In the ever-evolving landscape of today's business environment, the significance of Human Resources (HR) leadership has become increasingly crucial. Far beyond managing the daily needs of employees, HR leaders are now seen as strategic partners capable of driving organizational success by aligning human capital with business goals. This blog embarks on an in-depth exploration into the core aspects of HR leadership. We will uncover how effective HR leaders can shape the ethos and trajectory of their organizations, tackle diverse responsibilities, and utilize essential skills to make a meaningful impact.
The Role and Importance of Human Resource Leadership
HR leadership is the bridge that connects an organization's strategic vision to its most valuable asset—its people. Acting as a vital conduit, HR leaders ensure that organizational objectives are met while fostering a positive workplace culture. This not only enhances employee satisfaction but also ensures compliance with various legal and ethical standards. The value of proficient HR leadership is profound because it contributes to creating a workplace environment where both employees and the organization thrive.
From my own experience, I’ve seen HR leaders transform workplaces from tense, unmotivated spaces into environments where creativity and productivity flourish. A friend of mine who works in HR recently shared how her team revamped their onboarding process—incorporating mentorship programs and frequent check-ins—to help new employees feel more integrated and valued. The difference was palpable: retention rates improved, and employees reported a stronger connection to the company’s mission. It’s a small yet powerful example of how intentional HR leadership can make a significant difference.
Examples of Successful HR Leadership Impacting Business Positively
Many well-known companies owe a great deal of their success to strong HR leadership. Take Google, for instance. Their HR department, known as 'People Operations,' is renowned for using data-driven strategies to craft a workplace where innovation thrives. By analyzing metrics on employee performance and satisfaction, Google has refined its hiring practices to attract top-tier talent while creating a culture that fosters creativity and collaboration. This focus on nurturing their employees has played a significant role in their rise to the top of the tech industry.
Another example is Southwest Airlines, where HR leaders have emphasized a culture of care and inclusiveness, ensuring that employees feel valued. They’ve integrated recognition programs and leadership development opportunities, leading to higher morale and a sense of ownership among employees. It’s no wonder Southwest is often highlighted as a benchmark for employee engagement in the airline industry.
Negative Implications of a Lack of HR Leadership
The flip side of the coin shows just how devastating the absence of strong HR leadership can be. Think of Enron, one of the most notorious examples of a failed corporate culture. The lack of ethical leadership and proper HR oversight at Enron contributed to a culture that prioritized profit over integrity. This toxic environment led to unethical practices that ultimately resulted in the company's downfall, leaving thousands of employees jobless and tarnishing the firm's legacy. This example underscores the critical importance of HR governance in establishing a culture that aligns with ethical standards and transparency.
Even in less dramatic situations, poor HR leadership can still hurt organizations. For example, a small tech startup I worked with faced challenges in retaining employees due to a lack of clear HR policies. Without a solid framework for handling disputes or providing growth opportunities, the team felt undervalued, resulting in high turnover. It wasn’t until the company hired an experienced HR leader who implemented a structured development plan and clear communication channels that the situation began to improve. This experience taught me how vital HR leadership is, even for smaller enterprises.
Key HR Leadership Roles and Responsibilities
HR leaders wear many hats as they strive to integrate the human element into their organizations. Here are some of the most critical roles and responsibilities they undertake:
1. Talent Acquisition and Management
Recruiting the right talent is a fundamental aspect of HR leadership. HR leaders are the architects of recruitment strategies—from identifying the skills needed for specific roles to defining the organization's unique value proposition to potential hires. This requires an in-depth understanding of the labor market, as well as an ability to craft job descriptions that attract candidates aligned with the company’s culture.
In my own career, I’ve seen the impact of this firsthand. During a phase when my organization struggled to attract skilled applicants, a new HR leader revamped the recruitment process by partnering with local universities and utilizing social media platforms for job postings. The result? We quickly began seeing a better fit of candidates who were eager to contribute to our company’s mission.
2. Employee Relations and Engagement
Building and maintaining positive employee relations is essential for any HR leader. This involves creating open communication channels, addressing grievances, and resolving conflicts in a manner that is fair and respectful. Employee engagement is about ensuring that individuals feel valued, heard, and have a sense of purpose in their work.
Effective HR leaders use a range of tools to keep employees engaged. From recognition programs to career development paths, they strive to build a workplace where everyone feels they are making meaningful contributions. This might include initiatives like flexible work arrangements or mental health support programs, which have become even more crucial in today's work-from-home landscape.
3. Organizational Planning and Development
HR leaders also play a key role in strategic organizational planning, ensuring that the company is not only well-equipped for current challenges but is also prepared for the future. This often involves succession planning and leadership development—identifying high-potential employees and creating pathways for their growth. In an era where business landscapes can shift rapidly, the foresight to develop internal talent ensures that companies remain agile and resilient.
I recall a time when our HR team introduced a mentorship program aimed at identifying future leaders. It was transformative for our organization. Junior employees who participated in the program felt more connected to the company, and we saw several of them grow into leadership roles over time. This kind of planning makes a huge difference in maintaining a steady flow of capable leaders within a company.
4. Legal Aspects and Compliance
Navigating the complexities of employment law is a crucial part of an HR leader's responsibilities. They ensure that the organization complies with regulations regarding labor rights, workplace safety, diversity and inclusion, and other legal standards. A misstep in these areas can result in costly lawsuits and damage to the company's reputation.
It’s essential to stay current with legal changes, and this is where continuous learning through professional courses becomes vital. A close colleague of mine who works in HR recently took an online course in employment law, and it equipped her with the knowledge to revamp her company’s policies on remote work, ensuring compliance with recent regulations.
5. Employee Development and Training
Investing in employee development is a long-term strategy that pays off in innovation, loyalty, and productivity. HR leaders design and implement training programs that align with the company’s goals, ensuring that employees not only acquire new skills but also feel invested in their personal growth. From leadership workshops to technical skill-building courses, HR leaders understand that continuous learning is the backbone of a thriving workplace.
In a previous role, I watched our HR leader launch a series of workshops focused on developing emotional intelligence and conflict resolution skills. The impact was significant, as employees became better equipped to navigate interpersonal challenges and communicate more effectively, leading to a more harmonious workplace environment.
Essential Skills for HR Leaders
To fulfill these multifaceted roles, HR leaders need a robust set of skills. Here are some of the key capabilities that make a successful HR leader:
1. Interpersonal and Communication Skills
Strong interpersonal and communication skills are fundamental for building relationships within the organization. The ability to listen actively, provide constructive feedback, and foster an environment where employees feel safe to express their thoughts is crucial. Whether it’s delivering difficult news or inspiring a team, effective communication can make all the difference.
2. Decision-Making and Strategic Planning Skills
HR leaders often find themselves at the crossroads of complex decisions that require both strategic insight and empathy. This could mean making tough calls on downsizing during economic downturns or identifying opportunities for new hiring during expansion phases. Effective HR leaders are those who can assess situations quickly, consider various outcomes, and make decisions that balance organizational needs with employee welfare.
3. Knowledge of Labor Laws and HR Best Practices
In an ever-changing legal landscape, staying up-to-date with labor laws and HR best practices is non-negotiable. Continuous education, such as enrolling in HR online courses, is essential for maintaining this expertise. This knowledge not only ensures compliance but also helps HR leaders advocate for policies that reflect current standards and create a fair and inclusive workplace.
The Future of HR Leadership
As we look ahead, the field of HR leadership is evolving rapidly. Here are some of the trends that will define the future of this critical role:
1. The Emergence of AI and Big Data in HR
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data analytics are becoming indispensable tools for HR leaders. By using predictive analytics, HR can anticipate workforce needs, tailor recruitment strategies, and even personalize employee development plans. It’s exciting to think about how these technologies will shape the future of HR, allowing leaders to make data-driven decisions that were previously unimaginable.
2. Increased Focus on Employee Wellness and Remote Work
The rise of remote work has brought employee wellness into sharper focus. HR leaders must now find ways to support a geographically dispersed workforce while maintaining a cohesive company culture. From promoting mental health initiatives to designing flexible work policies, the emphasis on employee well-being is no longer a nice-to-have but a critical part of sustainable HR strategy.
In conclusion, HR leadership serves as the linchpin that binds organizational vision to human potential. The roles, responsibilities, and skills required of HR leaders are diverse, but all share a common goal: to create a work environment where employees feel valued and the company thrives. As the business landscape continues to change, the demand for skilled HR professionals who can navigate these challenges will only grow. It is vital for both current and aspiring HR leaders to invest in their development, perhaps through online courses and certifications, to remain at the forefront of this dynamic field.
References
"HR from the Outside In" – Dave Ulrich and Wayne Brockbank: Explores how HR leaders can take on the role of strategic partners within organizations.
Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM): Provides up-to-date research and guidelines on various aspects of human resource management.
Harvard Business Review: Offers a range of articles on HR leadership and emerging trends in the business world.
"The Essential HR Handbook" – Sharon Armstrong and Barbara Mitchell: Contains practical insights into core HR processes and leadership.
"Leading Change" – John P. Kotter: A classic guide for those looking to understand effective change management and leadership.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key traits that define an effective HR leader and how do they influence an organization's culture?
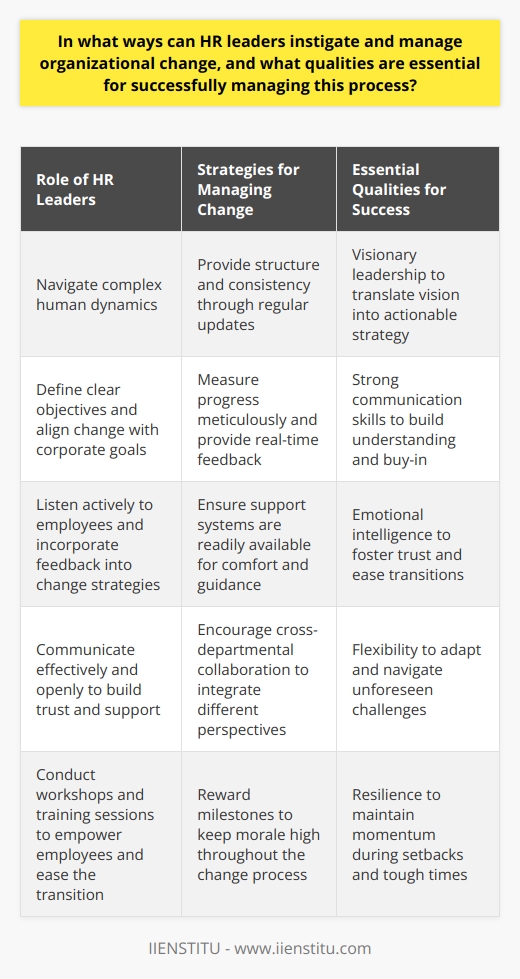
Key Traits of an Effective HR Leader
Vision and Strategy
An effective HR leader exhibits a clear vision. They articulate goals well. This vision sets the standard. It aligns with the organization's mission. Employees understand the direction. As a result, they can march towards common objectives. The leader's strategy becomes the guiding light.
Communication Skills
Communication remains key. Such leaders communicate clearly and effectively. They relay information succinctly. They listen actively. Feedback goes both ways. They understand non-verbal cues. Strong communication builds trust. It fosters an open environment. This encourages the sharing of ideas. Organizations benefit from diverse perspectives.
Empathy and Support
Empathy is critical. HR leaders show genuine care. They understand employees' needs. They provide support. This trait creates a supportive culture. Workers feel valued. Their concerns get heard. Empathy leads to stronger employer-employee relationships. Trust and loyalty grow in this soil.
Adaptability and Flexibility
Change is constant. Effective HR leaders adapt. They embrace change. Flexibility allows them to navigate complexities. They respond to shifting market dynamics. This ability impacts the culture. It encourages resilience. Employees learn to manage change. They become agile. The organization remains competitive.
Decisiveness
Decisions define leadership. HR leaders make tough calls. They assess situations quickly. They weigh options efficiently. Decisiveness prevents stagnation. It conveys confidence. This decisiveness influences the culture. Employees learn to trust their leader's judgment. This empowers them. They become decisive in their roles too.
Integrity and Ethics
Integrity is non-negotiable. HR leaders demonstrate high ethical standards. They walk the talk. Their behavior sets the benchmark. It influences the organization's moral compass. A strong ethics culture emerges. Employees mimic this behavior. They make choices that align with these values.
Inclusivity
Inclusivity drives modern workspaces. An inclusive approach is vital. HR leaders champion diversity. They appreciate different viewpoints. They build teams that reflect the world. An inclusive culture prospers. It draws talent. It nurtures innovation. Everyone feels they belong. Diverse ideas flourish.
Influence and Inspiration
Leaders inspire action. They motivate employees. Their influence extends beyond their team. They model behaviors. Employees emulate these traits. An inspired workforce becomes proactive. They tackle challenges head-on. They go beyond expectations. The leader's influence shapes the culture. It becomes one of motivation and engagement.
In sum, effective HR leadership encompasses various traits. These traits directly impact organizational culture. They foster environments where employees thrive. They allow adaptability in uncertain times. Leaders' actions and behaviors set a standard. Employees follow this standard. As a result, the culture grows. It supports the organization’s goals. It becomes a source of competitive advantage.
How does HR leadership foster employee engagement and productivity in the workplace?
Fostering Employee Engagement: A Central HR Leadership Role
HR leadership plays a critical role in shaping a workforce's engagement and productivity. When employees feel engaged, they often produce better work and have a stronger connection to their company’s goals and values. HR leaders employ several strategies to boost this engagement and productivity, fostering a robust organizational environment.
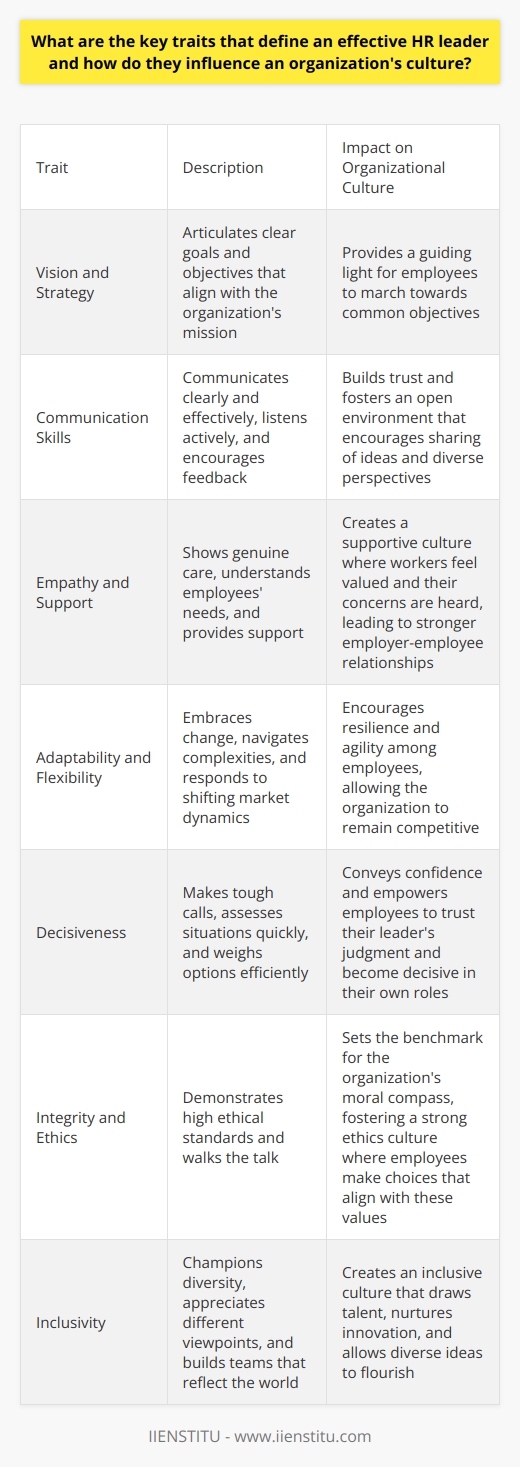
Setting Clear Expectations and Goals
HR leaders must establish clear expectations. They define roles, set achievable goals, and communicate these effectively. Employees align their efforts with these objectives. Clarity mitigates confusion and fosters a sense of purpose among staff.
Offering Professional Development Opportunities
Continuous learning drives engagement. HR invests in professional growth. Skills improvement and career advancement opportunities motivate employees. They feel valued and challenged, leading to increased productivity.
Encouraging Open Communication
Dialogue between employees and management is vital. HR fosters open communication channels. Feedback flows freely. Such transparency builds trust and ensures issues address swiftly.
Recognizing and Rewarding Performance
Recognition boosts morale. HR leaders implement recognition systems. These acknowledge achievements and hard work. Appreciation fuels employees’ drive and dedication.
Providing the Right Tools and Resources
Effective work requires proper tools. HR ensures staff have what they need. Access to technology and resources enhances productivity. It also reduces frustration and time wasted.
Prioritizing Work-Life Balance
Balance is key to preventing burnout. HR promotes policies that support work-life harmony. Flexible hours, remote work options, and sufficient time off serve this aim. Employees then remain fresh and focused.
Building a Positive Work Culture
Culture shapes the workplace atmosphere. HR crafts a culture of respect, diversity, and inclusion. A positive environment encourages collaboration and innovation. It attracts and retains top talent.
Investing in Employee Well-being
Happy employees work better. HR designs well-being programs. These cover health, mental wellness, and stress management. Employees stay healthier and more engaged.
HR leadership’s role extends beyond administrative tasks. Strategic engagement directly affects a company's success. Through these methods, HR leaders bridge the gap between employees and organizational objectives. They create a space where productivity thrives. It's a win for employees, management, and the company’s bottom line.
In what ways can HR leaders instigate and manage organizational change, and what qualities are essential for successfully managing this process?
Instigating Organizational Change
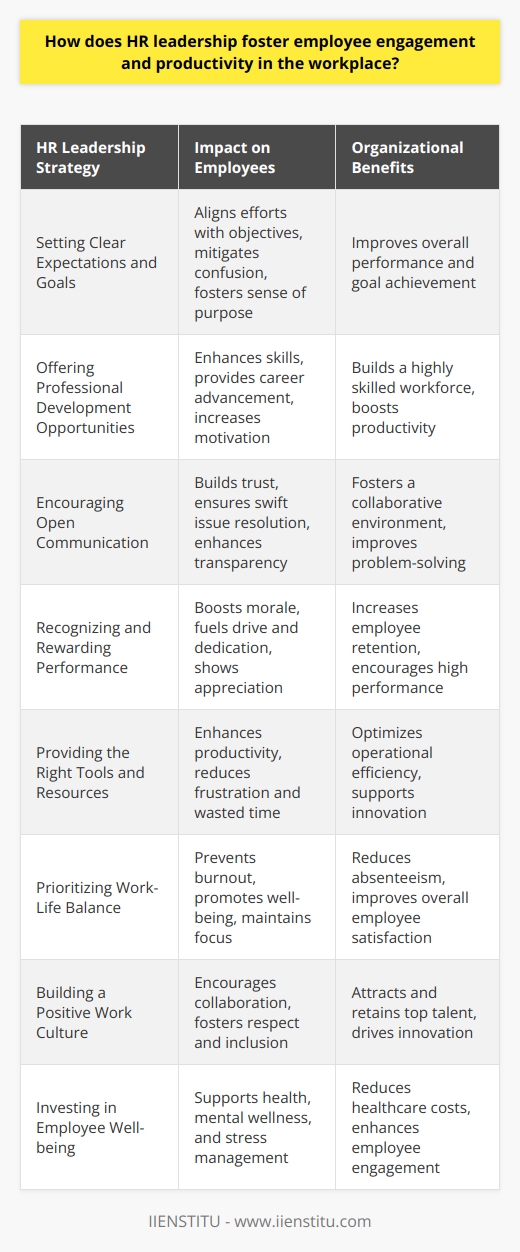
HR leaders play a vital role in organizational transformation. They must navigate complex human dynamics. Defining clear objectives is crucial. HR pioneers must listen actively to employees. This feedback shapes change strategies.
They must communicate effectively and openly. Transparency builds trust and support. HR should align change with corporate goals. Leaders need to involve every organizational layer.
Staff engagement matters significantly during change. HR can conduct workshops and training sessions. This empowers employees, easing the transition.
Robust plans are necessary to guide change. Contingencies must be in place. This ensures adaptability in a fluctuating environment.
Managing Organizational Change
Structure and consistency are vital for management. Regular updates provide a steady rhythm. Employees appreciate knowing where the company stands.
HR leaders measure the progress meticulously. Real-time feedback allows for agile adjustments. They reward milestones to keep morale high.
Support systems must be readily available. They provide comfort and guidance.
Cross-departmental collaboration also reinforces change. It integrates different perspectives and expertise.
Qualities Essential for Success
Several key qualities are essential:
Visionary Leadership
Leaders must see the end goal clearly. They translate vision into actionable strategy.
Strong Communication
Clear messaging builds understanding and buy-in. It requires concise language and repetition.
Emotional Intelligence
Empathy fosters trust and eases transitions. Leaders must understand the emotional landscape.
Flexibility
Changes do not always follow plans. Adaptability allows leaders to navigate unforeseen challenges.
Resilience
Setbacks are common in change processes. Resilience keeps momentum during tough times.
Strategic Thinking
Long-term impact is the focus. Every action ties back to the overarching strategy.
Commitment
Leaders must show dedication to inspire others. Their commitment encourages teams to follow suit.
- In conclusion, HR leaders spearhead and steer organizational change. They do this by setting clear goals and maintaining an open dialogue. Leaders need vision, communication skills, empathy, flexibility, resilience, strategy, and commitment. These attributes combined can lead to successful change management.