When I first stepped into the world of management, I was overwhelmed by the sheer number of theories and concepts that seemed essential to grasp. Over time, I realized that understanding these management theories wasn't just about academic knowledge; it was about applying these principles to real-world situations to drive organizational success.
Navigating the Landscape of Management Theories
In today's fast-paced business environment, it's more important than ever to have a solid grasp of the foundational management theories. They not only provide a roadmap for effective leadership but also offer insights into how organizations can adapt to changing dynamics.
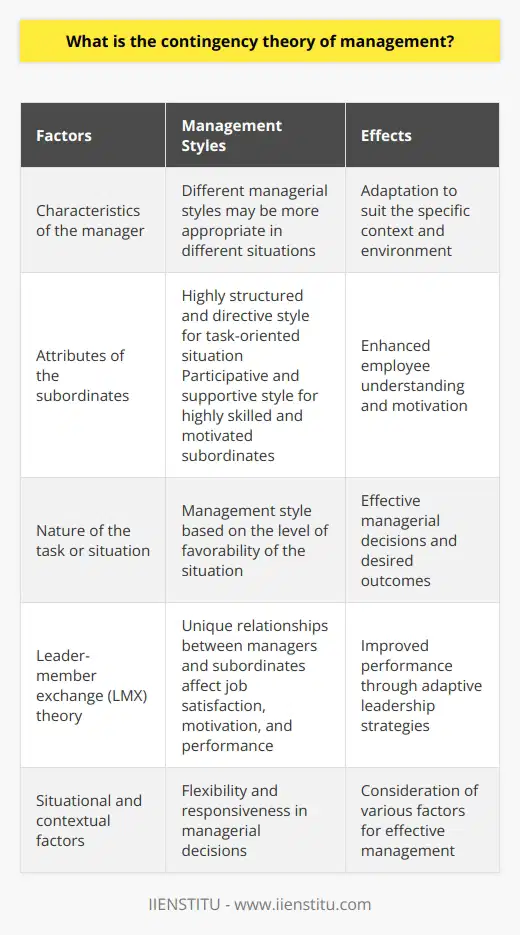
The Roots of Scientific Management: Striving for Efficiency
I recall working on a project where time was of the essence, and resources were limited. It was then that I truly appreciated Frederick Taylor's Scientific Management Theory. Taylor emphasized improving efficiency through systematic analysis and optimization of work processes. By conducting time and motion studies, we were able to identify redundancies in our workflow.
Some key takeaways from Taylor's principles include:
Division of Labor: Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable parts.
Standardized Procedures: Implementing uniform methods to perform tasks efficiently.
Systematic Training: Ensuring all team members are well-trained in their specific functions.
By applying these principles, our team not only enhanced productivity but also minimized waste—a crucial factor in any project's success.
Henri Fayol's 14 Principles: Building a Strong Foundation
During a leadership workshop, I was introduced to Henri Fayol's 14 Principles of Management. Fayol's framework provides a comprehensive guide for managers to create a harmonious work environment.
Some of Fayol's principles that resonated with me are:
1- Division of Work: Specialization allows for increased efficiency.
2- Authority and Responsibility: Balancing power with responsibility.
3- Unity of Command: Employees should receive orders from only one superior.
4- Esprit de Corps: Fostering team spirit improves morale and unity.
Implementing these principles in my team led to clearer communication channels and a more motivated workforce. It's fascinating how concepts conceived over a century ago remain relevant in today's corporate world.
Theory X and Theory Y: Decoding Employee Motivation
Understanding what drives people is pivotal. Douglas McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y shed light on two contrasting views of employee motivation.
Theory X assumes employees are inherently lazy and require strict supervision.
Theory Y believes employees are self-motivated and thrive on responsibility.
In my experience, treating team members as per Theory Y—entrusting them with responsibilities and acknowledging their contributions—leads to a more engaged and productive team. It's about empowering rather than micromanaging.
Balancing Acts with the Managerial Grid
Robert Blake and Jane Mouton's Managerial Grid is a tool I've found invaluable in assessing leadership styles. The grid maps leadership on two axes:
Concern for People: Prioritizing team members' needs and development.
Concern for Production: Emphasizing task completion and results.
Striking the right balance is crucial. I once leaned too heavily on task orientation, which led to team burnout. Adjusting my approach to also focus on team well-being made all the difference. After all, a happy team is a productive team.
Crafting Organizational Structure with Administrative Management Theory
Structure provides stability. Max Weber's Administrative Management Theory highlights the importance of a clear organizational hierarchy.
Key elements include:
Clear Hierarchy: Defining roles and responsibilities.
Formal Rules and Procedures: Establishing guidelines to ensure consistency.
Impersonal Relationships: Decision-making based on objective criteria rather than personal preferences.
Incorporating these elements helped our organization navigate growth phases without losing sight of our core objectives.
The Evolution of Management Thought
Reflecting on management's journey reveals a shift from purely task-oriented approaches to more human-centric ones.
From Classical to Modern Theories
Classical Management Theory focused on efficiency, emphasizing tasks and structures.
Behavioral Management Theory, introduced by thinkers like Mary Parker Follett, emphasized human relations and employee well-being.
Contingency Theory recognizes that there's no one-size-fits-all approach; managers must adapt to situational variables.
Understanding this evolution helps managers like us appreciate the multifaceted nature of leadership.
Embracing Change with Lewin's Change Theory
Change is the only constant. Kurt Lewin's Change Theory offers a roadmap for managing transitions:
1- Unfreezing: Preparing the organization for change.
2- Changing: Implementing new processes or structures.
3- Refreezing: Solidifying the changes for long-term success.
I remember when our company underwent a major software transition. By following Lewin's model, we minimized resistance and ensured a smoother adoption of new systems.
The Human Side of Management
Understanding human behavior is at the heart of Behavioral Management Theory. By appreciating factors like motivation, group dynamics, and leadership styles, managers can foster a more collaborative and productive environment.
Some strategies to enhance employee engagement include:
Open Communication: Encouraging feedback and discussions.
Recognizing Achievements: Celebrating both small and big wins.
Providing Growth Opportunities: Offering training and advancement paths.
These approaches not only improve morale but also drive organizational performance.
Adapting in a Dynamic World
In an ever-changing business landscape, flexibility is key.
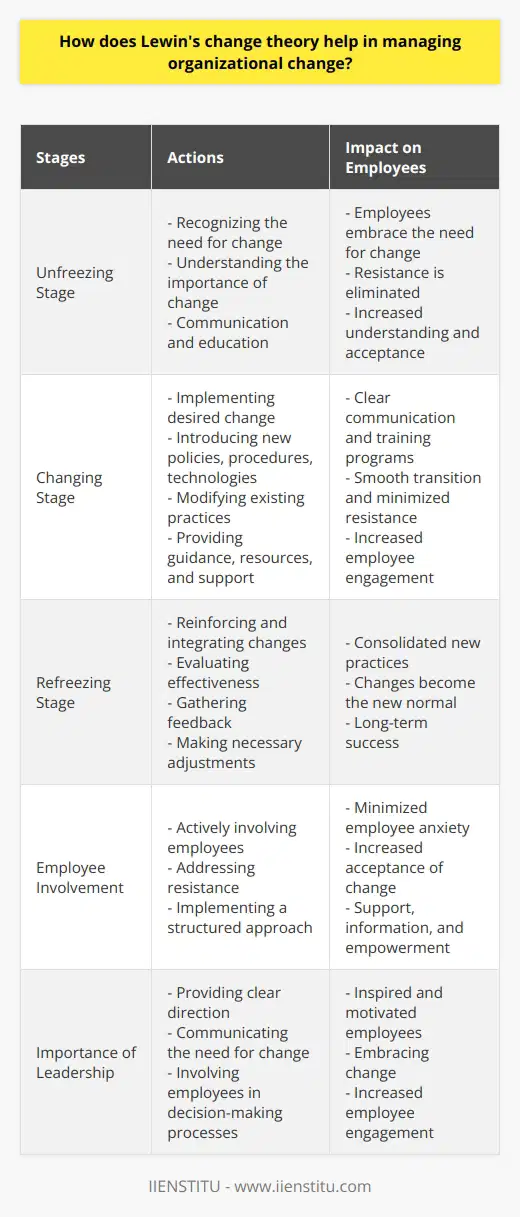
Applying Contingency Theory
The Contingency Theory of Management suggests that effective leadership depends on the specific situation. Factors to consider include:
Organization Size
Technology Used
External Environment
Individual Differences
By assessing these variables, managers can tailor their strategies. For instance, a startup might prioritize innovation and flexibility, while a large corporation might focus on stability and process optimization.
Integrating Modern Perspectives
Modern management theories integrate insights from various disciplines:
Psychology: Understanding individual and group behavior.
Sociology: Examining social structures within organizations.
Economics: Analyzing resource allocation and incentives.
This interdisciplinary approach equips managers with a holistic view, enabling them to navigate complexities more effectively.
Practical Tips for Managers
From my journey, I've compiled some practical tips that have proven invaluable:
1- Embrace Continuous Learning: The field of management is always evolving. Stay updated with the latest research and practices.
What Adds Up?: Math Enrollment and Graduation. https://eric.ed.gov/?q=student+success&pg=277&id=ED577056
14 Principles of Management by Henry Fayol - The Constructor. https://theconstructor.org/construction/14-principles-of-management-henry-fayol/36716/
2- Prioritize Communication: Clear communication prevents misunderstandings and fosters trust.
3- Cultivate Emotional Intelligence: Understanding your own emotions and those of others enhances leadership effectiveness.
4- Optimize Supply Chain Management Process Tips: Streamlining supply chain processes can significantly impact operational efficiency.
5- Encourage Collaboration: Foster a culture where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas and collaborating.
By incorporating these strategies, managers can create resilient and adaptive organizations.
The Role of Leadership Styles
Leadership isn't a one-dimensional concept. It's a spectrum that requires adaptability.
Insights from the Managerial Grid
Returning to Blake and Mouton's Managerial Grid, leaders can assess their default styles and adjust accordingly. For example:
Country Club Leadership: High concern for people but low concern for production.
Produce or Perish Leadership: High concern for production but low concern for people.
Team Leadership: High concern for both people and production.
Striving for Team Leadership often yields the best outcomes, promoting both employee satisfaction and organizational goals.
Navigating Change with Lewin's Model
Change can be daunting. Utilizing Kurt Lewin's Change Management Model can ease the transition:
Communicate the Vision: Clearly articulate the reasons and benefits of the change.
Empower Action: Remove obstacles and provide the necessary resources.
Anchor Changes: Reinforce new behaviors and practices through positive feedback.
When our organization shifted to remote work, applying these steps helped maintain productivity and morale.
Embracing Bureaucracy: A Double-Edged Sword
Bureaucratic Management Theory often gets a bad rap for being rigid. However, there are merits to structured approaches:
Consistency: Standard procedures ensure uniformity.
Accountability: Clear hierarchies delineate responsibilities.
Efficiency: Defined processes reduce ambiguity.
The key is to balance structure with flexibility, ensuring that bureaucracy doesn't hinder innovation.
Conclusion: The Timelessness of Management Theories
As we've journeyed through these management theories, one thing is clear: while the business landscape evolves, the core principles of effective management remain relevant. By understanding and applying these theories:
Managers can adapt to change.
Organizations can optimize performance.
Employees can find greater satisfaction and motivation.
In essence, these theories serve as tools in our leadership toolkit, enabling us to navigate challenges and drive success.
References
Fayol, H. (1949). General and Industrial Management. Pitman Publishing.
This classic work delves into Fayol's 14 principles, providing foundational knowledge for managers.
Taylor, F. W. (1911). The Principles of Scientific Management. Harper & Brothers.
Taylor's seminal book outlines the concepts of efficiency and productivity that revolutionized industrial operations.
McGregor, D. (1960). The Human Side of Enterprise. McGraw-Hill.
An exploration of Theory X and Theory Y, this book offers insights into employee motivation.
Blake, R. R., & Mouton, J. S. (1964). The Managerial Grid. Gulf Publishing Company.
A valuable resource for understanding leadership styles and their impact on team dynamics.
Lewin, K. (1951). Field Theory in Social Science. Harper & Row.
Lewin's work on change management provides practical frameworks for navigating organizational shifts.
Weber, M. (1947). The Theory of Social and Economic Organization. Free Press.
Weber's analysis of bureaucratic management underscores the importance of structure in organizations.
By weaving together these theories with personal experiences and practical applications, we not only gain a deeper understanding but also appreciate the timeless value they bring to the world of management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main principles of scientific management theory?
The main principles of scientific management theory, developed by Frederick Taylor, involve systematic analysis and optimization of work processes. Key principles include time and motion studies, division of labor, and standardized work procedures to enhance productivity and reduce waste.

How does Lewin's change theory help in managing organizational change?
Lewin's change theory provides a structured approach to managing organizational change through a three-step model: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing. This model helps managers identify and address barriers to change, implement new strategies and practices, and consolidate changes to ensure long-term success.
What is the contingency theory of management?
The contingency management theory proposed by Fred Fiedler and others emphasizes the importance of adapting management practices to suit the specific context and environment. This approach recognizes that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to management challenges and encourages managers to be flexible and responsive to changing conditions.