In an ever-evolving world where challenges are as diverse as they are complex, the ability to dissect and solve problems creatively is an invaluable skill. I remember a time not too long ago when I was faced with a daunting project at work. Traditional methods just weren't cutting it, and I felt like I was hitting a brick wall. That's when I realized that thinking divergently could be the key to unlocking a solution. It wasn't about working harder but thinking smarter.
Embracing the Journey of Creative Problem Solving
A Personal Encounter with Creativity
It all started when my team and I were tasked with improving our company's supply chain efficiency. We had to optimize supply chain management process tips to stay competitive. Honestly, it felt overwhelming at first. We were swimming in data, and every typical solution seemed inadequate. One day, over a cup of coffee, a colleague mentioned the power of lateral thinking. That casual conversation sparked an idea. Why not approach the problem from a completely different angle?
Understanding the Core of Creative Problem Solving
Creative problem solving isn't just about coming up with wild ideas; it's a structured process that enhances our problem solving skills. It combines critical thinking and imagination to find innovative solutions. Critical thinking as a skill allows us to analyze and evaluate, while creativity opens the door to new possibilities.
A Glimpse into the History of Creative Problem Solving
The Pioneers Who Paved the Way
The concept of creative problem solving has deep roots. Back in the 1940s, Alex Osborn introduced the term "brainstorming" in his book Your Creative Power (Osborn, 1948). He believed that fostering a free flow of ideas without criticism could lead to breakthroughs. Later, Sidney J. Parnes expanded on Osborn's work, developing the Osborn-Parnes Creative Problem Solving Process, a structured approach still used today (Parnes, 1967).
Evolution Over Time
Over the decades, this approach has been influenced by various fields, including psychology, education, and business. The integration of critical reasoning skills with creative techniques has made it a versatile tool for tackling complex issues.
The Theoretical Foundations
The Psychology Behind Creativity
At the heart of creative problem solving lies an understanding of how the mind works. Psychologist J.P. Guilford's research in the 1950s emphasized the importance of divergent thinking (Guilford, 1950). He argued that creativity involves generating multiple solutions, a key aspect of problem solving as a skill.
The Symbiotic Relationship of Creativity and Critical Thinking
Critical thinking and creativity are often seen as opposites, but they're two sides of the same coin. While creativity involves generating ideas, critical thinking skills help us evaluate and refine them. Together, they enhance our ability to solve problems skills effectively.
Conventional vs. Creative Problem Solving
The Limitations of Traditional Approaches
Conventional problem solving often relies on logical, step-by-step methods. While effective for routine issues, it may fall short when facing novel challenges. In our fast-paced world, sticking strictly to traditional methods can be like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole.
The Advantages of Creative Problem Solving
By contrast, creative problem solving encourages flexibility and openness. It allows us to explore uncharted territory and find unique solutions. This approach is particularly valuable in today's dynamic environment, where adaptability is key.
The Process of Creative Problem Solving
1. Clarify the Problem
The first step is to explain critical thinking in the context of the problem. Understanding the issue thoroughly sets the foundation for effective solutions.
Identify the real problem: Sometimes symptoms can mask the underlying issue.
Gather information: Research and data collection are essential.
Define objectives: Knowing what success looks like guides the process.
2. Generate Ideas
This is where creativity shines. Brainstorming without judgment allows ideas to flow.
Encourage wild ideas: No idea is too outlandish at this stage.
Use mind mapping: Visual tools can spark connections.
Collaborate: Different perspectives enrich the idea pool.
3. Develop Solutions
Now it's time to apply critical reasoning skills to evaluate and refine ideas.
1- Assess feasibility: Consider resources and constraints.
2- Prioritize options: Determine which ideas have the most potential.
3- Plan implementation: Outline steps to bring the solution to life.
4. Implement and Reflect
Putting the plan into action and learning from the outcome.
Monitor progress: Keep track of developments.
Be flexible: Adapt as necessary.
Reflect on results: Use insights for future problem solving.
Benefits and Limitations
The Pros of Creative Problem Solving
Innovation: Leads to groundbreaking solutions.
Adaptability: Helps navigate changing environments.
Engagement: Encourages active participation.
The Cons to Consider
Time-Consuming: May require more time upfront.
Uncertainty: Outcomes aren't always predictable.
Resource Intensive: Can demand additional resources.
Despite these limitations, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks, especially when dealing with complex challenges.
Tools and Techniques to Enhance Skills
Mind Mapping
A visual tool that helps organize thoughts and uncover connections. Underlined example: Creating a mind map of customer needs can reveal hidden opportunities.
SWOT Analysis
Evaluating Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats provides a comprehensive view of the situation.
Strengths: Internal advantages.
Weaknesses: Internal disadvantages.
Opportunities: External possibilities.
Threats: External challenges.
Lateral Thinking
Coined by Edward de Bono, lateral thinking involves approaching problems indirectly (de Bono, 1970). It's about shifting perspective to see new possibilities.
Metaphorical Thinking
Using metaphors to relate unfamiliar concepts to known ones. It can make complex ideas more accessible.
Applying Creative Problem Solving in Today's World
In Business
Companies are increasingly valuing critical thinking as a skill. In industries like technology and logistics, the ability to innovate can set a company apart. For instance, integrating optimize supply chain management process tips through creative strategies can lead to significant efficiencies.
In Personal Life
On a personal level, creative problem solving enhances problem resolution skills. Whether it's planning a unique vacation or finding a new hobby, thinking creatively enriches our experiences.
Cultivating Creative Problem Solving Skills
Practice Divergent Thinking
Set aside time for brainstorming.
Challenge assumptions.
Explore alternative scenarios.
Engage in Creative Activities
Activities like painting, writing, or playing music stimulate the brain's creative centers.
Collaborate and Share Ideas
Working with others exposes us to different perspectives, enhancing our own thinking.
Conclusion
Reflecting on the Journey
Looking back, embracing creative problem solving has been a game-changer for me. It not only improved my professional performance but also added a new dimension to my personal life.
The Road Ahead
As we navigate an ever-changing landscape, developing our problem solving skills becomes increasingly important. By fostering creativity and critical thinking, we're better equipped to face any challenge that comes our way.
References
1- Osborn, A. F. (1948). Your Creative Power. Charles Scribner's Sons.
2- Parnes, S. J. (1967). Creative Behavior Guidebook. Charles Scribner's Sons.
3- Guilford, J. P. (1950). Creativity. American Psychologist, 5(9), 444-454.
4- de Bono, E. (1970). Lateral Thinking: Creativity Step by Step. Harper & Row.
5- Runco, M. A., & Pritzker, S. R. (Eds.). (1999). Encyclopedia of Creativity. Academic Press.
Italicized note: Embrace creativity, and watch as doors you never knew existed begin to open.
Frequently Asked Questions
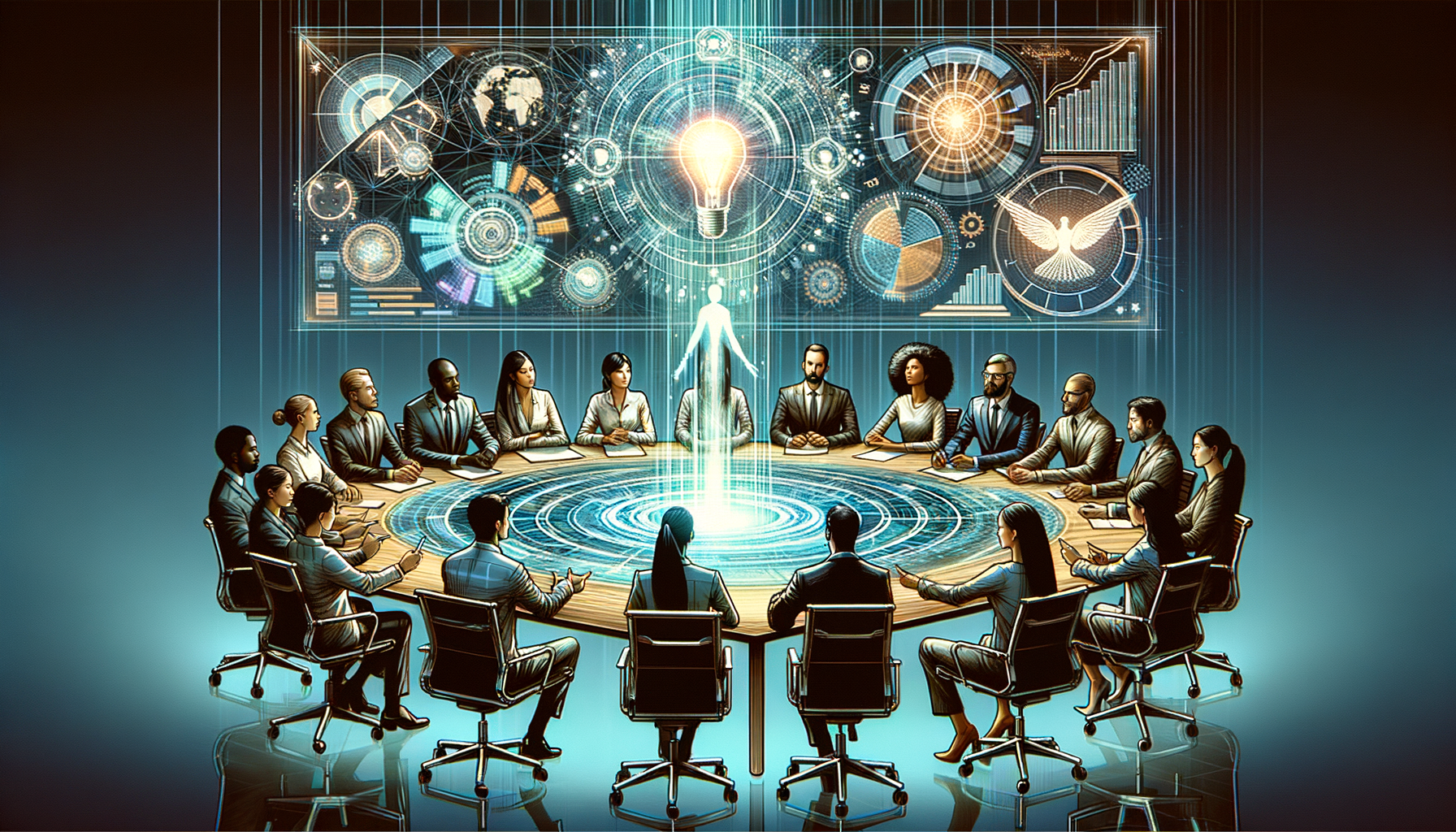
What are the different stages involved in the process of creative problem solving in the context of innovative thought?
The Essence of Creative Problem Solving
Creative problem solving stands at the heart of innovation. It transforms challenges into opportunities. The process entails distinct stages. Each demands attention and agility.
Identification and Preparation
Clarify the problem. This stage is crucial. Understanding the core question is vital. A misidentified problem misleads efforts. Hence, we focus on problem identification initially. Effective problem definition lays a robust foundation. It steers the entire creative process.
Preparation involves gathering information. One must understand the problem's context. This involves research and observation. Knowledge accumulation happens here. The goal is to immerse oneself fully. A deep dive into the issue follows. This ensures a comprehensive grasp of the situation.
Ideation
The ideation phase is where brainstorming thrives. We seek quantity over quality initially. Divergent thinking is the key here. Participants withhold judgment. They contribute ideas freely and spontaneously. The aim is to generate a vast idea pool. We encourage wild, even impractical suggestions.
Creativity emerges from unlikely connections. That's why we welcome all contributions. Cross-pollination often breeds innovation. Thus, we intertwine various perspectives during brainstorming. The more diverse the ideas, the better.
Incubation
After ideation, incubation begins. This stage is less visible. It involves subconscious processing. The mind works silently. People need breaks from deliberate thinking. This allows ideas to marinate. It promotes background synthesis of thoughts.
Incubation can take hours, days, even weeks. The timeline varies by project and problem. It is a time of rest and detachment. Yet, it is essential for creative insights to emerge.
Illumination
The "aha" moment defines illumination. Ideas click. Solutions surface unexpectedly. These insights often come unbidden. They can happen anytime, anywhere. The incubation period facilitates this. It enables the brain's reshuffling of information.
The illumination is not always dramatic. It can be subtle, incremental. Regardless, it marks a turning point. It signifies a breakthrough in thinking.
Verification and Implementation
The final stage deals with real-world application. Ideas face scrutiny here. We must evaluate their feasibility. Teams assess the practicality of solutions. They consider constraints and resources. Then follows refinement.
Refinement involves fine-tuning the idea. It might require iterations. Prototyping and testing are common activities. Feedback informs the development process.
Implementation is when an idea becomes reality. It moves from concept to execution. This phase demands as much creativity as the earlier stages. Adaptation and problem-solving continue.
Reflection
Reflection often goes unmentioned. But, it is a vital component. Here, teams review the problem-solving process. They learn for future endeavors. Mistakes become lessons. Successes inform best practices. Reflection closes the loop. It ensures continuous learning and improvement.
In conclusion, creative problem solving is dynamic. It interweaves diverse thoughts and strategies. Each stage builds on the previous. They form a cohesive pathway to innovation. This pathway is non-linear, often cyclical. Each problem may require revisiting stages. Creativity in problem-solving is thus evolutionary. It advances as we iterate and reflect.
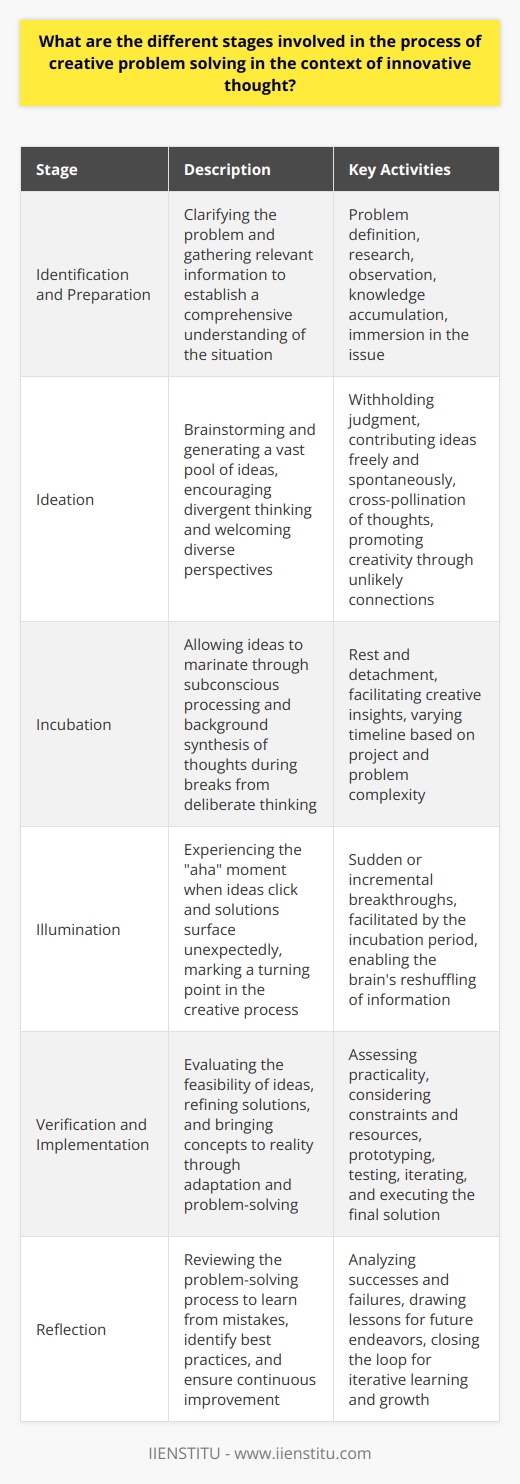
How does creative problem solving aid in overcoming cognitive biases and promote effective decision making?
Understanding Cognitive Biases
Cognitive biases affect judgement. They distort thinking, often unbeknown to us.
They spring from various mental shortcuts, known as heuristics. These biases can skew conclusions. They lead to poor decisions.
Creative Problem Solving: A Remedy
Creative problem solving contradicts biases' routine thinking. It involves lateral thinking. This challenges assumptions. It encourages fresh perspectives.
Breaking Mental Models
Biases stem from existing mental models. Creative problem solving dismantles these models. It builds new frameworks.
Generating Diverse Solutions
It thrives on diversity. Ideas come from different angles. This process questions biases directly. It offers counterpoints to embedded thinking.
Key Strategies in Creative Problem Solving
Encourage Curiosity
Curiosity kills cognitive biases. It provokes questions. It reveals hidden assumptions. Creative problem solving embodies this curiosity.
Embrace Failure
Fear of failure fuels bias. Creative problem solving embraces failure. It treats setbacks as learning steps. This mindset reduces the false confidence bias.
Seek Contrary Evidence
Confirmation bias confirms our beliefs. Creative problem solving seeks contrary evidence. It challenges existing notions. It promotes balanced decision making.
Foster Open Communication
Groupthink is a dangerous bias. Open communication deters groupthink. It invites all viewpoints. It encourages unbiased group decisions.
Use Structured Techniques
Techniques like the Six Thinking Hats or SCAMPER method can guide thinking. They offer structured creativity. They avoid hasty, biased conclusions.
Conclusion
Creative problem solving is essential. It counteracts stubborn cognitive biases. It offers a route to effective decision making. Embrace it. Overcome biases. Make better decisions.
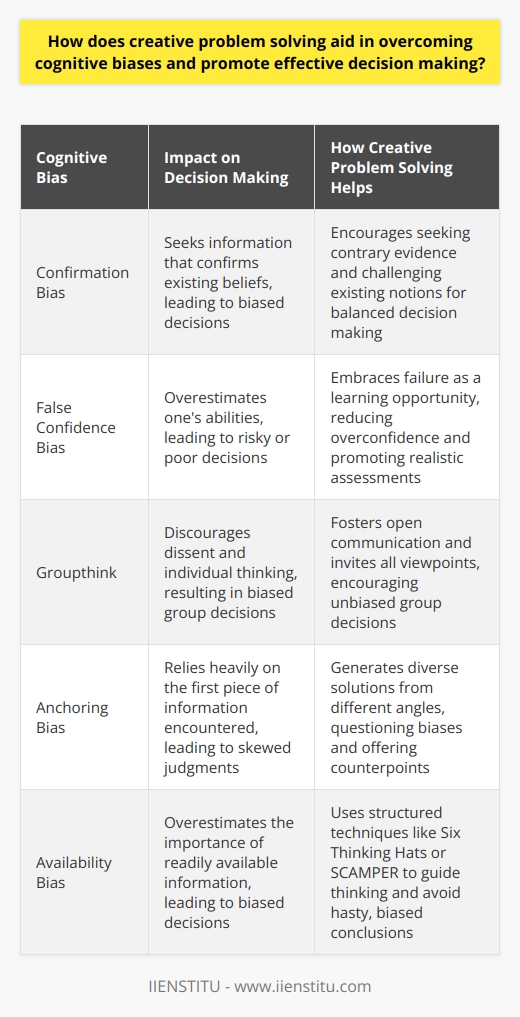
Can you explain the role of divergent and convergent thinking in unleashing the power of innovative thought through creative problem solving?
The Interplay of Divergent and Convergent Thinking
In the realm of creative problem-solving, innovation hinges on how one thinks. Two cognitive approaches stand out: divergent and convergent thinking. Understanding their roles is key to unlocking innovative potential.
Divergent Thinking: Exploring the Possibilities
Divergent thinking opens the mental floodgates. It allows for the exploration of numerous solutions. Here, quantity trumps quality. It thrives on curiosity and does not fear the absurd. Think of it as brainstorming; it's about generating many ideas.
- Encourages questioning norms
- Fosters a multitude of ideas
- Defies perceived limitations
Convergent Thinking: Zeroing In on Solutions
In contrast, convergent thinking narrows down options. It seeks a single, often logical solution. Practicality and feasibility are its cornerstones. Convergent thinking sorts and sifts through the ideas divergent thinking offers.
- Aims for the most viable answer
- Applies logical reasoning
- Prioritizes practicality and effectiveness
Harmonizing Divergence and Convergence
Creative problem solving demands a dance between the two. Each plays its part at different stages of ideation. Innovative thought arises when these thinking styles align.
The Innovation Process
Step 1: Invoking Divergent Thinking
First, we diverge. We seek breadth and defy boundaries. We ask "What if?" and "Why not?" We postpone judgment. Here, every idea gets a seat at the table.
- Embrace chaos
- Resist jumping to conclusions
- Consider the improbable
Step 2: Transition Through Reflection
Second, we pause. Reflection serves as the bridge between thinking styles. We ponder over the ideas. We weigh their merits. This pause is crucial.
- Reflect on ideas generated
- Assess feasibility
- Prepare for convergence
Step 3: Implementing Convergent Thinking
Finally, we converge. We use critical thinking to find the best solution, distilling the essence from the noise. We seek alignment with goals and constraints.
- Set criteria for selection
- Test against objectives
- Arrive at a solution
Conclusion: Dynamic Equilibrium for Innovation
The synergy between divergent and convergent thinking fuels innovation. Each has a role in creative problem-solving. Alone, each is incomplete. Combined, they form a dynamic strategy for unleashing innovative thought. Embrace both to solve complex problems with creativity and insight.