
Stress and anxiety are an inevitable part of life, affecting people from all walks of life. It is a natural response to challenging situations, but when it becomes chronic, it can take a significant toll on our physical and mental well-being. In today's fast-paced world, learning how to manage stress and anxiety effectively is more important than ever.
As someone who has struggled with stress and anxiety, I know firsthand how overwhelming it can be. There have been times when I felt like I was drowning in my own thoughts, unable to escape the constant worry and fear. It wasn't until I started to educate myself on the signs of physical stress in the body and the ways to reduce anxiety during stressful times that I began to find relief.
One of the most significant signs of physical stress in the body is muscle tension. When we are stressed, our muscles tense up, leading to pain and discomfort throughout the body. This tension can also trigger headaches and migraines, making it difficult to focus on daily tasks. I remember a particularly stressful period in my life when I was working long hours and dealing with personal issues. I started to experience severe neck pain and headaches that would not go away no matter what I tried. It wasn't until I started practicing yoga and meditation that I began to find relief.
Yoga and meditation are just two of the many stress relief techniques for anxiety and depression. These practices help to calm the mind and relax the body, reducing the physical symptoms of stress. Other techniques include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation. I find that taking just a few minutes each day to practice one of these techniques can make a significant difference in my overall well-being.
Another important aspect of managing stress and anxiety is identifying the common causes of stress in everyday life. For many people, work is a significant source of stress. Long hours, tight deadlines, and high expectations can all contribute to feelings of anxiety and overwhelm. Family issues, financial concerns, and health problems are also common stressors that can take a toll on our mental and physical health.
It's important to remember that emotional stress affects physical health just as much as physical stress does. When we are constantly worried or anxious, our bodies release stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Over time, this can lead to a weakened immune system, digestive issues, and even heart disease. That's why it's so important to find healthy ways to reduce anxiety during stressful times.
One of the most effective natural remedies for anxiety and stress relief is exercise. Regular physical activity helps to reduce stress hormones in the body while releasing endorphins, the body's natural mood boosters. Even just a short walk around the block can help to clear the mind and reduce feelings of anxiety.
Another natural remedy for stress and anxiety is herbal tea. Chamomile, lavender, and passionflower tea are all known for their calming properties. Drinking a cup of tea before bed can help to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality, which is essential for reducing the impact of stress on mental and physical well-being.
When it comes to managing stress and anxiety, it's important to remember that everyone is different. What works for one person may not work for another. That's why it's essential to experiment with different stress relief techniques until you find what works best for you.
One technique that I have found particularly helpful is breathing techniques to reduce stress quickly. When we are stressed or anxious, our breathing tends to become shallow and rapid. By taking slow, deep breaths, we can activate the body's relaxation response and calm the mind. One simple technique is to inhale for a count of four, hold for a count of four, and exhale for a count of four. Repeating this cycle for just a few minutes can help to reduce stress and anxiety quickly.
Another important aspect of stress management is self-care. When we are stressed, it's easy to neglect our own needs in favor of others. However, taking care of ourselves is essential for reducing the impact of stress on mental and physical well-being. This means getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and taking time for activities that bring us joy and relaxation.
One of my favorite self-care activities is reading. There's something about losing myself in a good book that helps to take my mind off of my worries and stressors. In fact, studies have shown that reading can reduce stress levels by up to 68% (Lewis, 2009). Other self-care activities might include taking a warm bath, practicing a hobby, or spending time with loved ones.
It's also important to recognize when stress and anxiety have become too much to handle on our own. If you find that your symptoms are interfering with your daily life or causing significant distress, it may be time to seek professional help. A mental health professional can provide additional stress relief techniques and support to help you manage your symptoms.
In conclusion, managing stress and anxiety is an ongoing process that requires patience, self-awareness, and a willingness to try new things. By understanding the signs of physical stress in the body, identifying the common causes of stress in everyday life, and experimenting with different stress relief techniques, we can reduce the impact of stress on mental and physical well-being. Remember, taking care of ourselves is not selfish – it's essential for living a happy, healthy life.
References:
Lewis, D. (2009). Galaxy Stress Research. Mindlab International, Sussex University.
Sapolsky, R. M. (2004). Why Zebras Don't Get Ulcers: The Acclaimed Guide to Stress, Stress-Related Diseases, and Coping (3rd ed.). Henry Holt and Company.
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2013). Full Catastrophe Living: Using the Wisdom of Your Body and Mind to Face Stress, Pain, and Illness. Bantam Books.
Hanson, R. (2013). Hardwiring Happiness: The New Brain Science of Contentment, Calm, and Confidence. Harmony Books.
Benson, H., & Klipper, M. Z. (2000). The Relaxation Response. HarperCollins.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors that contribute to climate change?
Key Factors Contributing to Climate Change
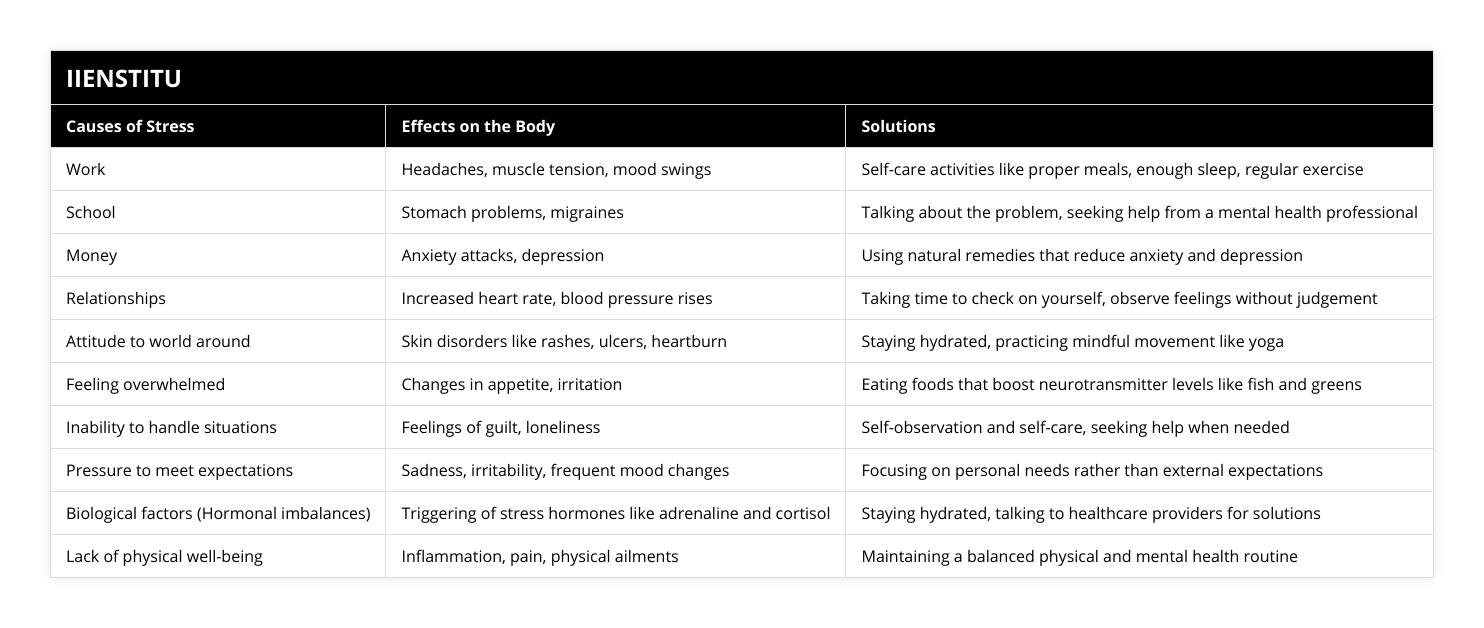
There are several key factors that contribute significantly to climate change. The most significant is the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas. When fossil fuels are burned, they release greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun, causing global temperatures to rise.
Deforestation is another major factor. Trees absorb and store carbon dioxide. When forests are cleared, that stored carbon is released. Deforestation also reduces the number of trees available to remove carbon dioxide from the air. Between 2015 and 2020, the world lost over 4 million hectares of forest per year.
Intensive livestock farming generates significant greenhouse gas emissions. Cows and sheep produce methane as part of their digestive process. Large scale cattle ranching leads to deforestation too. The livestock sector accounts for around 15% of global emissions.
Other contributors are fertilizers containing nitrogen and the burning of biomass. Overall, human activities are responsible for almost all of the increase in greenhouse gases over the last century. To mitigate climate change, we must transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy and prevent further deforestation. We must also reduce emissions from agriculture and other sources.
How does gender inequality manifest in different cultures?
Manifestations of Gender Inequality
Gender inequality refers to unequal treatment or perceptions of individuals based on their gender. This manifests in various ways across cultures. In many cultures, traditional gender roles cast women as caregivers and men as leaders. This leads to inequalities in domestic duties, employment, and positions of authority. For example, in parts of South Asia, women spend much more time on unpaid domestic work than men. In Saudi Arabia, strict laws prohibit women from traveling or working without a male guardian's permission.
Gender discrimination in education also perpetuates inequality. In Afghanistan, girls face barriers to attending school including lack of facilities, child marriage, and Taliban restrictions. Only 37% of Afghan girls complete primary education, compared to 66% of boys. This lack of education limits women's ability to participate in society.
Violence against women is another manifestation of gender inequality. Practices like female genital mutilation in parts of Africa, acid attacks in Southeast Asia, and honor killings in the Middle East target and control women. Up to 38% of murders of women worldwide are committed by intimate partners. Laws and enforcement often fail to protect women.
While many cultures have embedded gender inequalities, increased education for women and girls, activism, and legal protections are working to promote equal rights. Achieving gender equality requires changing long-held biases and practices.

What policies can governments implement to reduce poverty?
Policies to Reduce Poverty
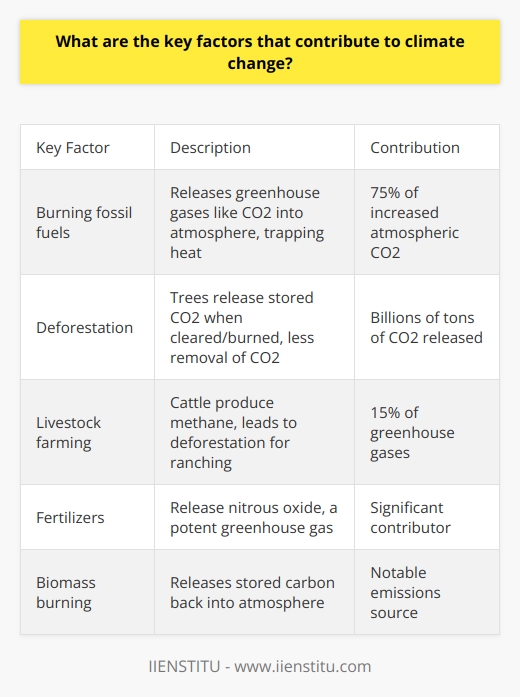
Governments can implement several policies to help reduce poverty. One important policy is to increase access to education. Governments can make primary and secondary education free and compulsory. They can also provide subsidies and scholarships to help low-income students attend college or vocational schools. Education gives people the skills needed to obtain better-paying jobs.
Another policy is to create more jobs and improve wages. Governments can invest in infrastructure and green technology to create construction and manufacturing jobs. They can set higher minimum wages and strengthen unions to improve pay. Policies that support small businesses can also lead to more job creation.
Governments can also strengthen social safety net programs. They can provide cash assistance, food stamps, and housing vouchers to help families meet their basic needs. Healthcare subsidies can make insurance more affordable. Increasing funding for childcare, disability, and unemployment benefits further aids those struggling financially.
Lastly, governments can reform tax policies to ease the burden on lower-income households. They can make tax systems more progressive by increasing taxes on the wealthy. Tax credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit can supplement wages for workers. Reducing regressive payroll and sales taxes helps increase take-home pay.
Implementing a mix of education, job creation, safety net, and tax reform policies can significantly reduce poverty. A comprehensive approach addresses both the symptoms and root causes of financial hardship for low-income families and individuals.
What are the long-term effects of stress on the body?
Stress is defined as the body's reaction to any change that requires an adjustment or response. Stress can come from any situation or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or anxious. Stress is your body's way of rising to a challenge and preparing to meet a tough situation. However, long-term exposure to stress can lead to serious health problems. This is because chronic stress keeps your body in a constant state of activation, which can disrupt nearly all processes and put you at risk for numerous health issues.
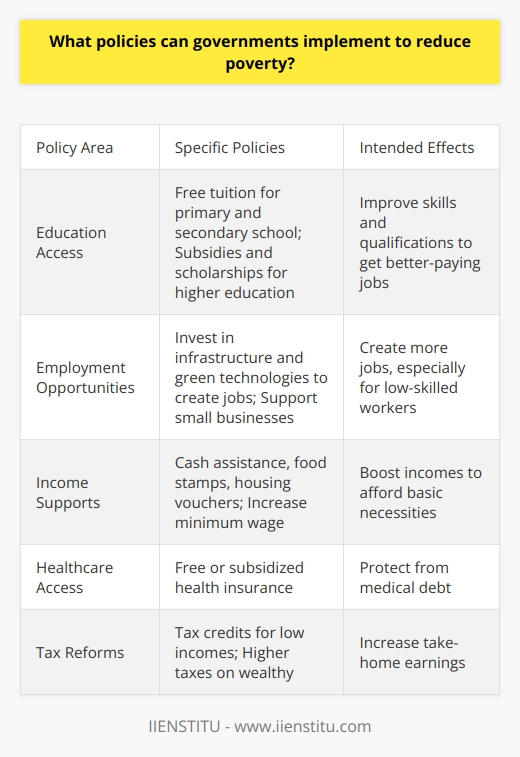
Effects on the Immune System
When you are stressed, your immune system's ability to fight off antigens is reduced. This is because chronic stress causes an imbalance between the immune system's two components - the innate and adaptive immune system. This makes you more susceptible to infections, colds, and other illnesses. Over time, prolonged stress can lead to lowered immunity and frequent sickness.
Effects on the Cardiovascular System
Stress hormones increase your heart rate and elevate your blood pressure. This places extra strain on the heart. Long-term exposure to stress leads to wear and tear of the cardiovascular system. It can also lead to heart disease, heart attacks, hypertension, arrhythmias, and strokes.
Effects on the Endocrine System
Chronic stress disrupts nearly all processes regulated by hormones. It leads to elevated levels of cortisol and suppresses the immune system. This imbalance impairs metabolism and can lead to weight gain. Prolonged stress also affects reproductive hormones like estrogen and testosterone.
Effects on the Nervous System
Stress hormones activate the sympathetic nervous system, providing the body with a boost of energy. However, chronic stress keeps the nervous system activated, leading to anxiety, insomnia, headaches, depression, and other mental health disorders.
In summary, long-term stress has detrimental effects on nearly all body systems. It impairs the immune system and can lead to frequent illness. It strains the cardiovascular system and increases the risk for heart disease and stroke. Stress disrupts hormonal balance and impairs metabolism. It also overstimulates the nervous system, leading to mental health issues. Managing stress effectively with lifestyle changes and relaxation techniques can help reduce its harmful effects on the body.
How does prolonged stress impact physical and mental health over time?
Impact of Prolonged Stress on Physical Health
Impact of Prolonged Stress on Mental Health
Conclusion
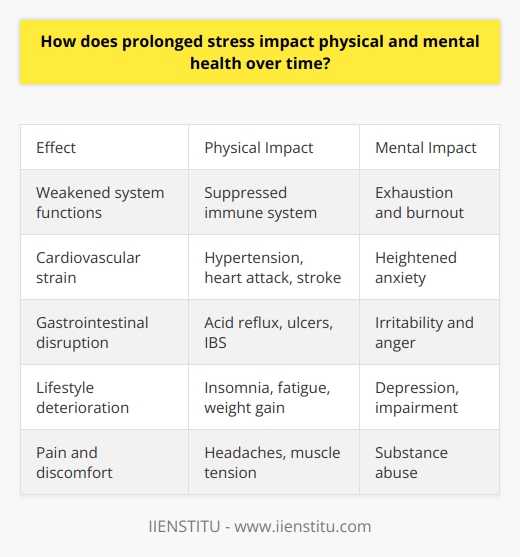
In what ways can chronic stress lead to adverse health outcomes if not properly managed?
Effects of Chronic Stress on Health
Chronic stress that continues for a long time can have many negative effects on physical and mental health if it is not managed properly. When people experience frequent or constant stress, their body remains in a heightened state of arousal for extended periods. This can disrupt nearly every body system and cause both short- and long-term health problems.
Impact on Immune System
Chronic stress weakens the immune system, making people more prone to frequent illnesses like colds and flu. It also takes longer to recover from illnesses. This is because stress hormones like cortisol suppress the immune system when they remain elevated for long periods. Chronic stress can reactivate latent viruses in the body like Epstein-Barr virus or shingles.
Cardiovascular Effects
Chronic stress contributes to high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. It raises blood pressure and heart rate, increasing wear and tear on blood vessels and the heart. Stress hormones also increase blood clotting, platelets, and inflammation, which can lead to blocked arteries and cardiovascular events.
Metabolic Changes
Chronic stress leads to excess belly fat accumulation as the body prepares to respond to perceived threats. It also contributes to insulin resistance, high blood sugar, and diabetes. Cortisol can raise blood sugar levels and the presence of excess belly fat also reduces insulin sensitivity.
Gastrointestinal Problems
Chronic stress commonly causes or worsens digestive issues like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and inflammatory bowel disease. It increases inflammation, alters gut bacteria, and affects gut motility and secretions.
Effects on Brain and Mental Health
Chronic stress can shrink parts of the brain involved in memory and reasoning and increase the risk of dementia. It also contributes to mental health problems like depression and anxiety disorders. Chronic activation of the stress response changes brain chemistry and structure over time.
Other Effects
Chronic stress also contributes to headaches, muscle tension and pain, fatigue, sexual problems, sleep disturbances, and weight gain. It is clear that uncontrolled chronic stress has wide-ranging detrimental effects on nearly every system in the body and mind.
Conclusion
In summary, chronic stress can have serious adverse impacts on health if it is not managed properly. From frequent illnesses to heart disease, digestive disorders, mental health issues, and more, uncontrolled chronic stress exacts a toll on the body. Using stress management techniques is essential to prevent these potential consequences.
What are some common symptoms of stress in women?
Stress is a common experience for many women. When under stress, the body reacts both physically and psychologically. Recognizing the symptoms of stress can help women identify when their stress levels are elevated and take steps to manage them. This paragraph will discuss some of the common physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms of stress that women may experience.
Physical Symptoms
There are many physical symptoms of stress that women may notice. Headaches, muscle tension, chest pain, fatigue, and changes in sex drive can all be caused by stress. The hormones released when stressed, like cortisol, raise blood pressure and heart rate. This leads to symptoms like headaches. Muscle tension occurs because stress hormones ready the body to respond to threat. Fatigue results from the body being in a heightened state. Women may also experience stomach issues from stress, like diarrhea, constipation, or nausea. Sleep disturbances, including insomnia and not feeling rested, are also common physical symptoms of stress.
Emotional Symptoms
In addition to physical symptoms, women may experience emotional symptoms when stressed. Anxiety, irritability, sadness, and moodiness are common. Difficulty concentrating and feeling overwhelmed are also signs of stress. Some women may experience depression and isolation when under high stress. Changes in eating habits, like emotional eating or loss of appetite, can occur. Stress also leads to negative thinking patterns like catastrophizing and self-criticism. Recognizing these emotional symptoms can alert women to address their stress.
Behavioral Symptoms
The behaviors of stressed women also tend to change. Nervous habits like nail biting and foot tapping increase for some women when stressed. Others may experience angry outbursts or be more impatient. Some behaviors reflect the emotional symptoms, like withdrawing from others when depressed or overeating to cope. Procrastination, neglecting responsibilities, and relying on alcohol or drugs to unwind can signal high stress levels. Women may also exhibit forgetfulness, clumsiness, or difficulty speaking when stressed. Being aware of these behavioral changes can help women identify rising stress.
In summary, women experiencing stress may notice many physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. Headaches, anxiety, and irritability are just a few examples. Recognizing the signs of stress in one's body and life is the first step to managing stress effectively. Women can then employ stress-reduction techniques and get support to improve their wellbeing.
How can women recognize when they are experiencing unhealthy levels of stress?
Recognizing Unhealthy Stress Levels in Women
Women often deal with high levels of stress related to responsibilities at work, home, and in relationships. It is important for women to be able to recognize when the stress becomes unhealthy. Monitoring both emotional and physical signs of excessive stress can help women identify problems early.
Emotionally, unhealthy stress levels may lead to increased anxiety, irritability, sadness, or other mood changes. Women experiencing unhealthy stress may have racing thoughts or constant worry. They may have difficulty relaxing or trouble sleeping. Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed can also indicate unhealthy stress.
Physically, unhealthy stress can cause tight muscles, headaches, stomach issues, and changes in appetite. Women may experience fatigue, muscle tension, rapid heart rate, or high blood pressure. Stress can also weaken the immune system, making women more prone to frequent illnesses.
The sources of stress provide important clues as well. While everyday stressors like a busy job or parenting responsibilities can be managed, long-term stresses like relationship conflict, financial struggle, or grief take a toll. Traumatic events or major life changes also contribute to high stress levels.
Women should monitor stress levels by noticing emotional and physical signs. Keeping a journal can help identify stress patterns over time. Prioritizing stress-reducing activities like exercise, meditation, or hobbies can help manage stress. Talking to supportive loved ones or a mental health professional can help gain perspective.
Recognizing unhealthy stress quickly allows women to take action to improve wellbeing. Identifying and managing the sources of stress, as well as engaging in self-care, can help women lead happier, healthier lives.
What steps can women take to manage stress symptoms and improve their overall wellbeing?
Managing Stress and Improving Wellbeing
Stress is a common issue for many women. High stress levels can negatively impact both physical and mental health. There are steps women can take to manage stress and promote overall wellbeing. Getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and practicing relaxation techniques are effective ways to reduce stress. Additionally, developing healthy social connections, pursuing enjoyable hobbies, and seeking professional help when needed can improve quality of life.
Sleep and Nutrition
Adequate sleep and proper nutrition provide the foundation for managing stress. Most adults need 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Eating a diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins gives the body vital nutrients. Avoiding excess caffeine, alcohol, and sugary foods also helps stabilize energy levels. Staying hydrated with water supports overall health.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise is a powerful stress reliever. Aerobic exercise releases endorphins which boost mood. Strength training builds muscle and improves self-esteem. Even light activities like walking benefit the mind and body. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Outdoor activities also expose people to nature which further reduces stress.
Relaxation Techniques
Activities that activate the body's relaxation response counter the effects of stress. Deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and tai chi are excellent options. Schedule time to practice these techniques daily. Mindfulness meditation helps calm the mind. Guided imagery and progressive muscle relaxation reduce muscle tension. Maintaining work-life balance and taking breaks from technology also limit stress.
Social and Professional Support
Connecting with supportive friends and family members provides comfort during difficult times. Joining community groups and volunteering allows people to help others while expanding their social network. Some individuals benefit from counseling to develop healthy coping strategies. Do not hesitate to seek professional services if feeling depressed, anxious, or overwhelmed by stressors.
Making positive lifestyle changes empowers women to take control of their health and wellbeing. Managing stress and improving quality of life is a process requiring commitment. However, the benefits to both physical and mental health make it a worthwhile endeavor.
What are some common physical and psychological chronic stress symptoms?
Chronic stress can have significant impacts on both physical and psychological health. When stress becomes an ongoing issue, the body's stress response systems remain activated for prolonged periods. This can lead to wear and tear on the body and mind, resulting in various chronic symptoms.
Physical Symptoms
Some of the most common physical symptoms of chronic stress include headaches, muscle tension, chest pain, fatigue, changes in appetite, stomach upset, and sleep disturbances. Headaches are very prevalent, as chronic stress causes muscle tension and tightness in the neck and scalp. Chest pain and discomfort may also occur, as stress hormones can cause chest muscles to constrict. Fatigue from depleted energy reserves is another hallmark of long-term stress.
Chronic stress often leads to changes in appetite and digestion issues like stomachaches, nausea, and diarrhea. It disrupts hormones that regulate hunger and fullness. Sleep is also impacted, resulting in insomnia or restless sleep. The constant state of arousal makes it difficult to fall and stay asleep. These physical symptoms can persist and worsen over time if stressors are not addressed.
Psychological Symptoms
In addition to physical effects, ongoing stress also causes many psychological symptoms. Increased anxiety and nervousness are common, as the body is stuck in fight-or-flight mode. Irritability and moodiness are also frequently reported, as stress hormones fluctuate. Chronic stress often leads to depression, especially when a person feels unable to escape their stressors.
Stress can also impair concentration, focus, and memory. It can lead to racing thoughts and a lack of mental clarity. Low motivation and feelings of being overwhelmed are other psychological symptoms. Chronic stress takes a toll on emotional health, often causing increased negativity, loneliness, and isolation. It can also lead to detrimental coping behaviors like drug use, overeating, and social withdrawal.
The psychological symptoms of chronic stress demonstrate why it is so important to manage stress effectively. If left unaddressed, these mental health effects can significantly impact happiness, relationships, and quality of life.
How might chronic stress impact cognitive functions and decision making?
Effects of Chronic Stress on Cognition
Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on cognitive functions like memory, attention, and decision making. When an individual experiences prolonged stress, their body is flooded with stress hormones like cortisol. High cortisol levels can cause changes in brain regions involved in memory and learning, such as the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.
One cognitive function negatively impacted by chronic stress is working memory. Working memory allows us to temporarily store and manipulate information for complex tasks. Studies show that individuals with high stress have reduced working memory capacity. This impaired working memory makes it difficult to stay focused, process information, and make decisions.
Chronic stress also diminishes attention span and the ability to filter out distractions. The prefrontal cortex controls attention and is vulnerable to prolonged cortisol exposure. People experiencing chronic stress struggle with focusing, multitasking, and staying vigilant over time. This attention deficit makes it challenging to absorb information needed for good decision making.
Furthermore, chronic stress can reduce cognitive flexibility, which is key for adapting to changing situations. Stressed individuals tend to develop fixed thinking patterns and struggle with set-shifting between concepts. This rigidity makes it hard to see alternative solutions when making difficult decisions.
Decision making itself is also compromised by chronic stress, as elevated cortisol impairs the ability to weigh risks and benefits. Stressed individuals tend to make more risky, impulsive choices rather than deliberate, well-reasoned decisions. They also struggle with overcoming confirmation bias when evaluating options.
In summary, the elevated cortisol and changes in brain function caused by chronic stress can significantly impair memory, attention, cognitive flexibility, and decision making abilities. Interventions like stress management, exercise, mindfulness, and counseling may help restore cognitive function in stressed individuals.
What lifestyle changes can help manage chronic stress symptoms?
Exercise and Physical ActivityRegular exercise and physical activity have been shown to help manage chronic stress and anxiety. Even light exercise like walking or yoga can help reduce muscle tension, release endorphins, and improve mood and sleep quality. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate activity most days of the week. Consider joining an exercise class or sports team for social interaction. Just be careful not to overdo it as too much intense exercise can increase stress.
Relaxation TechniquesPracticing relaxation techniques is key for counteracting the negative effects of chronic stress. Try deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, or mindfulness. These can lower blood pressure and heart rate, relax muscles, and calm the mind. Dedicate at least 15-20 minutes daily to relax through breathing, guided imagery, or meditation apps. Consider taking a yoga or tai chi class which combine physical activity with mindfulness.
Sleep Hygiene Getting adequate, high-quality sleep is essential for managing stress.Aim for 7-9 hours per night and go to bed and wake up at consistent times. Limit screen time before bed and avoid stimulants like caffeine late in the day. Create a restful sleep environment that is cool, dark and quiet. Consider trying sleep supplements like melatonin or magnesium if needed. Getting on a regular sleep schedule can improve mood, focus and resilience.
Healthy DietEating a balanced, nutritious diet can help combat the effects of chronic stress. Limit caffeine, alcohol, refined carbs and sugars which can exacerbate anxiety and mood swings. Eat more veggies, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats for sustained energy and focus. Stay hydrated by drinking enough water throughout the day. Taking vitamins like vitamin C, magnesium and omega-3s may also help regulate cortisol levels.
Social Support Network Having a strong support system of family and friends can help buffer the impacts of chronic stress. Make time for social activities you enjoy and share feelings with loved ones you trust. Join a support group to connect with others facing similar challenges. Consider counseling or therapy for coping strategies and to process difficult emotions. Don't isolate yourself as social interaction provides mood-boosting benefits.
How does stress affect your body and mind physiologically and psychologically?
Physiological Effects of StressStress activates the sympathetic nervous system, triggering the fight-or-flight response. This causes the adrenal glands to release stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Cortisol increases blood sugar levels to provide the body with energy. Adrenaline increases heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. Blood is diverted away from the digestive system and towards the muscles. The immune system is suppressed. Although this is helpful for short-term survival, chronic stress keeps the body in a constant state of arousal. This can lead to high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, and a weakened immune system.
Psychological Effects of StressStress affects brain function and mental health. Cortisol impairs memory and the ability to learn new things. Stress reduces connectivity between brain cells. The amygdala becomes more active, making people more anxious and irritable. Chronic stress causes dendrites in the prefrontal cortex to retract. This impairs executive function skills like focus, organization, and time management. Stress also contributes to mental health issues like depression and anxiety disorders. It can make symptoms worse in people with mental illnesses.
Improving Stress Resilience While some stress is inevitable, there are ways to mitigate its effects. Getting regular exercise helps the body cope with stress hormones. Relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing activate the parasympathetic nervous system. This reverses the fight-or-flight response. Maintaining social connections provides emotional support. Eating a healthy diet keeps the immune system strong. Getting enough sleep allows the brain to recover from stress. Setting aside time for hobbies and fun activities can relieve stress. Seeking professional help for chronic stress can prevent long-term health consequences.
What are the impacts of chronic stress on physical and mental health?
Chronic stress can have significant detrimental impacts on both physical and mental health. When an individual experiences frequent or constant stressors over an extended period of time, the body's stress response systems remain activated, leading to wear and tear that can manifest in various ways.
Physical Effects
Prolonged exposure to stress hormones like cortisol can disrupt almost all body systems. Chronic stress has been linked to increased risk for heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, gastrointestinal issues, impaired immune function, headaches, and other pain. It is thought to accelerate biological aging and brain changes. The constant state of arousal taxes the body and leaves it more vulnerable to illness and disease.
Mental Health
Chronic stress also takes a toll on mental health. It is associated with increased rates of depression, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse. Stress hormones and inflammation can impact brain regions involved in mood regulation. Furthermore, dealing with constant challenges can lead to feelings of helplessness, lack of control, and low self-esteem. Chronic stress may alter neural pathways, making the brain more reactive to perceived threats.
The mental health effects of chronic stress include cognitive deficits such as impaired memory and concentration. It can be more difficult to make decisions, solve problems, or focus under prolonged stress. This can impact work performance, relationships, and overall wellbeing. Chronic stress may also lead to maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors as coping mechanisms.
Mitigating Chronic Stress
Since chronic stress has widespread consequences, it is important to manage stress levels through healthy lifestyle habits. Regular exercise, proper nutrition, adequate sleep, and social connection can all help mitigate the impacts of stress. Relaxation practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing activate the body's relaxation response. Seeking professional help for mood disorders, addictions, or other mental health issues can also alleviate chronic stress.
While occasional stress is normal, chronic stress can seriously jeopardize physical and mental health. Managing stress through healthy coping strategies and getting treatment when needed can help minimize its detrimental effects over the long term.
What coping strategies can help mitigate the effects of stress on overall wellbeing?
Coping Strategies to Mitigate Stress
Stress is an unavoidable part of life that can negatively impact overall wellbeing if not properly managed. Research shows that developing healthy coping strategies can help mitigate the effects of stress on mental and physical health. This paper will discuss evidence-based coping strategies in three categories: cognitive strategies, relaxation techniques, and lifestyle changes.
Cognitive Coping Strategies
Cognitive coping strategies aim to change thought patterns and perceptions about stressors. Examples include positive self-talk, reframing situations positively, humor, and practicing gratitude. Studies show that optimistic thinking reduces anxiety and depression while boosting resilience and life satisfaction. Other effective cognitive strategies include planning and prioritizing tasks, accepting what cannot be changed, and avoiding catastrophizing and rumination. Mastering cognitive coping skills can reframe stressful situations as more manageable.
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques activate the parasympathetic nervous system to induce calmness. Deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, yoga, tai chi, and mindfulness have proven anti-stress benefits. One study found that mindfulness meditation significantly reduced anxiety, depression, and stress after just eight weeks of practice. Regular relaxation habits lower blood pressure, heart rate, and cortisol. Quieting the mind through relaxation techniques also increases focus, emotional resilience, and inner peace.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle mitigates stress over the long-term. Key lifestyle factors include regular exercise, adequate sleep, a balanced diet, and time set aside for fun and social connection. Maintaining work-life balance through proper time management and saying “no” to extra responsibilities also prevents burnout. Even small lifestyle tweaks like taking brief nature walks, journaling, or scheduling micro-breaks can alleviate daily stressors. Overall, a healthy lifestyle provides the physical and mental resources needed to cope effectively with unavoidable stresses.
In conclusion, developing cognitive, relaxation, and lifestyle coping skills can substantially protect wellbeing against the detrimental effects of stress. A multifaceted coping strategy approach provides individuals with a variety of tools to actively manage stressors and maintain health and resilience.
What are some of the main causes of stress?
Stress is a common part of life that can negatively impact mental and physical health if not properly managed. There are various factors that can lead to increased stress levels in individuals. Some of the main causes of stress include:
Work-Related Stressors
Many people experience high levels of stress related to their jobs. Heavy workloads, tight deadlines, long hours, and job insecurity can all contribute to work-related stress. Additionally, issues like difficult coworkers, micromanaging bosses, lack of autonomy, and work-life imbalance can lead to increased stress for employees.
Financial Problems
Money issues are a very common source of stress. Not having enough income to cover expenses, juggling multiple jobs, struggling with debt, and experiencing financial hardship can all heighten stress. Even for those who are financially secure, major expenses like buying a home or paying for college can still cause money-related anxiety.
Major Life Changes
Significant life changes and events require major adjustment, which can be stressful. Things like getting married, having children, starting a new job, moving, experiencing the death of a loved one, and going through a divorce or breakup can all trigger stress.
Health Problems
Dealing with illness and medical issues, whether your own health condition or that of a loved one, is highly stressful. Serious, chronic, or terminal illnesses especially contribute to anxiety and emotional strain. Additionally, pain, disabilities, hospitalizations, and medical treatments can cause stress.
Family Responsibilities
Caring for children, aging parents, or family members with special needs can lead to elevated stress levels. The demands of childcare, household duties, elder care, and coordinating family members' schedules takes a toll. For many, balancing family obligations with work adds extra pressure.
In summary, common causes of stress include a heavy workload, financial constraints, major life changes, health problems, and family responsibilities. Identifying the sources of stress is important for managing it effectively.
How can identifying the causes of stress help in managing it?
Identifying Causes of Stress
Stress is an unavoidable part of life that can negatively impact mental and physical health if not properly managed. Identifying the causes of stress is an important first step in developing effective coping strategies. Stress can be triggered by major life events such as the death of a loved one, divorce, or job loss. However, stress can also result from an accumulation of minor daily hassles like traffic jams, arguments with friends, or workplace deadlines. By recognizing the sources of stress, steps can be taken to alter situations, thought patterns, and behaviors in order to prevent or minimize stress.
Altering Situations
If the source of stress stems from the external environment, taking action to change the situation may be possible. For example, if a long commute to work is causing stress, consider moving closer to your job or asking if remote work options are available. If financial difficulties are mounting, developing a budget and reining in spending can help regain control. For interpersonal conflicts, openly communicating with the other party to find a resolution can be worthwhile. Prioritizing responsibilities and not taking on more than you can handle will also limit stress.
Changing Thought Patterns
Often, stress is exacerbated not by the situation itself, but rather our negative thought patterns surrounding the circumstance. When a stressful event occurs, we may catastrophize and ruminate on worst-case scenarios, making the problem seem insurmountable. Adopting a more positive mindset can help reframe challenges as temporary obstacles that can be overcome. Accepting that which cannot be changed while focusing energy on that which can be altered is also useful. Being mindful and staying grounded in the present moment can curb anxious thoughts about hypothetical situations.
Modifying Behaviors
Stressful situations may prompt unhealthy behavioral coping mechanisms like smoking, drinking, emotional eating, or lashing out at loved ones. By recognizing these unhealthy behaviors as reactions to stress, steps can be taken to replace bad habits with more effective stress management techniques. Healthy behaviors like exercise, meditation, listening to music, spending time outdoors, and engaging in hobbies can relieve both mental and physical tension. Don't take on too much. Scale back obligations and take time for self-care. Getting adequate sleep, eating a balanced diet, and taking breaks restores mental clarity to deal with challenges.
Conclusion
Identifying sources of stress is key to managing and reducing strain. Once triggers are recognized, situational factors can be altered when possible, thought patterns reframed, and coping behaviors modified. This multi-pronged approach enables development of a personalized stress management plan. By being aware of their unique stress response, individuals can react in a healthy manner, prevent burnout, and improve overall well-being.
What lifestyle changes can reduce the causes of stress?
Exercise RegularlyRegular exercise is one of the most effective ways to reduce stress. Exercise releases endorphins which improve mood and reduce feelings of anxiety and depression. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate exercise like walking, swimming or cycling most days of the week. Even short 10 minute bursts of exercise can help relieve stress. Get Enough Sleep Lack of sleep is a major cause of stress. Most adults need 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Going to bed and waking up at consistent times improves sleep quality. Avoid stimulants like caffeine and screens before bedtime. Use relaxation techniques like deep breathing to fall asleep more easily. Eat a Healthy DietEating a diet high in processed and sugary foods can exacerbate stress. Eat plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats. Avoid skipping meals which can cause blood sugar crashes. Stay hydrated by drinking enough water throughout the day. Reduce or eliminate alcohol and caffeine.Practice Relaxation Techniques Simple relaxation practices like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, tai chi and progressive muscle relaxation activate the body's relaxation response to counteract stress. Even taking a few minutes to listen to calming music or go for a short walk can help relieve stress. Practice these techniques regularly for maximum benefits.Set Aside Time for HobbiesMaking time for hobbies and activities you enjoy is vital for managing stress. Hobbies help take your mind off worries and provide a positive outlet for emotions. Reading, gardening, crafting, playing sports and spending time with pets are examples of stress-relieving hobbies. Schedule time for hobbies every day or several times per week.Spend Time with Loved OnesHaving strong social ties is important for reducing stress. Spend quality time with family, friends, co-workers and pets who make you feel loved, supported and relaxed. Share meals, go for walks, volunteer together or take a class to meet new people and form connections. Seek Professional HelpFor chronic or severe stress that interferes with daily life, seek help from a mental health professional. Therapists and counselors can provide stress management advice and help you work through underlying issues contributing to stress like trauma, depression or anxiety. Practicing healthy lifestyle habits alongside professional treatment is ideal.
What are some common emotional stress symptoms that people experience?
Stress is a normal part of life that can affect us both emotionally and physically. When someone is experiencing emotional stress, it can manifest in various symptoms. Some of the most common emotional symptoms of stress include anxiety, irritability, sadness, loneliness, anger, and frustration.
Anxiety is a very common symptom of emotional stress. This can present itself as constant worrying, racing thoughts, feeling tense, having panic attacks, and experiencing sleep issues like insomnia. Irritability is another frequent symptom, where someone is easily annoyed and has frequent mood swings. They may snap at loved ones over minor issues.
Feelings of sadness and loneliness often accompany stress. Someone may withdraw socially and feel hopeless about the future. They may also experience worthlessness and lack motivation for activities they once enjoyed. Anger and frustration are other emotions tied to stress. Someone may have a short temper and lash out at others.
Physical symptoms like fatigue, muscle tension, stomach upset, and headaches can also occur with emotional stress. However, the emotional impact can be longer lasting. Left untreated, emotional stress can lead to relationship problems, substance abuse, and serious conditions like depression or anxiety disorders.
There are many healthy ways to cope with emotional stress symptoms. Getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, practicing relaxation techniques, connecting with loved ones, and making time for hobbies are all excellent stress management strategies. If symptoms persist or worsen, it's important to consult a healthcare provider or mental health professional.
In summary, common emotional symptoms of stress include anxiety, irritability, sadness, loneliness, anger, and frustration. Stress can also manifest physically with fatigue, muscle tension, stomach issues, and headaches. Coping strategies like exercise, healthy eating, social connection, relaxation, and hobbies can help manage these symptoms. Seeking professional help is recommended if symptoms are overwhelming or lasting.
How can emotional stress symptoms negatively impact one's health and well-being?
Impact of Emotional Stress on Health and Well-Being
Experiencing emotional stress can lead to many negative health effects. When someone is stressed, their body produces stress hormones like cortisol. High cortisol levels over time weaken the immune system. This makes people more likely to get sick from viruses and infections. Emotional stress also raises blood pressure and heart rate. It increases the risk of heart disease. Stress causes muscles to tense up. This leads to headaches, back and neck pain. Stressed people are more likely to develop chronic pain.
Emotional stress also impacts mental health. It can worsen anxiety and depression. People under constant stress struggle to think clearly and concentrate. They may experience memory problems. Stress causes sleep issues like insomnia. Lack of sleep then increases anxiety and irritability. People may turn to unhealthy habits like overeating, smoking or drinking to cope with stress. This leads to weight gain, addiction and other issues.
Stress also affects relationships and social well-being. Stressed people are often irritable. This strains relationships with friends and family. People experiencing stress have less energy for social activities. They withdraw from their support networks. This increases feelings of loneliness and isolation. Stress also reduces work performance and satisfaction. People may lose their jobs due to stress-related issues. Financial problems then increase their stress.
There are many steps people can take to manage emotional stress. Getting regular exercise helps release tension and improves sleep. Relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing and yoga are beneficial. Setting aside time for hobbies and social activities creates balance. Talking to a mental health professional can help identify stressors and develop coping strategies. Practicing good sleep habits, healthy eating and limiting alcohol intake also reduce stress.
In conclusion, emotional stress has many negative effects on physical, mental and social well-being. However, people can take steps to successfully manage stress and reduce these impacts. Identifying stressors, improving lifestyle habits, connecting with others and seeking professional help when needed goes a long way towards improving overall health.
What coping strategies and lifestyle changes can help manage emotional stress symptoms?
Coping Strategies and Lifestyle Changes for Managing Emotional Stress
Experiencing emotional stress is common, but prolonged stress can negatively impact mental and physical health. Implementing positive coping strategies and lifestyle changes can help individuals manage stress symptoms and promote overall wellbeing. This paragraph outlines research-backed approaches to reduce stress.
Cognitive Coping Strategies
Cognitive coping strategies aim to change thought patterns that exacerbate stress. These include reframing negative thoughts, practicing mindfulness and gratitude, and challenging cognitive distortions. Reframing involves generating more positive perspectives on stressful situations. Mindfulness teaches present-moment focus and acceptance. Gratitude practices, like keeping a journal, shift attention to blessings versus burdens. Cognitive therapy helps identify and dispute irrational or exaggerated thoughts.
Behavioral Coping Strategies
Behavioral coping strategies target stress-induced behaviors. Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation elicit the body's relaxation response. Exercise boosts mood and manages anxiety, frustration, and anger. Social support provides emotional release and new perspectives. Time management skills and organizational tools reduce chaos that creates stress. Setting priorities, delegating tasks, and breaking large projects into steps are helpful time management approaches.
Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle factors directly influence stress levels. Adequate sleep, a healthy diet, and regular exercise keep the mind and body resilient to stress. Seven to nine hours of sleep nightly allows the brain to recharge. A balanced, nutrient-rich diet provides energy and supports focus. Aerobic exercise and strength training relieve tension, boost endorphins, and improve sleep. Limiting caffeine and alcohol prevents spikes and crashes in energy. Taking regular vacations and mini-breaks throughout the day enables rejuvenation. Finally, saying “no” to extra responsibilities reduces overload and burnout.
In summary, implementing cognitive, behavioral, and lifestyle changes can help individuals better manage emotional stress. Seeking support from mental health professionals, friends, and family also aids the stress management process.


