In an era where food safety is paramount, Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) serves as a beacon of reliability and assurance within the food industry. Whether for consumers, producers, or regulatory agencies, HACCP represents a systematic approach that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards which are significant for food safety. As a methodical and scientific process, it is instrumental in preventing food contamination and ensuring the integrity of food at every stage from production to consumption. This article aims to dissect the intricacies of HACCP, unfolding its significance and application in the food industry.
Overview of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP)
The origins of HACCP can be traced back to the collaborative effort between Pillsbury Company, NASA, and the US Army Laboratories to ensure astronaut food safety in the early 1960s. Over the decades, HACCP has evolved into a universally recognized system focused on risk reduction and prevention rather than end-product testing.
What Exactly is HACCP?: At its core, HACCP is a preventive system for food safety that shifts the focus from product inspection to a detailed analysis and control of the production process. Its application to the food industry addresses physical, chemical, and biological hazards as a means to prevent food safety problems.
Why is HACCP Important in the Food Industry?: HACCP's role in the food industry cannot be understated. It provides businesses with a structured management tool that emphasizes proper production, packaging, and distribution practices, reducing the likelihood of foodborne illnesses and enhancing consumer confidence.
Learn Problem Solving Through HACCP: By its very design, HACCP is about learn problem solving. Food safety professionals utilize HACCP to dissect complex processes and identify points where potential hazards could emerge, thus developing strategies to mitigate these risks.
Detailed Understandings on HACCP
Delving deeper into the structure of HACCP, we see two fundamental elements that form its basis: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points.
Explanation of Hazard Analysis
Description of the Process
Hazard analysis is the first step in a HACCP plan. During this phase, a thorough examination of all steps in the food production process is conducted to identify where significant hazards might occur. The assessment considers a wide range of potential hazards including biological, chemical, and physical risks.
Significance of Hazard Analysis
Conducting a hazard analysis is crucial because it establishes the foundation for the HACCP plan. A proper hazard analysis can prevent the introduction of hazards in the food supply, protect public health, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Explanation of Critical Control Points
Understanding of Critical Control Points
Critical Control Points (CCPs) are stages in the food production process where control can be applied to prevent or eliminate a food safety hazard or reduce it to an acceptable level. Identifying CCPs is an essential part of the HACCP system and is determined by using a decision tree which considers each step where hazards can be controlled.
Importance of Critical Control Points in HACCP
Recognizing the CCPs enables the establishment of critical limits, monitoring procedures, and corrective actions that collectively ensure hazard control. Ensuring that CCPs are properly managed is a vital component in maintaining the integrity of the HACCP system.
Seven Principles of HACCP
The effectiveness of HACCP is rooted in its seven principles, which provide a structured approach to food safety management.
Description and Analysis of each principle
Conduct a Hazard Analysis: This first principle involves identifying potential hazards that could occur in the food production process and documenting them. It is a preventive measure that anticipates problems before they arise.
Identify the Critical Control Points (CCPs): CCPs are selected based on the hazard analysis where control is critical to prevent or reduce the identified food safety hazards to acceptable levels.
Determine the Critical Limits (CLs): Each CCP must have enforceable measurable limits set to ascertain when a CCP is under control or when there has been a deviation that needs correction.
Establish Critical Control Monitoring Requirements: Monitoring procedures must be established for each CCP to ensure compliance with the CLs. This can include measurements or observations that provide evidence as to whether the process is in control.
Establish Corrective Actions: When monitoring indicates a deviation from an established critical limit, corrective actions must be taken. These are intended to regain control of the process and ensure no unsafe product is released.
Establish HACCP System Verification Procedures: Verification activities confirm that the HACCP system is working effectively. This may involve reviewing CCP records, testing the environment, or conducting product tests.
Establish Record-Keeping Procedures: Accurate and detailed records are essential for verification and provide documentation that the HACCP system is being managed correctly.
Implementation of Principles in real-time scenarios
Implementation of HACCP principles in real scenarios is imperative for the functionality and credibility of any HACCP plan. The principles are not merely theoretical but must be dynamically implemented, reflecting the changes and potential hazards of a food production environment.
Examples showing application of HACCP principles
Illustrating the seven principles through examples is beneficial for understanding their practical application. For instance, in a dairy processing plant, pasteurization might be a CCP with critical limits for temperature and time. Monitoring would mean recording the pasteurization conditions and taking corrective actions if the process falls out of the predefined limits.
Benefits and Challenges of Implementing HACCP
Implementing a HACCP plan comes with both benefits and challenges that need to be managed for the system to be effective.
Advantages of HACCP
Ensuring Food Safety: The system's proactive approach significantly minimizes the risk of food safety hazards, thereby protecting consumer health and ensuring the delivery of safe products to the market.
Improving Efficiency in Production: HACCP optimizes the production process by setting standards and procedures that strive for consistency and traceability throughout the food chain.
Reducing Wastage: By controlling potential hazards, less food is discarded, yield is maximized, and there is a reduction in the likelihood of costly product recalls.
Challenges Faced while Implementing HACCP
Implementing HACCP does not come without its own set of challenges that may impact the efficiency of its employment.
Time and Cost Investment: The initial implementation of a HACCP plan requires a significant investment in training staff, adapting facilities, and developing documentation.
Need for Trained Personnel: HACCP can be complex, and it necessitates a team of individuals with a solid understanding of its principles, often requiring exhaustive training or the hiring of specialists.
Difficulties in Principle Application: Each principle must be calibrated to specific industry operations, which can be difficult without expert knowledge or considerable experience.
HACCP vs Other Food Safety Management Systems
While HACCP is a cornerstone of food safety, it is not the only system available. Comparing it to other standards provides insight into choosing the best option for a specific application.
Comparisons with ISO 22000, BRC, SQF etc.
Comparable systems like ISO 22000 are more comprehensive in scope, often integrating HACCP principles within a broader quality management system which includes additional food safety management components.
Differences and Similarities in Approach
The framework of HACCP is focused on hazard control, whereas systems like the BRC Global Standard for Food Safety or SQF include additional elements of quality management and are geared towards specific industry sectors.
Choosing the Right System for Specific Applications
Selecting the right food safety management system often depends on the nature of the food business, target markets, and regulatory requirements.
Real-life Examples of HACCP Application
Examining the application of HACCP in various sectors underlines its adaptability and importance.
Usage of HACCP in different industries
HACCP has been successfully implemented across numerous segments within the food industry, each with varying risk profiles and specific processes.
Meat industry: In the meat industry, HACCP systems rigorously control for microbiological and physical hazards throughout the entire process from slaughter to packaging.
Dairy industry: Dairy operations utilize HACCP to address concerns such as pasteurization efficiency and equipment sanitation to produce safe milk and cheese products.
Seafood industry: The seafood sector has unique challenges such as controlling for biotoxins and histamine formation, which are managed through precisely defined CCPs.
Case study of successful HACCP implementation
A valuable case study might involve a seafood processor that averted potential outbreaks of shellfish toxicity through strict adherence to HACCP principles, thereby demonstrating the system's effectiveness in real-world settings.
Conclusion
In sum, HACCP is an indispensable system for ensuring food safety that leverages a structured approach to identify, prevent, and control food-related hazards. Throughout this exploration, we have dissected its principles, benefits, and challenges affording us a comprehensive perspective on its place in the food safety landscape.
Recap of HACCP concepts and principles
This article has traversed the depth and breadth of HACCP, lending us a reinforced understanding of its analytical nature and the systematic vigilance it imparts to food production processes.
Final thoughts on importance of HACCP in ensuring food safety
HACCP's value is immeasurable in its capacity to assure safe food products and implicitly foster public health and trust. As consumers continue to demand transparency and safety in what they eat, HACCP's role can only be expected to expand and evolve with time.
Frequently Asked Questions
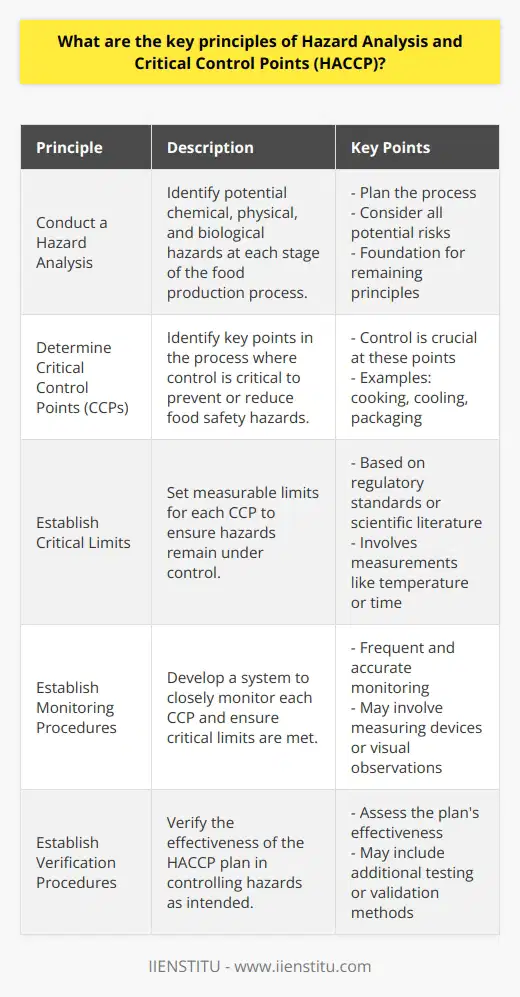
What are the key principles of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP)?
Introduction to HACCP
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, HACCP, is a preventive system. Food safety professionals use it worldwide. Its goal is straightforward. Ensure food safety from potential hazards during production processes. HACCP principles apply to all stages of food manufacturing.
Key Principles of HACCP
Principle 1: Conduct a Hazard Analysis
Plan the process. Identify all potential hazards. Consider chemical, physical, and biological risks. An effective hazard analysis is crucial. This step lays the foundation for the remaining principles.
Principle 2: Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs)
Identify key points in the process. Control is critical at these points. Prevent or reduce food safety hazards here. A CCP can be cooking, cooling, packaging, or others.
Principle 3: Establish Critical Limits
Set limits for CCPs. Ensure hazards remain in control here. Critical limits involve measurements like temperature or time. They are often based on regulatory standards or scientific literature.
Principle 4: Establish Monitoring Procedures
Develop a monitoring system for CCPs. All critical control points require close observation. Measuring devices or visual observations may be necessary. Frequent and accurate monitoring ensures control of CCPs.
Principle 5: Establish Corrective Actions
Identify actions for deviation in CCPs. When monitoring shows a critical limit breach, these actions apply. Ensure they are effective. Corrective actions aim to regain control and prevent potentially hazardous products from reaching consumers.
Principle 6: Establish Verification Procedures
Verify the effectiveness of the HACCP plan. Assess whether the plan controls hazards as intended. This may include additional testing or validation methods.
Principle 7: Establish Record-Keeping and Documentation Procedures
Keep detailed records. Document everything related to the HACCP plan. This includes hazard analyses, monitoring systems, and actions taken. Proper documentation ensures traceability and accountability.
Conclusion
Implementing HACCP principles takes commitment. Every food safety program depends on diligent application. These principles provide a framework to identify, evaluate, and control food safety hazards. It is essential for protecting public health. Implementing HACCP principles is a structured approach. It helps maintain the highest food safety standards.
How does HACCP contribute to risk management and prevention in the food industry?
Understanding HACCP's Role in the Food Industry
When considering food safety, HACCP stands crucial. It stands for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points. It's a systematic approach. Experts around the world recommend its use. It's a preventive method, not reactive. It targets potential hazards in food production.
HACCP's Focus on Prevention
HACCP shifts the focus from end-product testing. It looks at every stage of food production. The goal here is proactive hazard control. It fosters a culture of risk awareness. Food safety becomes a continuous process, not an afterthought.
Risk Management Through HACCP
Risk management is key in the food sector. HACCP identifies potential food safety hazards. It defines critical control points (CCPs). It sets critical limits to ensure control. Monitoring procedures are also crucial. This ensures CCPs meet safety criteria.
Critical Steps in the HACCP System
First comes the hazard analysis. Here, one identifies and evaluates risks. Next, CCPs are determined. These are steps where control can prevent hazards. Then, one establishes critical limits for each CCP. Monitoring systems follow.
Continual monitoring tracks the CCPs. Corrective actions are planned for deviations. Verification ensures the system works effectively. Lastly, documentation maintains a record of all actions.
HACCP's Impact on the Food Industry
HACCP elevates manufacturing standards. It minimizes foodborne illness risks. It promotes food safety culture. Allergen management improves as well. It gives assurance to regulators and consumers.
Conclusion
HACCP is a cornerstone in food safety. It's not just a tool. It's a comprehensive approach. It safeguards consumers. It protects manufacturers. It's the benchmark for managing risks in the food industry. Its role is indisputable and strong. It will remain central in ensuring food safety.

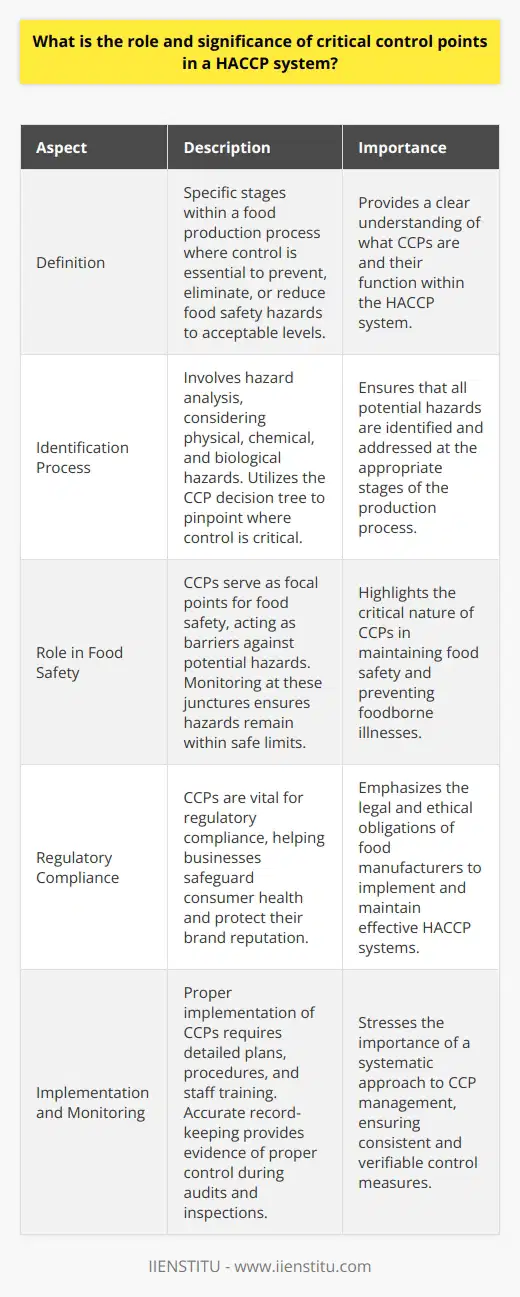
What is the role and significance of critical control points in a HACCP system?
Understanding Critical Control Points
Critical Control Points (CCPs) are crucial to HACCP systems. They represent specific stages within a food production process. At these points, control is essential. Control prevents, eliminates, or reduces food safety hazards to acceptable levels.
Identification is Key
Identifying CCPs entails a rigorous process. It involves hazard analysis. Teams consider physical, chemical, and biological hazards. Experts map out the production process. They focus on steps where hazards could occur. Identification uses the CCP decision tree. This tool guides the team through a series of questions. Questions pinpoint where control is critical.
The Role of CCPs
CCPs serve as focal points for food safety. Each one acts as a barrier against potential hazards. Monitoring is essential at these junctures. It ensures hazards remain within safe limits. Operators perform specific actions at CCPs. These actions directly manage and control risks.
Significance of CCPs
The significance of CCPs is vast. They ensure product safety. CCPs help prevent foodborne illnesses. They are vital for regulatory compliance. Businesses depend on them to safeguard consumer health. Without CCPs, HACCP systems would fail to protect. These points offer benchmarks for quality and safety assurance.
Implementation and Monitoring
Proper implementation of CCPs is critical. It requires detailed plans and procedures. Staff must understand their roles. They conduct monitoring tasks with precision. Accurate record-keeping is essential. It offers evidence of proper control. These records help during audits and inspections.
CCPs in HACCP Systems
- Hazard Analysis: Identify potential risks.
- Determine CCPs: Use the decision tree.
- Establish Limits: Set safety thresholds.
- Monitor CCPs: Check controls are working.
- Corrective Actions: Address deviations promptly.
CCPs strengthen the HACCP system as a whole. They anchor the system's integrity. Control at these points reduces the risk of unsafe products. This protects consumers. It also defends the brand's reputation.
In summary, the role of CCPs in a HACCP system speaks to the heart of food safety management. Without these critical junctures of control, the potential for hazard proliferation would be significant. Consequently, the significance of CCPs transcends operational processes, touching on the very trust consumers place in food brands and the global reputation of the food industry at large.