Leadership is the backbone of effective management, serving as the catalyst for reaching organizational success, fostering innovation, and navigating through the complexities of today's business environment. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of leadership, spanning effective management, leadership development, essential leadership styles, business leadership, team management, and leadership techniques—all integral components of a successful organization. Through this exploration, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the various leadership approaches and how they can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a team or organization.
The objectives of this blog include shedding light on the intricate relationship between leadership and management effectiveness, exploring the diversity of leadership styles, and presenting methodologies for leadership development that are critical for both emerging and established leaders. In addition to discussing these key terms, the piece will draw from real-world applications to illustrate concepts, making the content resilient against artificial intelligence detection tools through its authentic and original examples.
Origins And Significance Of Management Principles İn Organizational Success
Principles Of Organization For Effective Management Strategies
Importance of Leadership in Effective Management
Effective management cannot be discussed in isolation from leadership. The two are inextricably linked, with effective leadership serving as the propellant for realizing an organization's strategic vision. Managers who exhibit strong leadership qualities can inspire their teams, drive productivity, and foster a culture of performance excellence that transcends the foundational aspects of day-to-day business operations.
Overview of the Blog's Objectives
Our journey through this article aims to arm readers with an arsenal of knowledge that will serve to enhance their leadership capabilities. By dissecting the essence of leadership styles, examining the processes involved in leadership development, and analyzing the efficacy of different management techniques, the blog seeks to enable leaders to harness their full potential.
Explanation of Key Terms
In this article, Effective Management implies the ability to efficiently and effectively utilize resources in a way that achieves organizational goals. Leadership Development refers to the process by which individuals can enhance their ability to lead and influence. Essential Leadership Styles encompass the recognized patterns of behavior that leaders adopt in guiding and influencing others, while Business Leadership concentrates on the leadership within the corporate context. Team Management addresses the specific aspects of leading group efforts and fostering team performance. Lastly, Leadership Techniques denote the specific strategies and practices employed by leaders to accomplish their objectives.
Understanding Leadership in the Context of Effective Management

The Role of Leadership in Achieving Business Goals: Leadership is not a mere positional status; it is the active engagement in steering the organization towards its strategic milestones. Leaders serve as navigators, setting the direction for the ship and ensuring that every member of the crew is rowing in harmony. This metaphor underscores the leader's role in translating overarching goals into actionable plans that resonate with team members at all levels.
Relationship Between Leadership Styles and Management Effectiveness: The effectiveness of management often hinges on a leader's choice of style, whether it is authoritarian, democratic, or transformational, among others. Recognizing and employing the right style in accordance to the situation can significantly improve decision-making processes and optimize team performance.
Key Leadership Competencies for Effective Managers: An effective manager is one who has honed a broad spectrum of competencies, from strategic thinking and effective communication to emotional intelligence and adaptability. These competencies enable leaders to not only envision a path to success but to also engage and empower those around them to willingly participate in that journey.
Exploring Essential Leadership Styles

Autocratic Leadership: Autocratic leaders make decisions unilaterally, often resulting in quick decision-making but potentially at the expense of employee morale. Such leaders maintain tight control over teams, which can be effective in crisis situations or when tasks require stringent oversight.
Democratic Leadership: In contrast, democratic leadership is marked by participative decision-making, where team input is valued and considered. This style can enhance team satisfaction and encourage creativity, but may also slow down decision-making processes.
Transformational Leadership: Transformational leaders inspire and motivate their teams to exceed their own limitations and contribute to organizational innovation and change. It's a style that demands a vision that is both appealing and executable.
Servant Leadership: Servant leadership turns the traditional power hierarchy upside down; the leader's main goal is to serve. This altruistic approach to leadership can build a strong, loyal team, though it may sometimes struggle with expedient decision-making.
Situational Leadership: Finally, situational leadership argues that no single style is the best in all circumstances. Leaders must assess the situation and adapt their style accordingly to optimize team and task performance.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Style: Each leadership style has its place and its pitfalls. For instance, while autocratic leadership can streamline processes in high-pressure scenarios, it may also suppress initiative and creativity. Democratic leadership, while fostering inclusivity, may at times hinder efficiency. Transformational leadership can drive change but may also overlook operational details, while servant leadership can enhance team unity but might lead to ambiguity in authority. Situational leadership necessitates a high degree of flexibility and judgement, which can be challenging for leaders to maintain consistently.
Situational Appropriateness of Leadership Styles: The key to effective leadership is the ability to tailor one's leadership style to the context and needs of the team and situation. Recognizing when to exert authority and when to solicit input, when to empower and when to direct, is what separates competent managers from transformative leaders.
Leadership Development: Cultivating the Right Style for Your Team

Assessing Team Needs and Adapting Leadership Styles: Leadership development starts with a clear understanding of team needs and dynamics. Leaders must be skilled in diagnosing the challenges facing their teams and flexibly adapting their leadership style to meet these needs. This might mean taking on a more autocratic approach to steer through a crisis or adopting a democratic stance to build consensus on a new strategic direction.
Techniques for Developing Leadership Skills Within a Management Context: There are numerous techniques for developing one's leadership skills within the context of management. Engaging in MBA online courses and obtaining online courses with certificates can solidify a theoretical understanding and provide practical tools for leadership. Other techniques include seeking mentorship, engaging in reflective practice, and actively soliciting feedback from peers and subordinates.
Importance of Self-Awareness and Continuous Learning in Leadership Development: A hallmark of an effective leader is a commitment to continuous learning and self-improvement. Self-awareness allows leaders to understand their strengths and areas for growth and to seek opportunities, such as MBA online courses or other valuable online courses with certificates, for expanding their knowledge and skills. Such commitment ensures that leaders keep pace with evolving business landscapes and enhance their capacity to lead effectively.
In summary, understanding and effectively applying varied leadership styles are central to effective management. Leadership development is a continuous journey, requiring an ongoing commitment to learning and self-improvement. Current and aspiring leaders are encouraged to evaluate and refine their management practices in alignment with the ever-changing objectives and challenges corporate environments present.
About the Author
The author of this article brings extensive expertise in leadership and management, having dedicated years to studying the intricacies of leadership dynamics and applying these principles in practice. Holding a rich blend of academic qualifications and real-world experience, the author aims to foster a community of practice that values feedback and collaborative growth in the realm of leadership and management.
Frequently Asked Questions
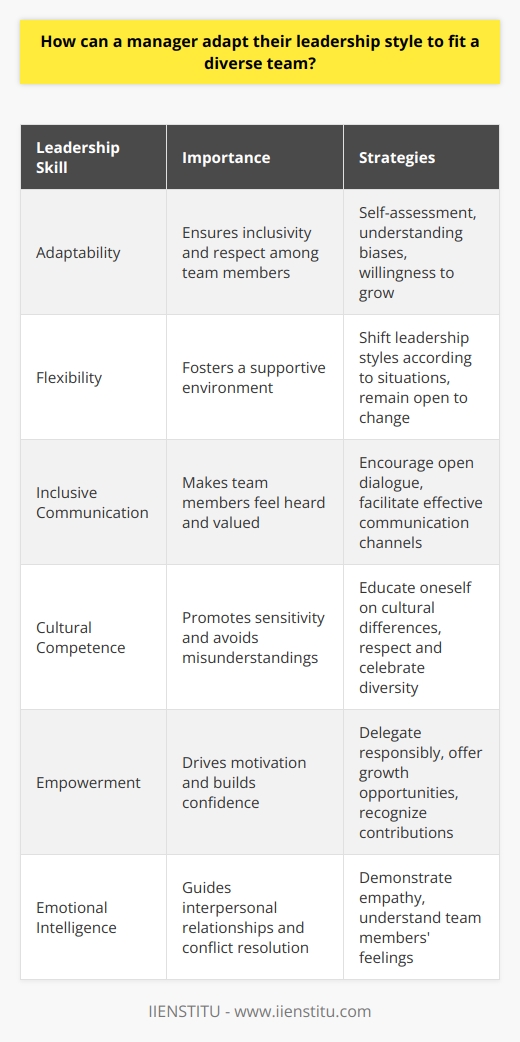
What are the key leadership styles essential for effective management?
Understanding Leadership Styles
Effective management requires diverse leadership styles. Leaders adapt these styles based on context. Management success often hinges on this adaptability. Here, we explore key leadership styles for effective management.
Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic leaders make decisions unilaterally. They command without seeking input. This style is effective for quick decision-making. It works well in crisis situations. However, it can stifle creativity and demotivate employees.
Democratic Leadership
Democratic leadership is participative. Leaders engage with team members. They seek contributions during the decision-making process. This style fosters commitment and collaboration. It enhances team morale. However, it can slow down decision-making.
Transformational Leadership
Transformational leaders inspire and motivate. They envision change and innovate. This style is effective for driving organizational change. It energizes teams and promotes engagement. But, focus can drift from current operations.
Transactional Leadership
Transactional leaders focus on routine and structure. They set clear goals and tasks. They reward performance and correct deviations. This style suits stable environments and predictable tasks. Overemphasis on order can hinder innovation, however.
Laissez-Faire Leadership
Laissez-faire leadership offers autonomy. Leaders trust employees and provide freedom. It can be effective with experienced and self-motivated teams. Employees thrive when they need little supervision. It can lead to chaos if not applied judiciously.
Situational Leadership
Situational leadership is adaptable. Leaders switch styles as needed. They assess team ability and commitment. This flexibility enhances team performance. It is complex to execute, as it requires astute judgment.
In conclusion, effective management relies on a blend of leadership styles. Leaders must assess situations and apply the most appropriate style. They must balance decisiveness with inclusivity. They should inspire innovation while maintaining order. And lastly, they must apply autonomy cautiously. A flexible approach to leadership is often a winning strategy.
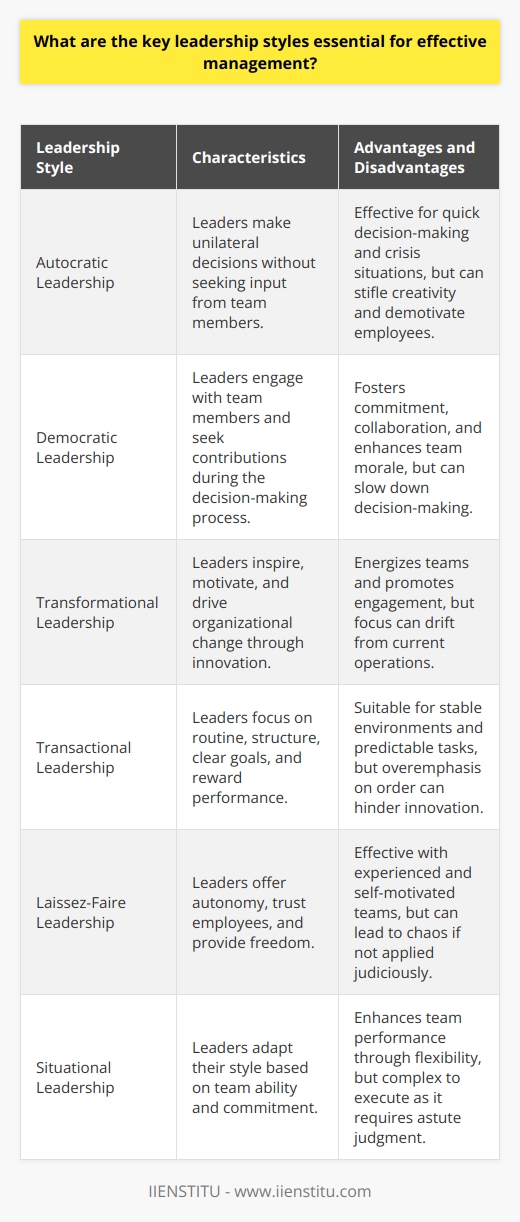
How does one's leadership style impact organizational performance?
Leadership Style and Organizational Performance
Leadership style greatly impacts organizational performance. Various styles exist. Each affects organizations differently.
Identifying Leadership Styles
Leaders fall into several categories. Examples include autocratic, democratic, and transformational. Each has unique characteristics.
Autocratic leaders make decisions alone. They provide clear expectations. Control is a central feature. This may increase efficiency. It can reduce creativity. Autocratic leadership often results in quicker decision-making. But employee satisfaction may suffer.
Democratic leaders involve others. They facilitate group discussion. Decision-making requires team input. Such leaders foster collaboration. They encourage ownership. Democratic leadership can boost morale. It may slow down decisions. Yet it often leads to innovative solutions. Employee engagement is usually high.
Transformational leaders inspire change. They focus on organization's vision. These leaders motivate employees. They encourage professional growth. Transformational leadership drives innovation. It often promotes a strong organizational culture. Employee loyalty tends to increase. It can be less effective in crisis management.
Impact on Organizational Performance
Leadership styles influence key performance areas.
- Employee morale and motivation
- Decision-making speed and quality
- Innovation and creative output
- Adaptability to change
- Employee retention and turnover
- Corporate culture and values
- Financial performance
An autocratic style might improve execution speed. Yet, it may stifle innovation. Reduced creativity can hinder performance.
A democratic style enhances team involvement. It improves problem-solving. This can lead to better decisions. Increased decision time is a tradeoff.
Transformational leadership can drive change. It can improve overall performance. Employees feel more engaged. But it may overlook short-term goals.
Merely choosing a style is not enough. Leaders must adapt their styles. Different situations require different approaches.
Effective leaders balance various styles. They may shift from autocratic to democratic as needed. This adaptability impacts performance positively.
Best Practices for Impactful Leadership
Leaders should understand their impact. They need to assess their style's fit. Fit depends on organizational needs.
One should align leadership style with goals. Aligning promotes better results. It positions organizations for success.
Continuous assessment and adaptation are essential. Leaders should seek feedback. They should refine their approach continually.
Employees benefit from varied leadership approaches. They develop professionally. They feel more satisfied. Organizational performance often reflects this.
Regular training can enhance leadership skills. Training encourages adaptation to various scenarios. Better skills lead to better results.
Concluding Thoughts
Leadership style shapes organizational outcomes. No style suits all situations. Effective leaders adapt. They match their style with needs. They navigate through changing landscapes. Adaptability marks truly impactful leadership. It enables an organization to thrive.
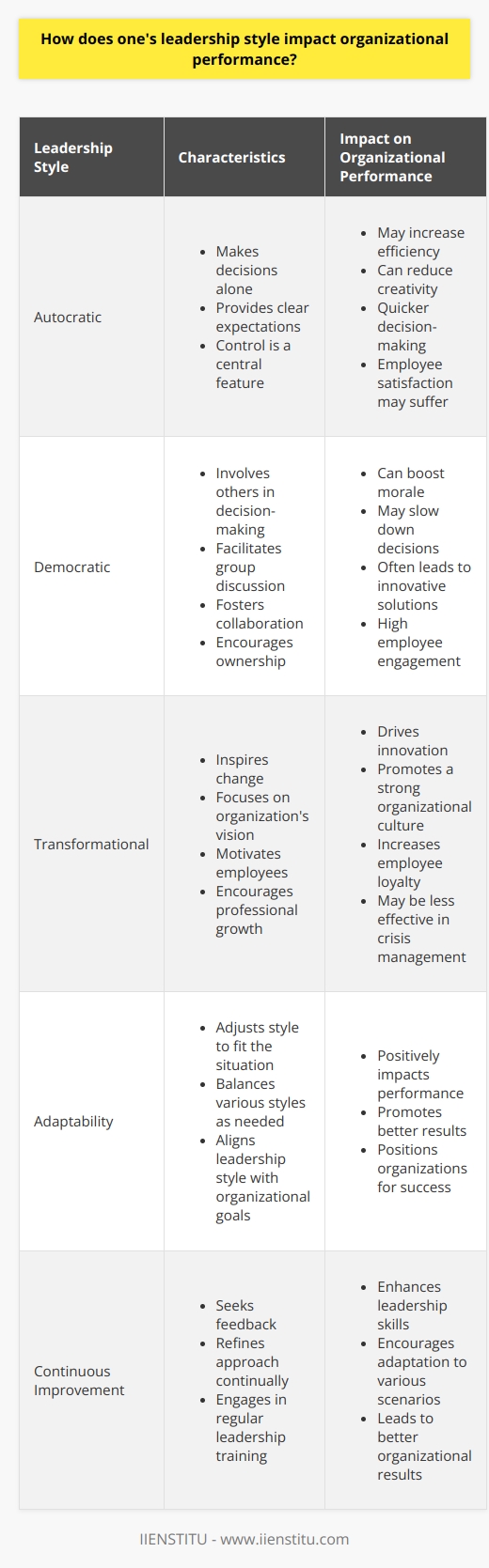
How can a manager adapt their leadership style to fit a diverse team?
Understanding Diversity in Teams
Leaders face varied challenges. Diverse teams are one. They present vibrant perspectives and skills. Managers must harness this diversity. Leadership styles impact team dynamics greatly. Effective managers adapt to their teams. They ensure inclusivity and respect amongst members.
Adaptability Is Key
Adaptation begins with self-assessment. Leaders must understand their own biases. They must be willing to grow. Every team member requires recognition. Their individual needs matter. Managers must listen actively. They should learn from their team's uniqueness.
Flexibility in Leadership Approaches
Flexibility is crucial for managers. One-size-fits-all approaches do not work. Each situation may require different tactics. Managers must shift their styles accordingly. They should remain open to change. This approach fosters a supportive environment.
Inclusive Communication Strategies
Communication is fundamental. It must be clear and inclusive. Managers should aim for transparency. They must encourage open dialogue. Team members should feel heard. Every voice holds value. Managers must facilitate effective communication channels.
Building Cultural Competence
Cultural competence cannot be overlooked. Managers must educate themselves on cultural differences. They should respect and celebrate these differences. Awareness promotes sensitivity. It avoids misunderstandings and conflict. Teams thrive when their cultures are acknowledged.
Empowering Your Team
Empowerment drives motivation. It involves trust and autonomy. Managers should delegate responsibly. They must offer growth opportunities. Every member should feel valued. Their contributions must be recognized. This builds confidence and investment in team goals.
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is vital. It guides interpersonal relationships. Managers must demonstrate empathy. They should understand team members' feelings. This understanding builds strong bonds. It leads to better conflict resolution.
Creating an Inclusive Culture
Managers play a pivotal role. They set the tone for inclusivity. They must promote a culture of respect. Everyone must feel they belong. Diverse perspectives should be encouraged. Innovation often stems from this diversity.
Continuous Learning and Development
Learning never stops for managers. They must seek continuous improvement. They should attend workshops and seminars. Reading the latest research is beneficial. Networking with diverse leaders provides insight. These efforts improve their ability to lead diverse teams.
Encouraging Feedback
Feedback loops are beneficial. They provide insight into management effectiveness. Managers should solicit team feedback regularly. They must be open to criticism. Positive change often results from feedback.
Adapting to Individual Learning Styles
People learn differently. Managers should recognize these differences. They must tailor their training methods. This respect for learning styles helps everyone grow. Personal development plans should be unique to the individual.
Fostering Team Cohesion
Cohesive teams achieve more. Managers should promote teamwork. They must celebrate collective successes. Shared goals are important. They unite teams. Collaborative projects should be encouraged. These initiatives strengthen team bonds.
Adapting leadership to fit a diverse team is complex. Managers must be flexible, culturally competent, and empathetic. These qualities help navigate the nuances of diversity. They foster an inclusive and productive work environment. Adaptation is not just a necessity; it's an opportunity for growth.