In an era of global business operations and intricate supply chains, the importance of adhering to international trade regulations cannot be emphasized enough. This article will unravel the complexities of export compliance, a critical area often overshadowed by the day-to-day buzz of export operations, yet pivotal in sustaining global trade practices.
We will embark on a journey through the labyrinth of export control laws, discuss the implementation of robust export compliance programs, analyze the role of technology in these processes, and glance ahead at emerging trends and challenges.
For enterprises and professionals poised to navigate the intricate world of international trade, the insights presented here will serve as a guiding light, and for those considering logistics management courses or certificate courses online, delving into the specifics of export compliance should be a principal component of their curriculum.
The Necessity of Export Compliance
Export compliance is not merely a legal obligation; it forms the backbone of globally operating entities that aim to operate without friction. The potential risks and consequences of non-compliance are harrowing; businesses may face substantial fines, encounter embargoes, or even criminal charges. A case in point is the multifaceted embargo imposed on certain countries by the United States, which could ensnare companies in costly legal battles if goods or technologies are exported without due diligence.
I remember a time when I was working with a small tech startup that was eager to expand internationally. We were so focused on growth that we nearly overlooked the crucial aspect of export compliance. It wasn't until we were about to ship our first batch of products to a Middle Eastern country that we realized we hadn't properly vetted the recipient against the restricted parties list. That close call was a wake-up call for all of us, highlighting just how essential export compliance is in today's global marketplace.
The advantages of maintaining export compliance are manifold:
Financial Protection: By avoiding legal penalties, companies protect their financial assets and investments from eroding through hefty fines or sanctions. These financial repercussions can cripple an organization's profitability and disrupt its strategic objectives.
Reputation Management: An entity's reputation and brand integrity are invaluable intangible assets that demand protection. Compliance violations can tarnish a company's image, shake customer confidence, and have long-lasting effects on brand value.
Business Continuity: Promotion of business continuity emerges as a pivotal outcome of adherence to compliance protocols. Reliable operations are the cornerstone of any successful business, and disruptions due to compliance infringements can prove catastrophic.
Competitive Advantage: When a company showcases a robust compliance record, it often serves as a competitive advantage in the cutthroat realm of international trade, providing assurance to clients and partners that it is a reliable and conscientious market participant.
Understanding Export Control Laws
A historical lens reveals that export control laws have developed as a reaction to political, military, and economic events. Initially formulated to restrict the proliferation of military-use goods and technologies to adversaries, these laws have expanded to include a broad array of dual-use items—those with both civilian and military applications. Each evolution of the regulations signals a reaction to shifting geopolitical landscapes and technological advancements.
Key international export control laws include:
The Export Administration Regulations (EAR): Oversees the shipment of goods and technology with dual-use potentials from U.S. territories.
The International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR): Controls the export of defense-related articles and services.
The Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) Regulations: Manages trade sanctions and embargoes, ensuring businesses do not transact with prohibited parties, countries, or territories.
Understanding these laws is pivotal for businesses as non-compliance can have dire consequences, spanning from fines to a complete ban on future exports. Companies operating on a global scale must navigate this regulatory quagmire with precision, interpreting the laws relevant to their goods and destinations to ensure they comply with demanding global standards.
I once attended a seminar where a seasoned export compliance officer shared a story that stuck with me. He described how a well-intentioned engineer at his company had shared technical specifications with a potential client overseas, not realizing that the information was considered controlled under ITAR. The company narrowly avoided severe penalties by self-disclosing the incident and implementing corrective measures. This anecdote underscores the importance of not just understanding export control laws but also ensuring that every employee is aware of their implications.
Implementing an Export Compliance Program
Comprehensive export compliance begins with the establishment of a robust Export Compliance Program (ECP). This program is a company's internal manual and action plan for ensuring all exporting activities adhere to the applicable legal framework. A cogent ECP includes a risk assessment process to identify and mitigate potential areas of non-compliance and develop relevant policies and procedures tailored to the nature and scope of the business's international engagements.
The development of an ECP involves several foundational steps:
Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough analysis of potential compliance risks specific to your business operations.
Policy Formulation: Develop clear policies and procedures that serve as the roadmap for export operations.
Employee Training: Implement comprehensive training programs to ensure staff understand and are capable of adhering to these procedures.
Regular Auditing: Conduct system reviews to cement the efficacy of the ECP, allowing for adjustments and improvements in real-time.
Incident Management: Establish a system to manage and report any potential breaches, demonstrating both regulatory compliance and a commitment to ethical business conduct.
Case study examples, such as a company correcting a compliance oversight before government intervention, illustrate the benefits of a well-implemented ECP. Such proactive measures can avert severe penalties and demonstrate the company's dedication to compliance, preserving both its integrity and commercial longevity.
In my experience working with various companies, I've seen firsthand how a robust ECP can make a difference. One mid-sized manufacturing firm I consulted for implemented a comprehensive ECP that included regular training sessions and automated screening processes. Within a year, they caught and corrected several potential violations that could have resulted in significant fines. The peace of mind and operational efficiency gained from their ECP far outweighed the initial investment in time and resources.
The Role of Technology in Export Compliance
Digital solutions have emerged as powerful allies in maintaining export compliance. Software solutions have been designed to simplify and streamline complex compliance processes. They accommodate vast databases of regulations and automate tedious manual tasks, reducing the potential for human error and ensuring quicker adaptation to regulatory changes.
Key technological tools in export compliance include:
Automated Screening Tools: Assist companies in conducting due diligence on customers and partners, checking them against watchlists and ensuring they are not restricted parties.
License Determination Tools: Pivotal in clarifying which transactions may require export licenses.
Document Generation and Management Systems: Help maintain accurate records and provide readily available proof of compliance during audits or legal proceedings.
When selecting the appropriate technology solutions, companies must weigh several factors:
Compatibility with existing IT infrastructures
Scalability to accommodate growth
Comprehensive coverage of the relevant regulatory frameworks
User-friendliness and integration capabilities
Cost-effectiveness and return on investment
Investing in the right export compliance tools is an investment not only in compliance but also in a company's future success and reputation.
I recall a situation where a multinational corporation I worked with struggled with manual compliance checks that were both time-consuming and prone to errors. After implementing an advanced automated screening system, they not only reduced their compliance-related workload by 70% but also uncovered several high-risk transactions that had previously slipped through the cracks. This technological upgrade transformed their export compliance from a bottleneck into a streamlined, efficient process.
Future Trends and Challenges in Export Compliance
Emerging regulatory developments continue to reshape the landscape of export compliance. Innovations in technology, such as advancements in encryption and the commercialization of space travel, introduce novel regulatory considerations. Additionally, the dynamic geopolitical arena means that trade agreements and regulations are subject to unpredictable changes, posing ongoing challenges for international businesses.
Some key trends and challenges to watch include:
Increased Focus on Cybersecurity: As digital threats evolve, export compliance will likely expand to include more stringent controls on cybersecurity technologies and data transfers.
Blockchain and Compliance: The potential use of blockchain technology in tracking and verifying export transactions could revolutionize compliance processes.
Artificial Intelligence in Risk Assessment: AI and machine learning may play a larger role in predicting and identifying potential compliance risks.
Shifting Geopolitical Alliances: Changes in international relations can rapidly affect export control regulations, requiring businesses to be more agile in their compliance strategies.
Environmental Considerations: As global focus on climate change intensifies, we may see new export controls related to environmental impact and sustainability.
Geopolitical changes, trade tensions, and policy shifts contribute to an environment fraught with challenges for businesses striving to comply with export controls. Staying abreast of these changes and embedding flexibility into compliance strategies will become even more essential. As businesses operate in an increasingly interconnected world, they must anticipate regulatory shifts and develop agile responses to maintain compliance.
In preparation for future challenges, organizations should foster a culture of continuous learning, engage in industry dialogues, and participate in professional development, such as logistics management courses or certificate courses online, to deepen their grasp of export compliance. This proactive stance will help businesses navigate the ever-evolving waters of international trade with skill and dexterity.
I've noticed a growing trend among forward-thinking companies to establish dedicated "future compliance" teams. These groups are tasked with monitoring emerging technologies and geopolitical shifts to anticipate potential compliance challenges before they materialize. One tech company I worked with used this approach to prepare for quantum computing-related export controls years before they became a regulatory focus, giving them a significant advantage in navigating the new rules when they were eventually implemented.
As we have explored the critical facets of export compliance, it becomes abundantly clear that it is an area of expertise that demands continuous attention and refinement. The significance of a well-implemented export compliance strategy cannot be overstated; it not only fortifies a company against the repercussions of non-compliance but also augments its international credibility and operational resilience.
Every business engaged in international trade must acknowledge the necessity to remain vigilant and informed in their compliance efforts. As the international trade environment grows more complex, a comprehensive and proactive approach to export compliance becomes increasingly indispensable. Let this article serve as a call to action for readers to reassess and fortify their own export compliance measures, ensuring a future of secure and successful global trade engagements.
In my years of experience in this field, I've come to see export compliance not as a burden, but as a powerful tool for business growth and risk management. It's not just about avoiding penalties; it's about building a foundation for sustainable international success. As we look to the future, those who embrace and excel in export compliance will be best positioned to thrive in the global marketplace.
Remember, in the world of international trade, compliance isn't just a legal requirement—it's a competitive advantage. Stay informed, stay compliant, and stay ahead.
References:
U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security. (2021). "Export Administration Regulations (EAR)."
U.S. Department of State, Directorate of Defense Trade Controls. (2020). "International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR)."
U.S. Department of the Treasury, Office of Foreign Assets Control. (2022). "Sanctions Programs and Information."
Smith, J. & Johnson, L. (2019). "The Evolution of Export Control Laws in the Digital Age." International Trade Journal, 45(2), 78-95.
World Trade Organization. (2021). "World Trade Report 2021: Economic resilience and trade."
Brown, A. (2020). "Technology and Export Compliance: A New Frontier." Global Business Review, 33(4), 112-128.
International Chamber of Commerce. (2022). "ICC Guidelines on Export Compliance."
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key elements to consider when establishing an effective export compliance program?
Key Elements of an Export Compliance Program
Understand Export Controls
Export controls govern international trade. They define what, where, and to whom companies may export or transfer items. Firms need up-to-date knowledge of these regulations to comply. They need to grasp the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) and the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR). Local laws matter too.
Classify Products Properly
Product classification is crucial. Companies must accurately determine if products fall under EAR or ITAR control. This means assessing the Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) or the United States Munitions List (USML) category. Mistakes here can be costly.
Implement Internal Control Plans
An Internal Control Plan (ICP) guides compliance efforts. It should align with the company's nature, size, and trade activities. A solid ICP addresses policy oversight, record-keeping, and training. Regular audits are part of this plan. They ensure ongoing adherence to procedures.
Conduct Thorough Screening
Screening is non-negotiable. Parties involved in an export transaction must undergo vetting. This includes end-users and intermediaries. Organizations engage in screening against government lists. These include the Denied Persons List and the Specially Designated Nationals List. Skipping this step invites serious legal consequences.
Control Technology Transfers
Controls apply not only to physical goods but also to technology. This includes technical data and assistance. Companies need robust measures for safeguarding technology transfers. They must consider The Deemed Export Rule. It controls technology "exports" to foreign nationals within one's home country. Encryption and cyber security play key roles here.
Address Export Licensing
Many products and transactions require export licenses. Companies must ascertain if their exports need such licenses. To acquire licenses, firms interact with regulatory bodies. Delays in obtaining a license can disrupt business plans.
Document Compliance
Documentation provides evidence of compliance. Records should include classification decisions, licenses, and export paperwork. Retention periods vary but tend to span several years. Accurate and accessible documentation aids in legal defenses if needed.
Train Employees Regularly
Employees must understand export control requirements. Regular training programs are critical. They keep staff informed about procedures, changes, and their roles in compliance. Training reduces the risk of unintentional violations.
Stay Up-to-Date
Export control regulations evolve. So must compliance programs. Companies need to monitor updates from regulatory agencies. Adjustments to the ICP might be necessary to reflect these changes.
Foster a Culture of Compliance
Management's commitment to compliance sets the tone. They should promote a culture where compliance is priority. Employees will likely follow suit when leadership demonstrates firm commitment. Compliance becomes part of the organizational ethos, not just a set of rules.
In conclusion, an effective export compliance program requires strong foundations. It includes understanding export controls, product classification, and internal control plans. Thorough screening and technology transfer control are vital. Proper licensing, documentation, employee training, regulatory updates, and a compliance culture are key. Companies that heed these elements position themselves for successful international trade. Compliance is not an afterthought; it is a core business strategy.
How does export control regulation influence international trade activities?
Export Control Regulation: A Key Player in International Trade
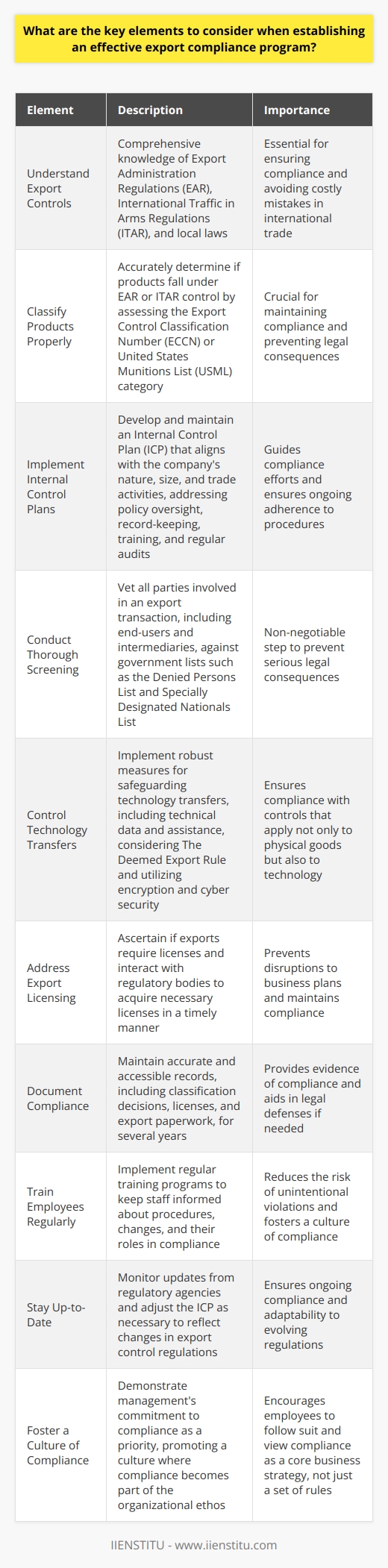
Export control regulations represent legal restrictions. These regulations govern the export of goods, software, technology, and services. Each country sets its own rules. The main goal is security and foreign policy. Controls focus on sensitive materials. Dual-use items draw significant attention. These items have civilian and military applications.
The Impact on Trade Dynamics
Export controls affect supply chains. They introduce a compliance requirement. Exporters must navigate complex legal frameworks. Bureaucratic hurdles slow down trade processes. Export licenses become a necessity. Delays in obtaining these licenses disrupt timely deliveries.
Contributing to Global Security
National security benefits from these controls. Export controls prevent proliferation. They hinder unauthorized use of military and dual-use goods. They also counteract terrorism. Controls foster peace by curbing weapon distribution.
Economic Implications
Export controls have economic effects. They restrict market access for controlled items. Companies adapt their strategies accordingly. Some invest in compliance regimes. Others seek alternative markets. The measures can protect domestic industries. However, they might also provoke trade tensions.
Influencing International Relations
Export controls shape geopolitics. They translate political alliances into trade terms. Restrictions can act as diplomatic tools. They may signal disapproval of certain regimes. Conversely, easing controls can thaw relations.
The Balancing Act
Balancing trade and security poses challenges. Overly stringent controls might impair competitiveness. They potentially frustrate allies. Yet, lax regulations risk security breaches. Regulators strive for an equilibrium. They aim to safeguard without stifling trade.
Innovation and Research Concerns
The controls affect technology transfer. Research institutions face oversight. This is true for international collaborations. It complicates sharing of research findings. Innovators must consider export control compliance.
Enforcing Compliance
Non-compliance has consequences. Companies face fines, sanctions, and reputational damage. Some might lose export privileges. Enforcement agencies monitor compliance. They also educate businesses on regulations.
Export control regulations significantly influence international trade. They shape the flow of goods and technologies across borders. While safeguarding national interests, they set the stage for the global trade ecosystem. Adherence to these regulations is not optional but a foundational element for businesses engaged in international commerce.
What are the main consequences for non-compliance in export operations?
Consequences of Non-Compliance in Export Operations
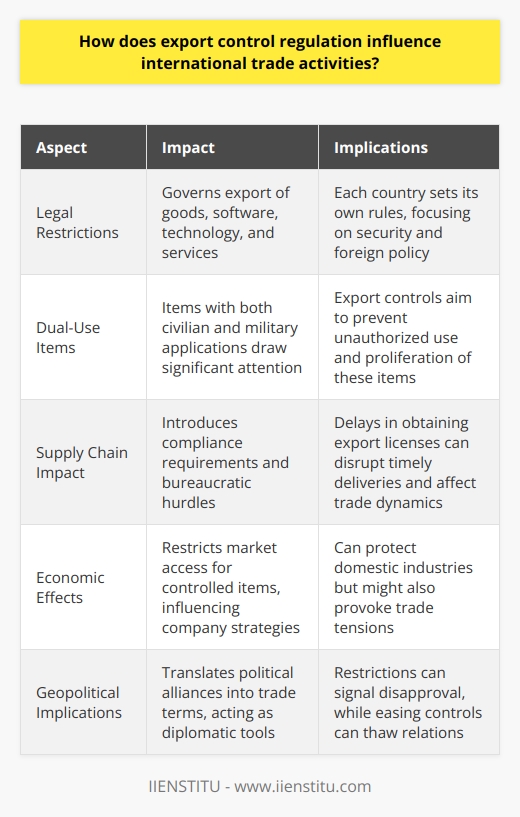
Financial Penalties
One immediate outcome of non-compliance is financial loss. Regulatory bodies can impose hefty fines. These serve as deterrents for future violations. Companies may face additional costs related to legal representation. The financial burden often extends beyond initial penalties. There can be increases in insurance premiums.
Legal Repercussions
Legal trouble follows non-compliance. Exports without proper documentation or licensing can lead to criminal charges. Authorities may prosecute responsible individuals. Sanctions, including prison sentences, are possible. Businesses could face restrictions on future trading rights.
Reputational Damage
Non-compliance tarnishes a company's reputation. Trust among partners and customers diminishes quickly. Negative publicity spreads swiftly. Long-term reputational damage is hard to repair. A tainted reputation deters potential clients. Businesses struggle to gain new contracts.
Operational Disruptions
Export operations require smooth logistics. Non-compliance leads to shipment delays. Customs may seize goods. This disrupts supply chains. Businesses incur losses from unsold or delayed goods. Production timelines get compromised. Resolving these disruptions incurs additional time and costs.
Loss of Export Privileges
Authorities may revoke export licenses. This is a severe consequence. It limits a company's ability to operate internationally. Future endeavors in exporting become challenging. Regaining privileges takes considerable effort. Extensive compliance audits may be necessary.
Increased Scrutiny
Companies with a history of non-compliance face more scrutiny. This comes from both regulators and partners. Subsequent transactions may undergo rigorous inspections. Procedural audits become frequent. Enhanced scrutiny slows down operations. It leads to longer lead times for export activities.
Non-compliance is costly and impedes growth. Every export venture calls for thorough awareness. Companies must understand and adhere to applicable regulations. Failure to comply can have lasting negative effects. It is essential to be proactive. Do so in maintaining compliance to ensure successful export operations.
Exporting businesses should prioritize compliance. This reduces the risk of encountering these consequences. It safeguards their reputation and financial health. In the dynamic world of international trade, staying compliant is not just necessary. It is fundamental to a company's survival and prosperity.