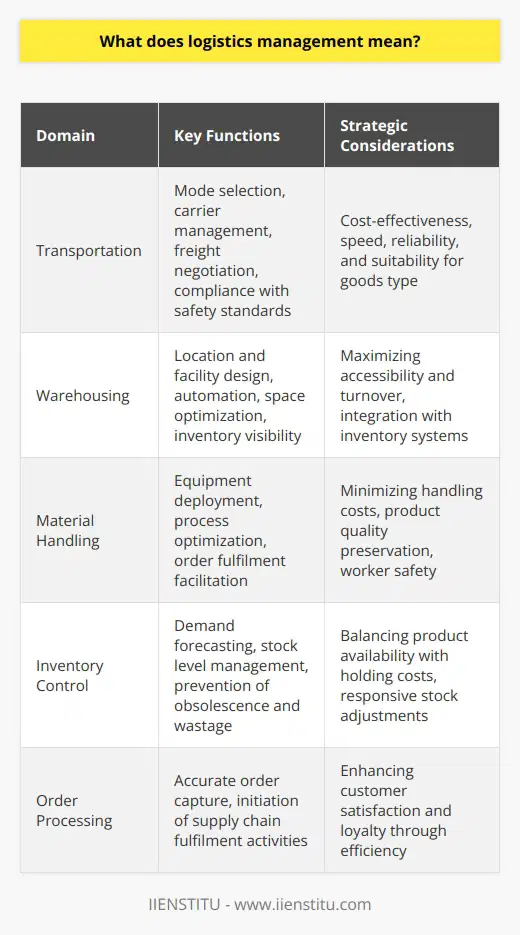
What does logistics management mean?
Role and Scope of Logistics Management
Logistics management is a vital component of supply chain management that involves planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, cost-effective flow and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, finished goods, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Logistics management aims to ensure that goods and services are available to customers at the right time, place, and quality.
Key Components of Logistics Management
The process of logistics management consists of several interconnected components, including transportation, warehousing, material handling, inventory control, and order processing. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the coordinated delivery of products and services to customers.
Transportation: One of the essential elements of logistics management is the movement of goods between various stages of the supply chain. Efficient and cost-effective transportation systems are crucial for the timely delivery of products.
Warehousing: The storage of goods and materials is another vital aspect of logistics management. Properly managed warehouses provide safe and organized storage facilities that maintain product integrity and availability.
Material Handling: The movement and handling of goods within the warehouse or between transportation modes are crucial for smooth logistic operations. Material handling equipment, such as forklifts or pallet jacks, ensures the safe and effective handling of goods.
Inventory Control: Monitoring and managing inventory levels is a critical aspect of logistics management. Accurate tracking of inventory levels ensures that adequate supplies are available to meet customer demand while avoiding overstocking or stock-outs.
Order Processing: Processing customer orders is another vital logistics management function. Order processing involves collecting and organizing customer order information, coordinating with warehouse operations, and initiating transportation activities.
Logistics Management Strategies
Companies can rely on several strategies to improve their logistics management. These strategies include outsourcing, adopting advanced technologies, and continuous improvement initiatives. By implementing these strategies, organizations can achieve cost reductions and operational efficiencies, leading to increased customer satisfaction and overall profitability.
Outsourcing: Many companies choose to outsource their logistics operations to third-party providers, allowing them to focus on their core competencies. This practice can offer cost savings and improved performance through specialized expertise.
Advanced Technologies: The use of advanced logistics technologies, such as transportation management systems and warehouse management systems, offer significant benefits for efficiency and cost control. These technologies facilitate real-time tracking and monitoring of logistics operations, enabling more informed decision-making.
Continuous Improvement: By continuously reviewing and refining logistics processes, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement changes to maintain competitive performance in the market.
In conclusion, logistics management is an essential aspect of supply chain management, responsible for the timely and efficient delivery of products and services to customers. By comprehending and effectively managing its core components, companies can ensure their logistical processes run smoothly, meet customer expectations, and maintain overall profitability.
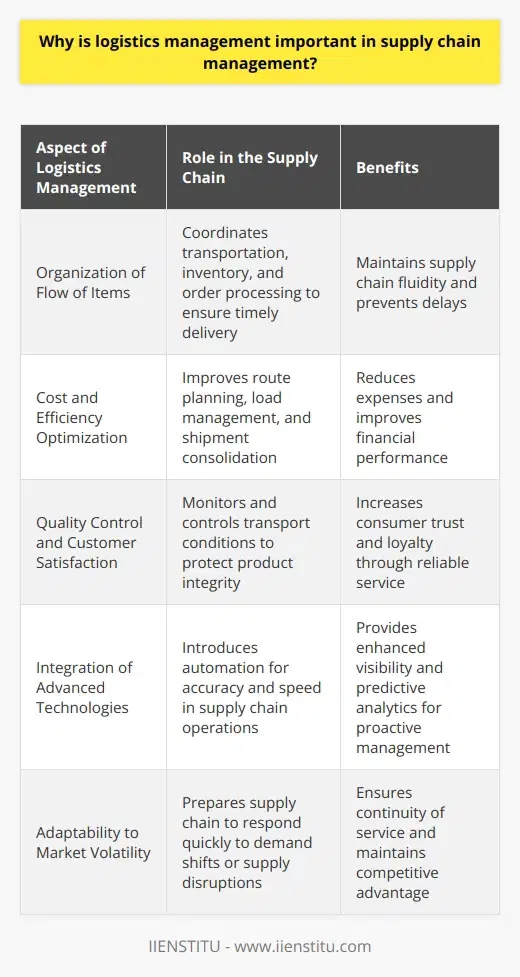
Why is logistics management important in supply chain management?
Significance of Logistics Management
In the realm of supply chain management, logistics management plays a pivotal role in ensuring the efficient and seamless movement of goods and services from one point to another. It encompasses various functions such as transportation, warehousing, and inventory management, all of which are vital for the overall effectiveness of a supply chain.
Facilitating Timely Delivery
One of the primary goals of logistics management is the timely delivery of products to the intended destination. In order to achieve this, logistics managers systematically plan, implement, and control the transportation of goods. This, in turn, leads to increased customer satisfaction, which is crucial for businesses to remain competitive in today's market.
Inventory Management for Cost-Effectiveness
Logistics management is also responsible for inventory management, which directly contributes to the cost-effectiveness of any supply chain. By monitoring and controlling inventory levels, logistics managers can optimize stock quantities and minimize excess inventory. Consequently, businesses can reduce storage costs, spoilage, and opportunity costs of valuable resources tied up in stock.
Mitigating Risks
An efficient logistics management system is essential to mitigating risks in supply chain management. The inability to promptly deliver goods on time can result in a domino effect, causing disruptions throughout the entire supply chain. Logistics managers, therefore, devise strategies to prevent unforeseen contingencies such as natural disasters and transportation disruptions from impacting the supply chain significantly.
Enhancing Communication and Collaboration
Effective logistics management ensures smooth communication and collaboration among various stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, transporters, and retailers. This transparent exchange of information fosters better decision-making and promotes a high level of synchronization within the supply chain.
Driving Sustainability
Lastly, logistics management plays a significant role in advancing supply chain sustainability. By adopting greener transportation means and optimizing packaging, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable business environment.
In conclusion, logistics management is vital to realizing a well-functioning supply chain. By facilitating timely delivery, optimizing inventory levels, mitigating risks, enhancing communication, and driving sustainability, logistics management contributes to a more streamlined and effective supply chain system.
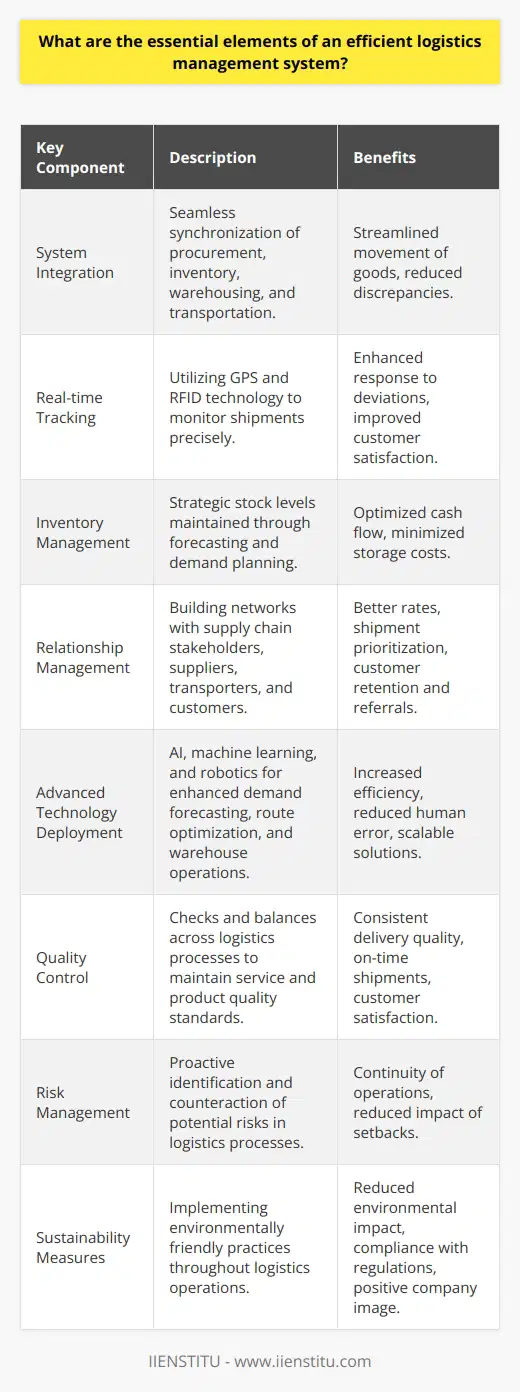
What are the essential elements of an efficient logistics management system?
System Integration
An efficient logistics management system necessitates seamless integration of various processes. This enables systematic coordination between procurement, warehousing, transportation, and delivery operations.
Real-time Tracking
Tracking goods in real-time forms a crucial element in any logistics management system. This not only ensures efficient supply chain visibility but also reduces risks associated with loss or damage.
Inventory Management
Managing inventory is paramount for any logistics system. Optimized inventory control eliminates overstocking and understocking situations, enhancing warehouse efficiency and reducing unnecessary costs.
Relationship Management
Strong relationships with suppliers, transporters, and clients are fundamental to an effective logistics management system. Such linkages improve communication, enhance feedback mechanisms, and foster a cooperative working environment.
Advanced Technology Deployment
The use of advanced technology such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics can transform the logistics landscape. These tools assist in automation, reduce human error, speed up processes, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Quality Control
Quality control is another essential element. Regular monitoring and evaluation of services and processes guarantee compliance with standards, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement.
Risk Management
Risk management plays an essential role in logistics management. An efficient system should identify potential risks, develop contingency plans, and implement mitigation strategies to minimize disruption in operations.
Sustainability Measures
The incorporation of sustainability measures is crucial in modern logistics management systems. Environmental consciousness can lead to cost reductions and improved brand reputation while ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
In essence, an efficient logistics management system balances cost-effectiveness, timeliness, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. It requires strategic planning, seamless integration, continuous improvement, the application of advanced technology, and sustainable practices.
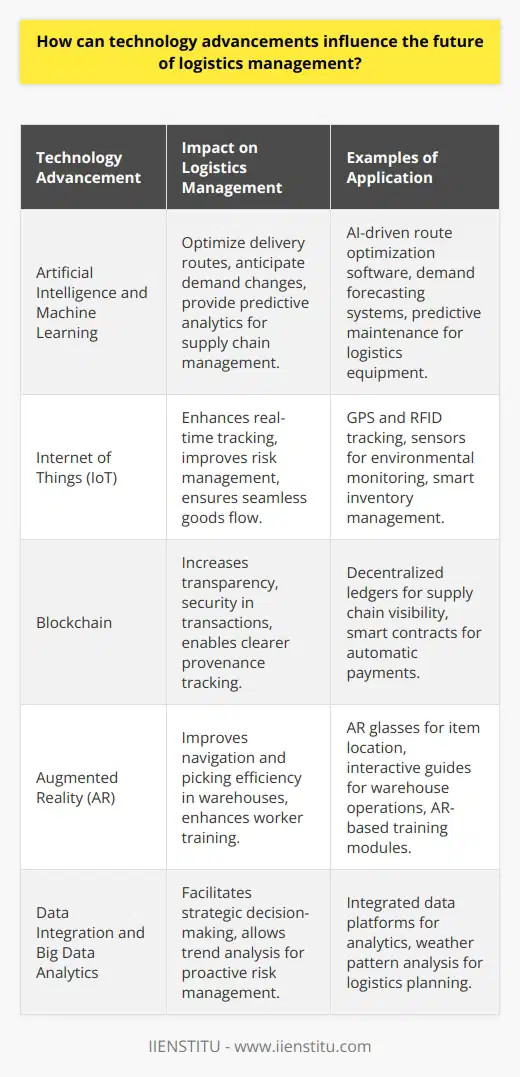
How can technology advancements influence the future of logistics management?
Technology-Driven Efficiency
Advanced technology will streamline logistics management in multiple ways. Intelligent automation can reduce errors, increase efficiency, and enhance accuracy. The automated system can perform repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more complex duties.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) can make logistics management more efficient. AI can predict what might go wrong in the supply chain and suggest potential solutions. ML can learn from past data, adapt to new inputs, and improve decision making.
Internet of Things in Logistics
The Internet of Things (IoT) will provide real-time data, enhancing visibility and traceability in the supply chain. Sensors and smart devices will facilitate proactive maintenance, reducing delays and breakdowns.
Blockchain Technology in Logistics
Blockchain technology will enhance transparency and security in logistics. It can record transactions, revealing the authenticity and origin of products. This will reduce fraud and increase customer trust.
Augmented Reality (AR) in Warehouse Management
AR can significantly improve warehouse operations. Workers wearing AR glasses will see digital overlays of what they need to fulfill orders, reducing search times and improving accuracy.
Data Integration and Analytics
Data integration will combine data from various sources into a cohesive whole. This will provide a complete view of operations, improving decision-making. Big data analytics will analyze large amounts of data to identify trends and patterns that can optimize operations.
To sum up, technological advancements will significantly enhance logistics management in the future. These advancements will make logistics more efficient, accurate, transparent, and customer-driven. This transformation will directly impact profitability and customer satisfaction.
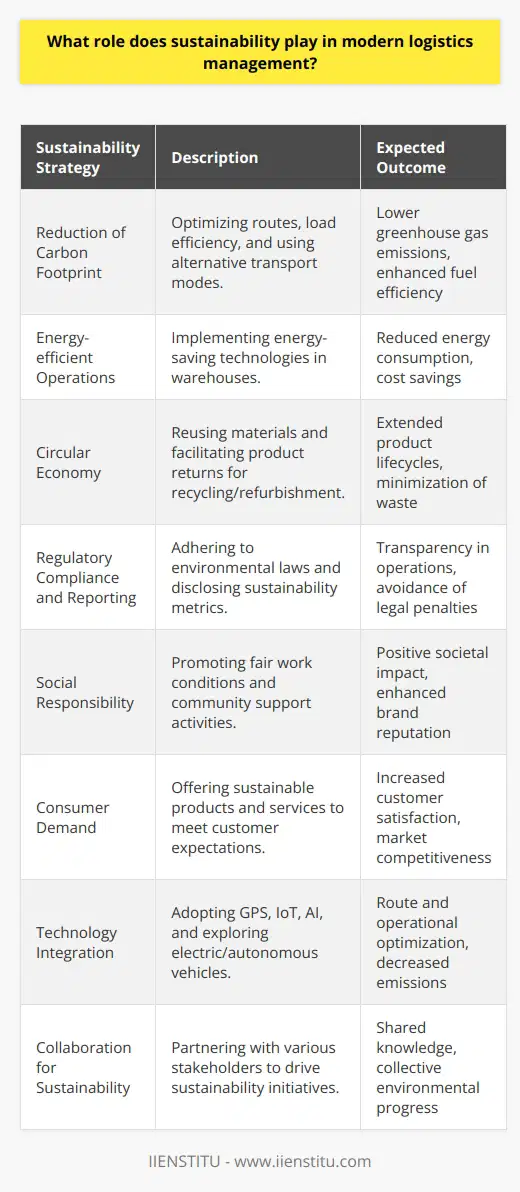
What role does sustainability play in modern logistics management?
Role of Sustainability in Modern Logistics Management
Sustainability is now a critical focus in modern logistics management. It involves promoting environmentally-friendly and ethically-responsible practices. This approach aligns with global efforts to protect our environment and ensure ethical business operations.
Environmental Considerations
Eco-friendly practices in logistics result in a reduction of carbon emissions. By opting for efficient vehicles or renewable fuels, companies reduce their environmental impact. Similarly, effective route planning helps to decrease fuel consumption. Initiatives such as waste management and prioritizing recyclable materials also contribute to sustainable logistics.
Ethical Business Operations
Placing emphasis on ethical practices is another key aspect. This includes fair labor practices and promoting diversity and inclusion. Further, engaging with suppliers committed to ethical operations supports a sustainable supply chain. These approaches enhance the reputation of businesses, boosting their appeal to both consumers and potential partners.
Cost-effectiveness
Sustainability often aligns with cost-effectiveness. Efficient resource utilization reduces operational costs. An example is reducing packaging materials and optimizing delivery routes. This not only aids the environment but also decreases expenses.
Innovation and Adaptation
Finally, sustainability encourages innovation and flexibility. Adapting to new technologies, like electric vehicles or automated systems, propels the industry forward. It also builds resilience against potential future shocks, such as fuel price spikes. It makes the logistics industry adaptable to changes, securing its future.
In conclusion, sustainability plays a pivotal role in modern logistics. It promotes environmentally-friendly practices, encourages ethical operations, supports cost management, and furthers innovation. Sustainability shifts the focus from short-term gains to long-term success, driving both growth and responsibility.