This article discusses the differences between Diversity, inclusion, and equality, as well as HRM's role in creating workplace equity. It also outlines the challenges companies face when implementing equity, such as employee resistance, inadequate resources, and a lack of understanding of the concept.
Introduction
Creating Equity Through HRM
Challenges of Implementing Equity
Conclusion
Takeaways
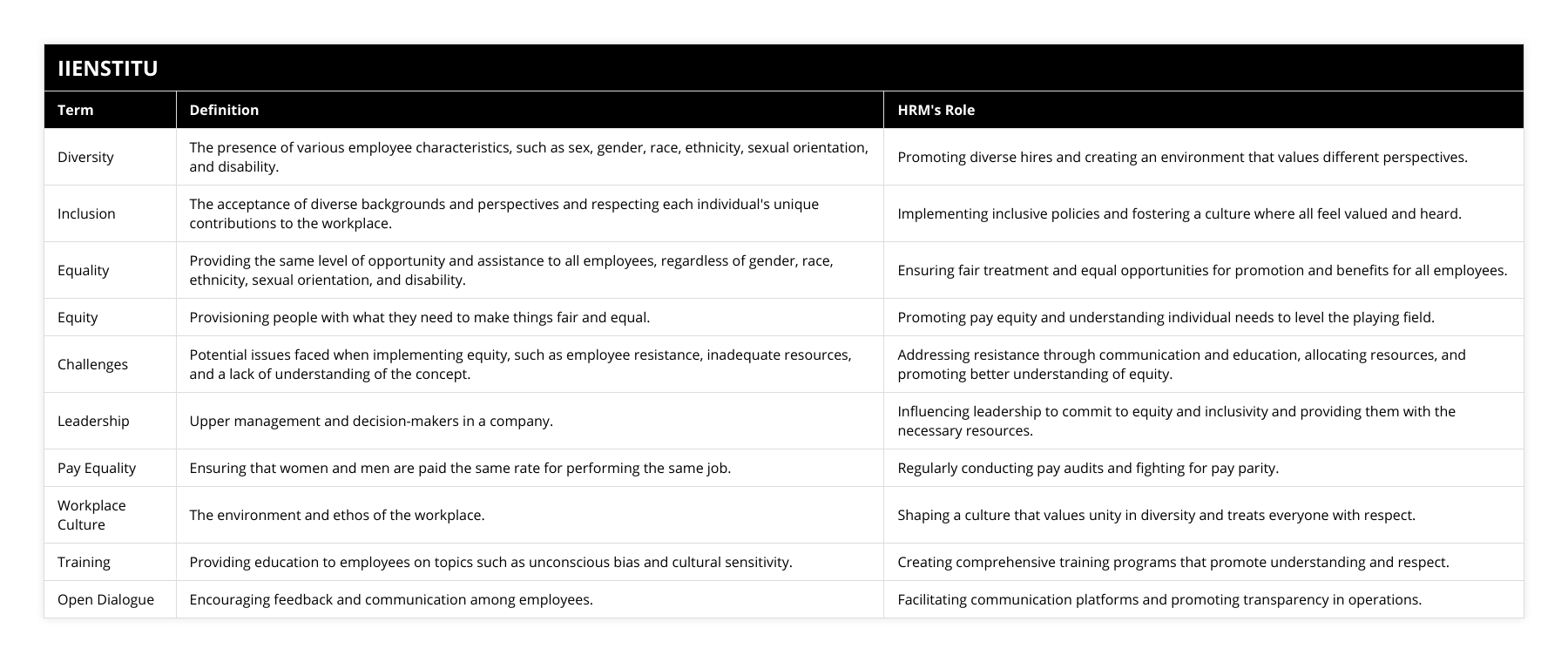
Introduction: Diversity, inclusion, and equality are terms often used interchangeably, but they mean different things. Diversity is the presence of various employee characteristics, such as sex, gender, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, and disability.
Inclusion is the acceptance of these diverse backgrounds and perspectives and respecting each individual's unique contributions to the workplace. Equality is providing the same level of opportunity and assistance to all employees, regardless of gender, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, and disability. Finally, equity is the next step, providing people with what they need to make things fair and equal.
Creating Equity Through HRM
The Human Resources Management (HRM) department plays a vital role in creating and maintaining equity in the workplace. Pay equality is critical in creating equity, as it ensures that women and men are paid the same rate for performing the same job. HRM should also invest in positive, forward-thinking movements that promote diversity, inclusion, and equality. This includes providing education and training to employees on topics such as unconscious bias and cultural sensitivity. Additionally, HRM should encourage open dialogue and feedback among employees to ensure everyone's voices are heard and respected.
Challenges of Implementing Equity
Despite the best efforts of HRM, there is still a significant amount of work to achieve accurate equity in the workplace. Companies often face challenges when implementing equity, such as employee resistance, inadequate resources, and a lack of understanding of the concept. Furthermore, some companies may be getting worse regarding diversity, inclusion, and equality. This is due to several factors, such as a lack of commitment from Leadership, a lack of resources, and a lack of understanding of the concept.
Related Course: Leadership Development Course
Conclusion: Creating equity in the workplace is an ongoing process that requires dedication and commitment from Leadership, HRM, and employees. It is essential to recognize that diversity, inclusion, and equality are not the same and that equity is the next step in creating a truly equitable workplace.
Additionally, companies face several challenges when it comes to implementing equity, including employee resistance, inadequate resources, and a lack of understanding of the concept.
Takeaways
Diversity, inclusion, and equality are different concepts, and equity is the next step in creating a truly equitable workplace.
HRM plays a vital role in creating and maintaining equity in the workplace, such as investing in positive, forward-thinking movements that promote diversity, inclusion, and equality.
Companies often face challenges when implementing equity, such as employee resistance, inadequate resources, and a lack of understanding of the concept.
Equality is not achieved through words alone but through action in the workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What strategies can be used to create equity through HRM in terms of diversity, inclusion and equality?
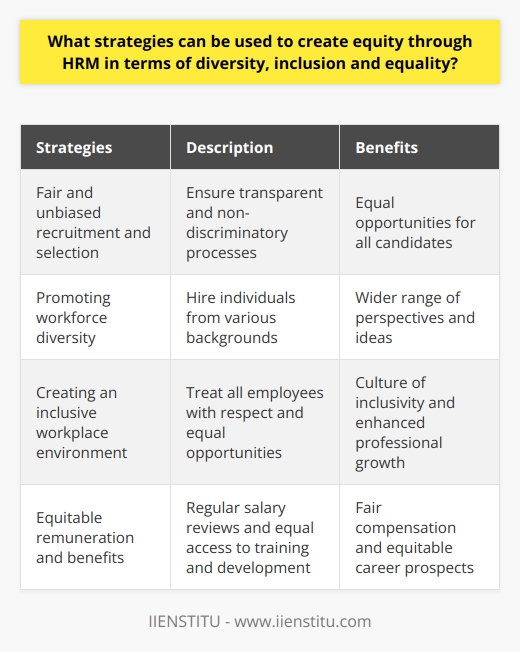
Any organization's human resources management (HRM) function is essential to its success. As such, it is vitally vital that HRM strategies are developed and implemented to create equity through diversity, inclusion, and equality. This article will discuss the various strategies which can be used to achieve this goal.
The most effective way to create equity through HRM is to ensure that all recruitment and selection processes are fair, transparent, and non-discriminatory. This can be achieved by providing that job descriptions and selection criteria are transparent and unbiased. All candidates are assessed on an equal footing and given equal opportunities to demonstrate their skills and experience. Additionally, it is essential that adequate diversity in the workforce is achieved and that all employees are treated equally and with respect.
Organizations should also seek to create an inclusive workplace environment by ensuring that all employees, regardless of their background, are treated with respect and given equal opportunities to progress and develop. In addition, it is essential to ensure that all employees have reasonable access to resources and support and that they are provided with a safe and supportive working environment.
Furthermore, organizations should strive to create an equitable workplace by taking proactive steps to ensure that remuneration and other benefits are fair and honest. This can be achieved by conducting regular salary reviews to confirm that payment is reasonable and appropriate to the individual's experience level and qualifications. Additionally, organizations should ensure that all employees have access to training and development opportunities that are implemented fairly and equitably.
In conclusion, several strategies can be employed to create equity through HRM regarding diversity, inclusion, and equality. By ensuring that recruitment and selection processes are fair and transparent, that the workplace is inclusive and equitable, and that remuneration and other benefits are fair and honest, organizations can create a workplace where all employees are treated equally and with respect.
How can companies ensure pay equality when creating equity through HRM?
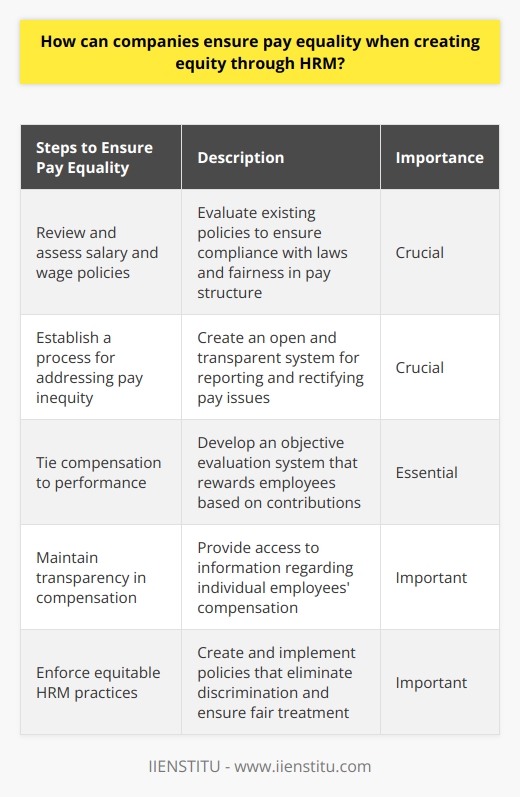
Pay equality is an important issue that companies must address when creating equity through Human Resources Management (HRM). Organizations must develop policies and procedures to ensure that all employees are paid equitably, regardless of gender, race, or other factors. This article will outline strategies companies can use to ensure pay equality and create equity through HRM.
The first step in creating pay equality is to ensure that salary and wage policies are fair and consistent. Companies should review their current salary and wage policies to ensure that they comply with state and federal laws, as well as any internal policies. Companies should also check their existing pay structure to ensure that wages are commensurate with the job duties, skills, and experience required for the position. It is important to remember that pay should be based on the value of the job, not on gender or other factors.
The second step in creating pay equality is to create a system for addressing pay inequity. Companies should establish a process for employees to report any issues related to pay inequity and create a plan for responding to those reports promptly. Companies should also establish a policy for reviewing and adjusting pay for employees who are not paid equitably.
The third step in creating pay equality is to ensure that compensation is based on performance. Companies should create a system for evaluating performance and rewarding employees for their contributions. This system should be based on objective criteria and free from bias. Companies should also ensure that their compensation system is transparent and that employees can access information about their compensation.
Finally, companies should ensure that their HRM practices are equitable. Companies should create and implement policies and procedures that ensure that recruitment, hiring, and promotion practices are free from discrimination and bias. Companies should also develop and implement policies and procedures that ensure that employees are treated fairly and equitably, including pay, benefits, and leave policies.
Following these steps, companies can ensure pay equality and create equity through HRM. By developing and implementing fair and equitable policies and procedures, companies can ensure that all employees are paid equitably and treated fairly. This will help create an environment of trust and respect in the workplace, leading to greater productivity and success for the organization.
What challenges do companies face when implementing equity through HRM?
When companies decide to implement equity through Human Resources Management (HRM), they face several challenges that can have a significant impact on their organization. The most prominent challenges include creating a culture of equity, addressing pay gaps, and addressing recruitment and retention issues.
Creating a Culture of Equity
One of the main challenges companies face when implementing equity is creating a culture of equity. This involves creating a workplace environment where all employees feel respected and valued regardless of gender, race, ethnicity, or other characteristics. This can be difficult because it requires companies to identify and address existing disparities. To do this, companies must implement policies that promote diversity and inclusion, such as flexible working hours, recruitment strategies that focus on variety, and training and development programs that focus on equity.
Addressing Pay Gaps
Another major challenge that companies face is addressing pay gaps. Pay gaps occur when employees of similar experience and qualifications are paid differently based on their gender, race, ethnicity, or other characteristics. This can create a sense of inequality and resentment among employees, hurting morale and productivity. To address this issue, companies must ensure that their pay structures are equitable and transparent and that employees are given equal opportunities for promotion and career progression.
Addressing Recruitment and Retention Issues
Companies must also address recruitment and retention issues when implementing equity. This includes ensuring that job postings are written inclusively, that recruitment processes are fair and accessible to all qualified candidates, and that retention strategies are in place to retain talented employees. Companies should also ensure that their recruitment and retention practices align with current laws and regulations and that their HR practices are up-to-date and compliant with the latest standards.
In conclusion, when companies decide to implement equity through HRM, they face several challenges that can have a significant impact on their organization. To successfully implement equity, companies must create a culture of equity, address pay gaps, and address recruitment and retention issues. By doing so, companies can ensure that their HR practices are equitable and compliant and that their employees feel respected and valued.
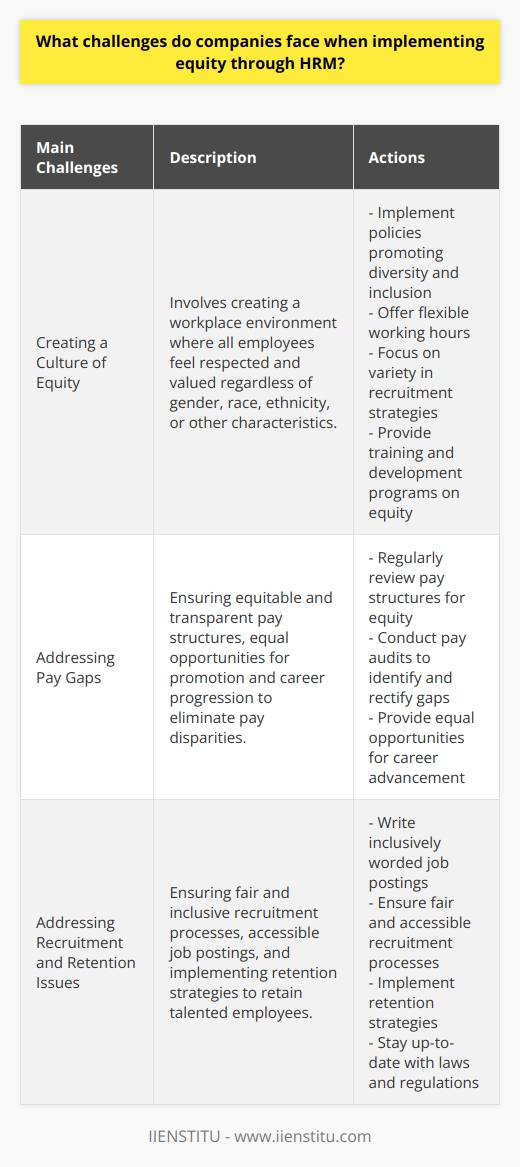
How can HR promote diversity and inclusion in the workplace?
Creating a Culture of Inclusiveness
To promote diversity and inclusion in the workplace, Human Resources (HR) should actively target strategies that foster an inclusive environment. This begins with building a diverse workforce by ensuring equitable recruitment processes. HR can accomplish this by addressing potential unconscious biases in job advertisements, screening, and interviews, as well as offering bias training to hiring personnel.
Implementing Inclusive Policies
Companies must also develop comprehensive and inclusive policies tailored to their employees' needs. HR can establish guidelines regarding work-life balance, parental leave, and accommodations for individuals with disabilities. Moreover, openly promoting non-discrimination and equal opportunity policies highlights a company's commitment to diversity and inclusivity, which attracts candidates from various backgrounds.
Cultivating an Open Workplace Environment
An essential part of fostering an inclusive workplace is nurturing open communication and collaboration. HR should create safe spaces for employees to express their thoughts, opinions, and concerns, as well as provide channels for reporting incidents of discrimination or exclusion. Regularly conducting employee engagement activities, such as workshops and team-building exercises, allows staff to learn from one another and embrace different perspectives.
Investing in Training and Development
To further reinforce its commitment to inclusion, HR must invest in ongoing training and development programs to expand employees' understanding of diversity and inclusion topics. These activities can range from hosting diversity training sessions to encouraging participation in industry-specific seminars focusing on equity and inclusion. By continuously deepening employees' knowledge, organizations can create a culture where all individuals feel valued and respected.
Celebrating Employee Differences
Finally, HR can promote diversity and inclusion by celebrating employees' unique qualities and experiences. Hosting events or dedicating a month to recognizing different cultures, traditions, and backgrounds allows staff to learn more about one another and appreciate the richness that diversity brings to the workplace. This practice helps foster a sense of belonging and inspires employees to contribute their perspectives and ideas.
In conclusion, HR plays a crucial role in promoting diversity and inclusivity by adopting targeted strategies, implementing supportive policies, and fostering an open workplace culture. By nurturing a diverse and inclusive environment, companies not only contribute to a more just society but also gain a competitive advantage by leveraging the unique skills and perspectives of their diverse workforce.
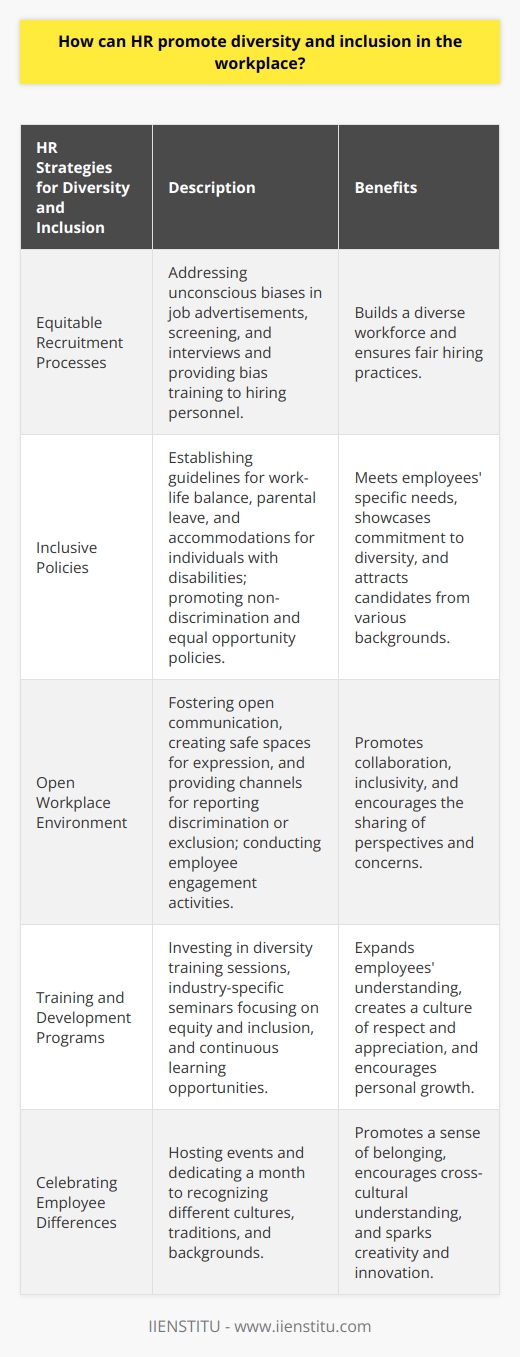
How does equity fit into your workplace's diversity and inclusion efforts?
Equity in Workplace Diversity and Inclusion Efforts
Understanding Equity
In the context of workplace diversity and inclusion efforts, equity refers to the fair treatment, access, opportunity, and advancement for all employees, while identifying and addressing the barriers that prevent the full participation of marginalized groups. Equity is crucial in creating a truly diverse and inclusive organization, as it ensures that all employees receive equal opportunities regardless of their differences, such as gender, ethnicity, age, and other factors.
The Role of Equity
Enhancing Organizational Culture
Equity in workplace diversity and inclusion efforts is essential for cultivating a positive organizational culture, where employees feel valued and respected regardless of their differences. By fostering an equitable environment, organizations are better able to engage employees, enhance collaboration, and increase overall job satisfaction.
Promoting Fair Opportunities
Achieving equity in the workplace ensures that all employees have equal access to opportunities and resources, regardless of their individual backgrounds or characteristics. This includes equal opportunity for career development, training, and advancement, as well as access to mentoring and support programs. By providing fair opportunities, organizations create an inclusive environment that enables all employees to reach their full potential.
Addressing Unconscious Bias
Incorporating equity into diversity and inclusion efforts involves addressing unconscious bias - the subtle, often unintentional, forms of discrimination that can hinder the success of marginalized employees. By committing to equitable practices and ongoing bias training, organizations can minimize the impact of unconscious bias on their employees, thereby fostering a more inclusive workplace culture.
Tailoring Inclusion Strategies
To promote equity in workplace diversity and inclusion efforts, organizations must tailor their strategies to address the specific needs and challenges faced by different groups within their workforce. By conducting regular assessments and engaging in open dialogue with employees, organizations can better identify the barriers that hinder diverse employees from fully participating in the workplace, and adjust their policies and practices accordingly.
Measuring and Monitoring Progress
Finally, equity in workplace diversity and inclusion efforts requires organizations to continually measure and monitor their progress. This involves setting clear diversity and inclusion objectives, tracking key performance indicators, and conducting regular evaluations to assess the effectiveness of their strategies. By continuously monitoring their progress, organizations can ensure that their diversity and inclusion efforts effectively promote equity for all employees.
In conclusion, equity plays a critical role in workplace diversity and inclusion efforts by fostering a positive organizational culture, promoting fair opportunities, addressing unconscious bias, tailoring inclusion strategies, and measuring and monitoring progress. By incorporating equity into their diversity and inclusion initiatives, organizations can create an environment where all employees have an equal opportunity to contribute to the success of the organization, regardless of their individual differences.

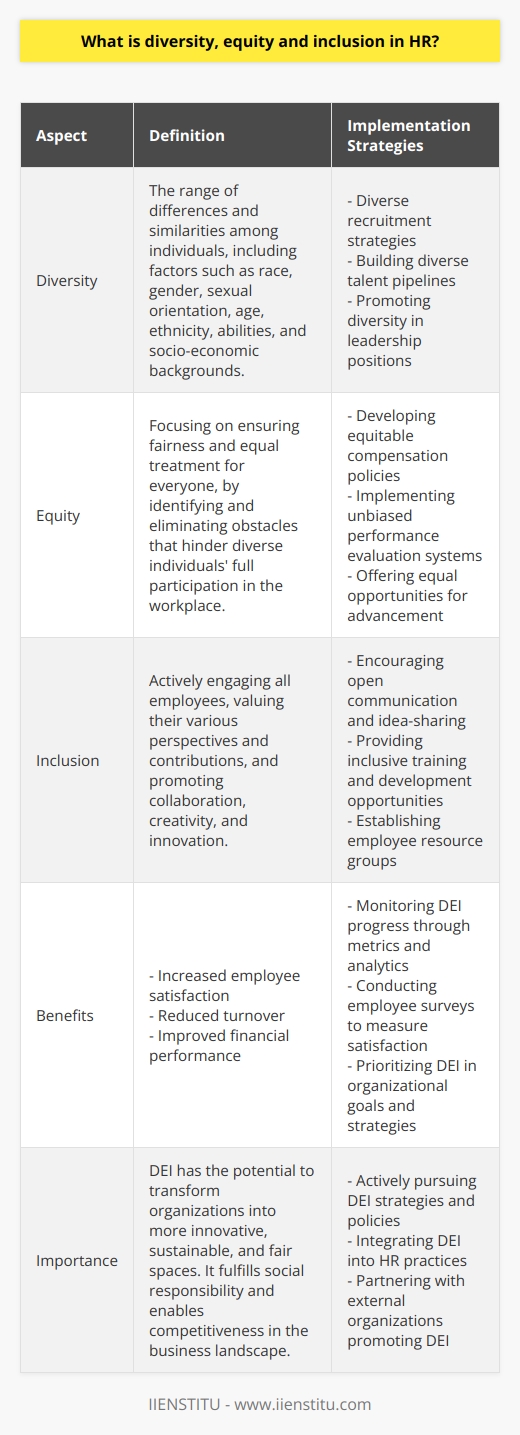
What is diversity, equity and inclusion in HR?
Defining Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) are crucial components of human resources (HR) management in organizations today. Diversity refers to the mixture of differences and similarities that exist among individuals, including aspects such as race, gender, sexual orientation, age, ethnicity, abilities, and socio-economic backgrounds.
Understanding Equity
Equity is about ensuring fairness and equal treatment of all individuals within an organization. This involves identifying and removing barriers that prevent the full participation of diverse individuals in the workplace. In essence, equity recognizes that people have different needs and requires organizations to adopt strategies and policies that cater to these unique requirements.
The Importance of Inclusion
Inclusion refers to the active involvement of all employees in the organization's processes, valuing their diverse perspectives and contributions. An inclusive workplace fosters a sense of belonging and encourages collaboration, creativity, and innovation. Thus, inclusion is the bridge that connects diversity and equity, creating a positive and nurturing work environment where all individuals feel valued, respected, and included.
Implementing DEI in HR
For HR professionals, implementing DEI involves adopting diverse recruiting strategies, fair compensation policies, and comprehensive professional development programs. Furthermore, HR must monitor the organization's culture and work to eliminate unconscious biases that may exist within the workplace. This includes providing regular training and education on DEI best practices for employees at all levels.
The Benefits of DEI in HR
Organizations that effectively manage DEI in HR can experience numerous benefits, such as increased employee satisfaction, reduced turnover, and improved financial performance. Additionally, a diverse and inclusive workforce can drive innovation and creativity, enabling organizations to better adapt in a rapidly changing global economy. Beyond business outcomes, DEI can help organizations fulfill their social responsibility by promoting a more inclusive and equitable society.
In conclusion, diversity, equity, and inclusion play a vital role in human resources management, with the potential to transform organizations into more innovative, sustainable, and equitable spaces. HR professionals must actively pursue strategies and policies that foster a diverse, inclusive, and equitable work environment to remain competitive in the current business landscape.
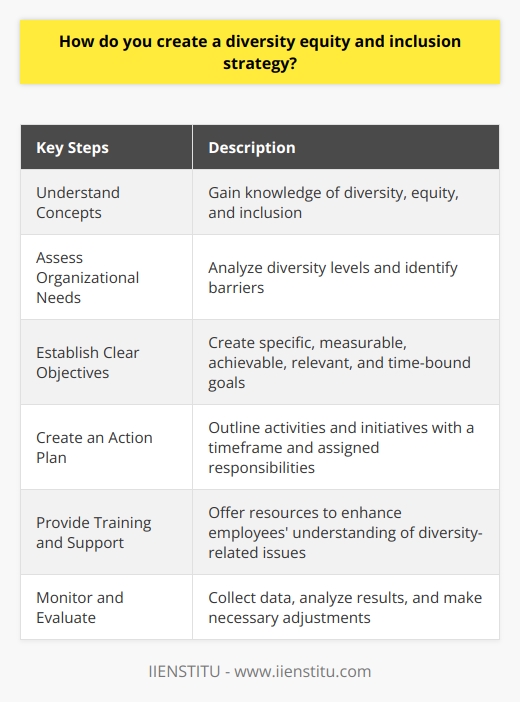
How do you create a diversity equity and inclusion strategy?
Developing a Framework for Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
Understanding Key Concepts
To create a successful diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) strategy, one must first comprehend the fundamental concepts involved. Diversity refers to the various differences between people, such as ethnicity, gender, and socio-economic status. Equity implies equal opportunities for everyone, while inclusion encompasses a sense of belonging and involvement within the community.
Assessing Organizational Needs
A vital step to implementing a DEI strategy is evaluating the specific needs of an organization. This involves conducting a thorough analysis of the current workforce's diversity levels, assessing policies and procedures, and identifying potential barriers to achieving an equitable and inclusive environment. A comprehensive assessment will help guide the development of a robust DEI plan.
Establishing Clear Objectives
Next, clear objectives should be set to outline the desired outcomes of the DEI strategy. These goals must be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART), serving as a roadmap to guide the implementation process. Moreover, these objectives should align with the organization's overall mission and values, ensuring that their progress contributes to the collective vision.
Crafting an Action Plan
With objectives in place, a well-defined action plan can be formulated to address the identified gaps within the organization. This plan should outline the activities and initiatives required to achieve the set objectives, with a focus on promoting diversity, fostering equity, and facilitating inclusion. Additionally, the action plan should provide a timeframe for implementation and allocate responsibilities to specific individuals or teams to ensure accountability.
Providing Training and Support
A successful DEI strategy requires ongoing training and support for employees. This involves providing resources, such as workshops, seminars, and e-learning, designed to improve knowledge and awareness of diversity-related issues. When employees feel empowered and educated, they are better equipped to contribute to an inclusive and equitable work environment.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Lastly, regular monitoring and evaluation of the implemented DEI strategy is necessary to track progress and assess its effectiveness. By routinely collecting data and analyzing the results, organizations can make any necessary adjustments to ensure that the strategy remains relevant and impactful. Moreover, this evaluation process enables organizations to celebrate successes and identify areas for continuous improvement.
In conclusion, developing a successful DEI strategy requires a comprehensive understanding of the key concepts, an assessment of organizational needs, the establishment of clear objectives, and the formulation of a well-defined action plan. Additionally, providing employees with training, support and continuous monitoring and evaluation will ensure a lasting impact within the organization.
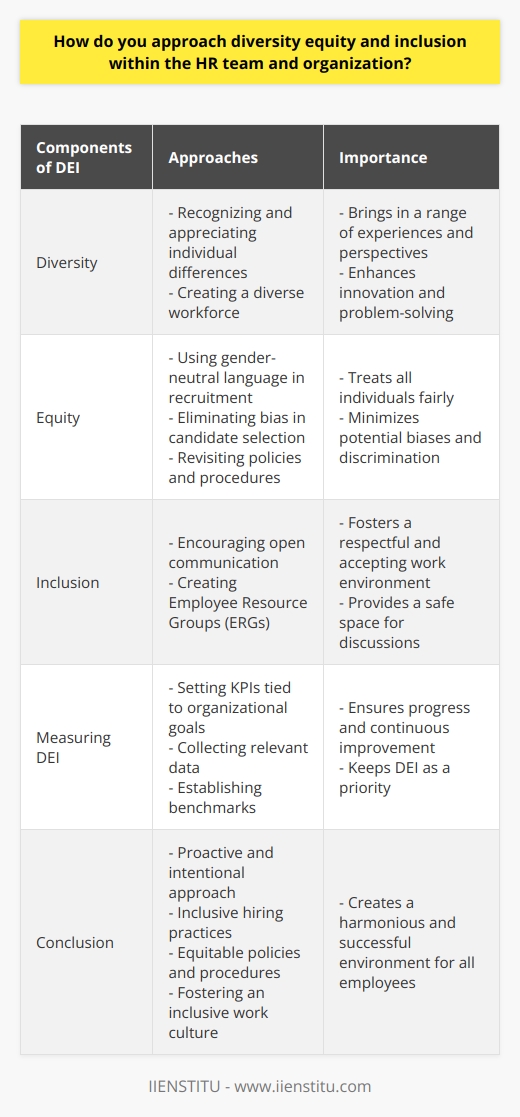
How do you approach diversity equity and inclusion within the HR team and organization?
Understanding Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
To approach diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) within the HR team and organization, it is crucial to understand the concept of DEI and its components. Diversity encompasses the variety of personal experiences, values, and perspectives that people bring into the workplace. Equity entails fair treatment to all individuals, minimizing potential biases, and recognizing structural inequality. Inclusion signifies the active efforts involved in creating an environment that respects, accepts, and values all individuals.
Promoting DEI within the HR Team
The HR team must promote DEI through various processes, including recruitment, employee retention, performance management, and professional development. By implementing inclusive hiring practices such as using gender-neutral language in job descriptions and eliminating bias in candidate selection, HR professionals can attract diverse talent. Additionally, offering ongoing training and development programs that address DEI concerns can help employees feel equipped to handle diverse workplace issues.
Creating Equity in Policies and Procedures
Organizational policies and procedures should be designed to promote equity and minimize discrimination. This means revisiting policies with a critical lens, removing any systemic barriers, and having clear guidelines to address all forms of unconscious bias. Training and awareness programs should also be provided to educate employees on equitable policies and practices.
Establishing Inclusive Work Cultures
HR professionals should actively engage in fostering a culture of inclusion within the organization. This involves encouraging open communication, creating Employee Resource Groups (ERGs) that cater to various minority groups, and establishing a safe space for dialogues on DEI issues. By encouraging collaboration and feedback, HR teams can better understand employees' needs and enhance the overall inclusivity of the workplace.
Measuring DEI Progress
To ensure continued improvement in DEI, the HR team should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that are tied to organizational goals. For instance, setting measurable targets for diverse employee representation or inclusive programming initiatives can help evaluate the organization’s progress. Collecting relevant data and establishing benchmarks will allow HR professionals to track success and ensure that DEI remains a priority.
In conclusion, HR professionals must take a proactive and intentional approach to diversity, equity, and inclusion in their organizations. Through developing inclusive HR practices, equitable policies, and fostering a welcoming workplace culture, organizations can embrace DEI values and create a more successful and harmonious environment for all employees.
How does equity fit into your workplace's diversity and inclusion efforts?
Equity in Workplace Diversity and Inclusion Efforts
Defining Equity
Equity refers to the fair treatment, access, and opportunity for all employees, involving recognizing and addressing any existing disparities among the workforce. A committed approach to equity ensures a level playing field for every worker, irrespective of their diverse backgrounds or identities.
Balancing Representation and Opportunity
An essential component of workplace diversity and inclusion efforts is striking the right balance between representation and opportunity. Employee equity involves not just maintaining diverse representation in the workforce, but also providing equal opportunities for career development, promotions, and mentorship for everyone.
Promoting a Culture of Inclusivity
Equity plays a substantial role in fostering a culture of inclusivity in the workplace. By making conscious efforts to be more equitable, businesses can nurture a work environment where differences are acknowledged, addressed, and celebrated. Employees feel respected and valued when their unique perspectives are heard and considered in decision-making processes.
Cultivating Employee Engagement
Equity also contributes to increasing employee engagement and motivation. When employees see organizational commitment to fairness and equal opportunity, they feel a higher sense of attachment towards their workplace. This heightened engagement results in improved productivity, reduced turnover, and a healthier work culture.
Addressing Unconscious Bias
To achieve workplace equity, it is crucial to tackle unconscious biases that can unintentionally influence decision-making processes. By providing regular training and guidance on recognizing and addressing these biases, organizations can make their inclusion efforts more effective and meaningful to all employees.
Evaluating Progress and Setting Goals
Organizations must continue to evaluate their progress regarding equity and set meaningful goals to achieve better workplace diversity and inclusion. By keeping track of metrics related to equity, such as demographic representation, pay gap, and employee experiences, it becomes possible to identify areas that need improvement and prioritize effective action.
In conclusion, equity is a vital component of any workplace's diversity and inclusion strategy. By incorporating fair treatment, access, and opportunity in every aspect of employee experiences, organizations can create a more inclusive work environment, effectively mitigating disparities and helping employees thrive.

How can HR effectively measure the impact of diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives in an organization?
Assessing Impact through Key Indicators
To effectively measure the impact of diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives, HR professionals should rely on specific key indicators. These indicators include employee engagement, diverse representation, retention rates, and the overall company culture.
Employee Engagement
First, HR can evaluate employee engagement by conducting regular surveys that gauge the level of commitment, satisfaction, and motivation within the workforce. This quantitative data can then be analyzed to determine whether DEI initiatives are having a positive impact on employees' experiences.
Diverse Representation
Next, HR professionals can track diverse representation by analyzing the demographics of their workforce. This entails monitoring the percentage of underrepresented groups within different levels of the organization and comparing these figures to established goals. Such data can demonstrate the effectiveness of DEI programs in promoting diversity and equal opportunities.
Retention Rates
Third, HR can measure the retention of diverse employees, as high retention rates often signal a healthy and equitable working environment. By comparing these rates among various demographic groups, HR can gauge whether an organization is successfully fostering an inclusive atmosphere that encourages diverse individuals to remain with the company.
Company Culture Assessment
Lastly, through qualitative approaches such as focus groups, interviews, and open forums, HR can capture the impact of DEI initiatives on the company culture. These discussions can reveal employees' perceptions of diversity, equity, and inclusion in their workplace, offering insights on areas of improvement and the overall success of the initiatives.
By continuously monitoring these key indicators, HR professionals can effectively measure the impact of DEI initiatives within an organization. This data-driven approach will enable them to make informed decisions and drive improved outcomes for a more diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplace.

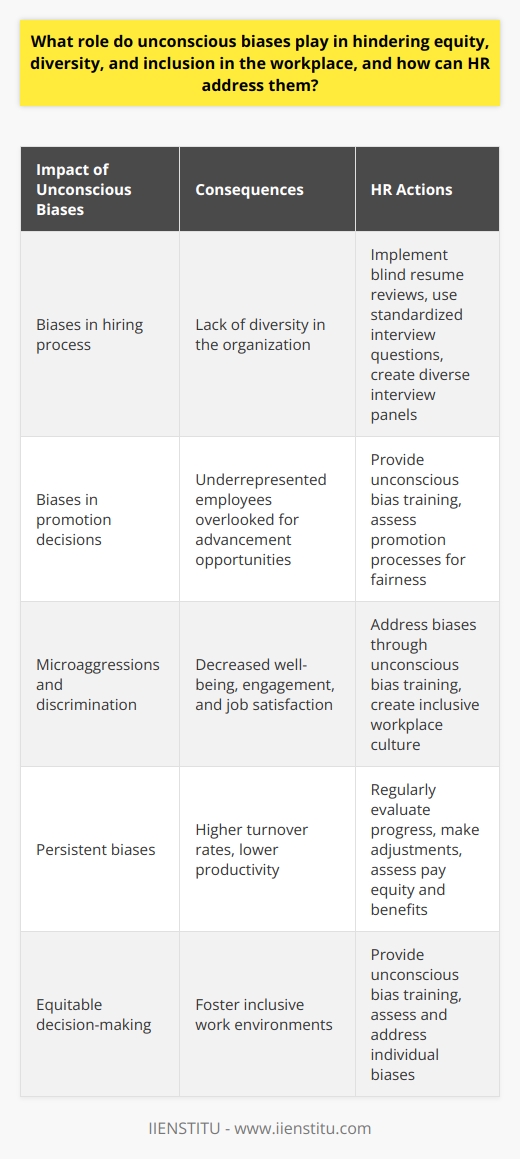
What role do unconscious biases play in hindering equity, diversity, and inclusion in the workplace, and how can HR address them?
Role of Unconscious Biases
Unconscious biases significantly hinder equity, diversity, and inclusion in the workplace. These biases encompass subjective attitudes, beliefs, and assumptions that individuals unknowingly hold towards others. Such mindsets often lead to unfair treatment, limiting opportunities for underrepresented groups and promoting unequal workplaces.
Impact on Decision-Making
Unconscious biases affect crucial decision-making processes such as hiring, promotions, training, and performance appraisals. For example, in the hiring process, interviewers may unintentionally favor candidates with similar backgrounds, experiences, or appearances to their own, creating homogenous work environments. This issue extends to promotions, where underrepresented employees may be overlooked due to preconceived notions about their capabilities and potential.
Influence on Workplace Culture
These biases also create barriers to creating inclusive workplace cultures, where employees feel valued and respected regardless of their background. Unconscious biases can manifest in microaggressions or subtle forms of discrimination, which can negatively impact employees' well-being, engagement, and overall job satisfaction. Consequently, workplaces with persistent biases may experience higher turnover and lower productivity.
HR's Role in Addressing Unconscious Biases
Human resource departments must take proactive measures to address and mitigate unconscious biases in the workplace. Providing unconscious bias training for employees, particularly managers and executives, can be an essential first step in raising awareness and fostering more inclusive work environments. This training can also help identify specific biases and promote equity in decision-making processes.
Additionally, HR can implement equitable hiring practices, such as using standardized interview questions, blind resume reviews, and diverse interview panels, to reduce the influence of unconscious biases. Regularly reviewing policies and practices to identify potential areas for improvement, such as pay equity, promotion processes, and employee benefits, is essential to ensuring that organizations actively work towards mitigating the impact of unconscious biases.
Finally, organizations must commit to continuous improvement, routinely assessing progress towards diversity, equity, and inclusion goals, and adjusting strategies accordingly. By actively addressing unconscious biases, HR can create a more inclusive workplace that values and respects all employees.
How can HR implement training and development programs to foster a culture of equity, diversity, and inclusion among employees?
Creating a Tailored Strategy
To foster a culture of equity, diversity, and inclusion among employees, Human Resources (HR) can implement training and development programs designed specifically for this purpose. The first step to creating these programs entails conducting a thorough assessment of the organization's current environment to identify gaps and areas for improvement.
Designing Customized Training Programs
Based on the assessment results, HR can design customized training programs that address identified issues and support the organization's objectives. Such programs should include elements such as unconscious bias training, cultural competency development, and diversity workshops. Moreover, HR should integrate these training modules into talent management processes, employee onboarding, and leadership development initiatives to holistically address the organization's diversity and inclusion goals.
Monitoring and Evaluating Progress
For these training programs to be effective, HR must establish clear metrics to evaluate their impact on the organization's culture. HR should monitor employee engagement, retention, and promotion rates, as well as survey employees periodically to gauge their awareness and understanding of diversity and inclusion issues. By regularly assessing the training's effectiveness, HR can make data-driven decisions to iterate and improve upon the programs.
Promoting Internal Collaboration
Creating a diverse and inclusive environment is not solely the responsibility of HR but should be a collaborative effort across the organization. HR should encourage cross-departmental collaboration in planning and implementing training programs. This approach ensures that diversity and inclusion initiatives encompass diverse perspectives, which benefits the entire organization.
Leadership Support and Commitment
HR should work closely with senior leadership to gain their commitment to equity, diversity, and inclusion initiatives. Leaders should demonstrate their support by making public statements, attending training sessions, and promoting a culture of continual learning and development. Their visible commitment encourages all employees to engage in training programs and contribute to a culture of equity, diversity, and inclusion.
In conclusion, HR plays a critical role in fostering a culture of equity, diversity, and inclusion among employees. By creating tailored strategies for training and development, collaborating with other departments, and ensuring leadership support, HR can positively impact the organization's culture and promote an inclusive work environment.

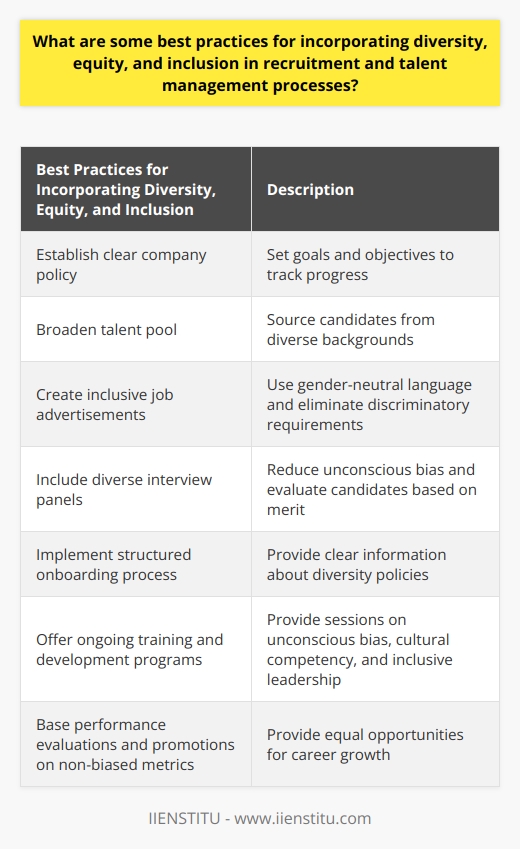
What are some best practices for incorporating diversity, equity, and inclusion in recruitment and talent management processes?
Best practices for diversity, equity, and inclusion in recruitment and talent management
Establishing a diverse workforce
One critical step to incorporate diversity, equity, and inclusion in recruitment is to create a well-defined company policy that emphasizes its commitment to maintaining a diverse workforce. This includes setting up specific goals and objectives to measure the progress over time, to ensure that the organization maintains its focus on enhancing diversity.
Expanding talent pools
Another essential practice is to broaden the search criteria for potential employees by exploring different channels for talent acquisition. This involves sourcing candidates from various cultural backgrounds, educational qualifications, and work experience levels, to encourage a diverse pool of applicants that can bring a wide range of perspectives to the organization.
Inclusive job advertisements
It is pivotal to create inclusive job advertisements that promote an organizational culture embracing diversity. This can be achieved by using gender-neutral language, eliminating any requirements that may be unintentionally biased against specific demographic groups, and highlighting the company's commitment to equity and inclusion.
Utilizing diverse interview panels
During the recruitment process, it is essential to assemble diverse interview panels to minimize the occurrence of unconscious bias. By including multiple perspectives and experiences in the decision-making process, organizations can better evaluate candidates based on their merits, rather than on demographic factors or predispositions.
Creating inclusive onboarding processes
Having a well-structured onboarding process that openly communicates the organization's commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion can set the tone for new employees. Providing clear information about the company's policies and initiatives ensures that the new team members understand the expectations for fostering an inclusive work environment.
Ongoing training and development
Incorporating diversity, equity, and inclusion in talent management requires continuous learning and development programs for the employees. This includes offering training sessions on unconscious bias, cultural competency, and inclusive leadership, contributing to the overall enhancement of an organization's inclusive outlook.
Performance evaluations and promotions
Organizations should evaluate all employees based on non-biased performance metrics and provide equal opportunities for career growth and development. Encouraging diverse representation in leadership positions can contribute to a more equitable and inclusive work culture.
In conclusion, incorporating diversity, equity, and inclusion in recruitment and talent management processes goes beyond just meeting quotas or legal requirements. It requires establishing comprehensive organizational policies, adopting inclusive practices, and providing ongoing learning opportunities for employees. These steps contribute positively to creating a more diverse, equitable, and inclusive work environment, yielding benefits such as increased innovation, improved problem-solving capabilities, and enhanced employee satisfaction.
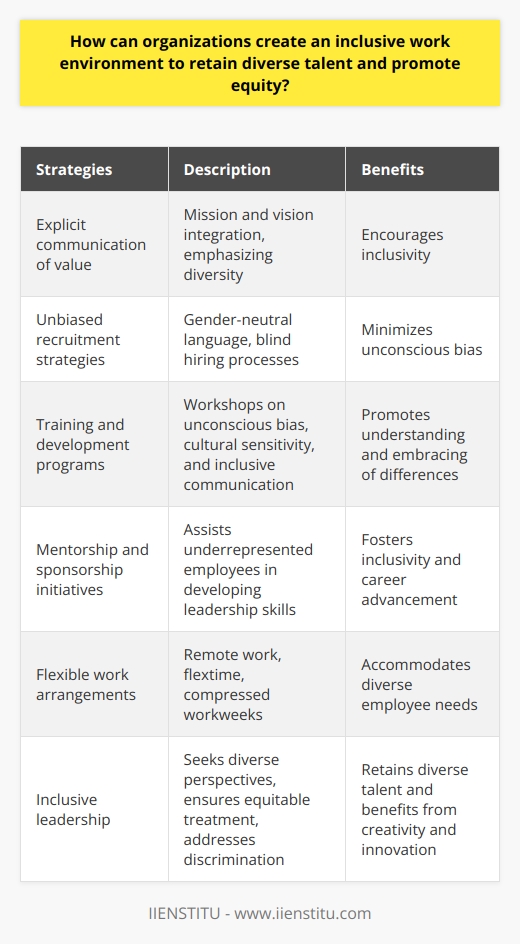
How can organizations create an inclusive work environment to retain diverse talent and promote equity?
Strategies for Inclusive Work Environment
Organizations can create an inclusive work environment by implementing specific policies and practices that promote equity and foster an inclusive culture. Firstly, organizations must explicitly communicate the value of diversity and inclusion, making it a core component of their mission and vision. By doing so, they convey the importance of cultivating a diverse and supportive workplace to all employees.
Recruitment and Selection Process
To retain diverse talent, organizations must begin with their recruitment and hiring processes. They need to adopt unbiased recruitment strategies, such as using gender-neutral language in job postings and adopting blind hiring processes to minimize unconscious bias. Additionally, considering candidates from various educational and professional backgrounds can further contribute to the organization's diversity.
Training and Development Programs
Organizations must also invest in training and development programs that help employees understand and embrace differences among colleagues. This can include workshops on unconscious bias, cultural sensitivity, and inclusive communication. These training sessions should be ongoing and tailored to address the unique needs of the specific workforce.
Mentorship and Sponsorship Initiatives
Establishing an effective mentorship and sponsorship program can further promote an inclusive work environment and improve equity. These programs help underrepresented employees develop leadership skills, advance in their careers, and reach their potential. Furthermore, these initiatives serve to create an inclusive workplace culture by fostering authentic relationships among colleagues with diverse backgrounds.
Flexible Work Arrangements
Inclusive work environments should also consider flexible work arrangements, such as remote work, flextime, and compressed workweeks. By offering flexibility, organizations can better cater to the diverse needs of their workforce, including caregivers, people with disabilities, and employees pursuing personal interests or professional development opportunities.
Inclusive Leadership
Lastly, organizations must commit to inclusive leadership at all levels, from executives to team managers. Inclusive leaders actively seek diverse perspectives during decision-making, ensure equitable treatment of all employees and work to address any instances of discrimination or bias within the workplace. By fostering an inclusive work environment, organizations can not only retain diverse talent, but also benefit from the creativity, innovation, and problem-solving abilities that such a workforce brings.
How can HR professionals address and mitigate instances of discrimination and bias in the workplace to foster a culture of equity, diversity, and inclusion?
Addressing Discrimination and Bias
HR professionals must tackle instances of discrimination and bias by implementing well-defined policies and promoting a culture that values diversity and inclusion. To achieve this, they should focus on the following strategies:
Training and Education
It is essential for HR professionals to develop comprehensive training programs that emphasize the importance of diversity and inclusion. These programs should raise awareness about the different forms of discrimination and bias, as well as provide practical skills to address these challenges. Educating employees and leaders about unconscious bias, cultural sensitivity, and communication is vital for fostering a culture of equity.
Establishing Reporting Mechanisms
HR professionals need to create accessible, transparent, and anonymous reporting mechanisms for employees to share their concerns and experiences related to discrimination and bias. It is crucial to ensure confidentiality and provide protection from retaliation to build trust and encourage open conversations about diversity and inclusion issues.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Regular evaluations and reviews of organizational practices are essential in identifying and addressing potential discrimination and bias. HR professionals should analyze recruitment practices, performance assessments, and promotions to ensure that they are fair, objective, and bias-free. Data-driven insights are key for enhancing equity and driving change.
Inclusive Leadership
Encouraging and supporting diverse leadership is crucial in fostering a culture that values equity, diversity, and inclusion. HR professionals should identify and develop leaders with diverse backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives, as well as provide them with opportunities to lead diversity and inclusion initiatives.
Recognizing and Celebrating Diversity
Celebrating diversity and promoting an inclusive work environment go hand in hand. HR professionals can facilitate events, workshops, and dialogues that honor and recognize the unique contributions of diverse employees. These activities should emphasize the importance of embracing different perspectives, cultures, and talents.
In conclusion, HR professionals have a crucial role in addressing discrimination and bias in the workplace. By focusing on education, reporting mechanisms, monitoring, inclusive leadership, and celebration of diversity, they can foster a culture that supports equity, diversity, and inclusion. These strategies, implemented effectively, will benefit the organization in terms of increased creativity, higher performance, and better employee engagement.

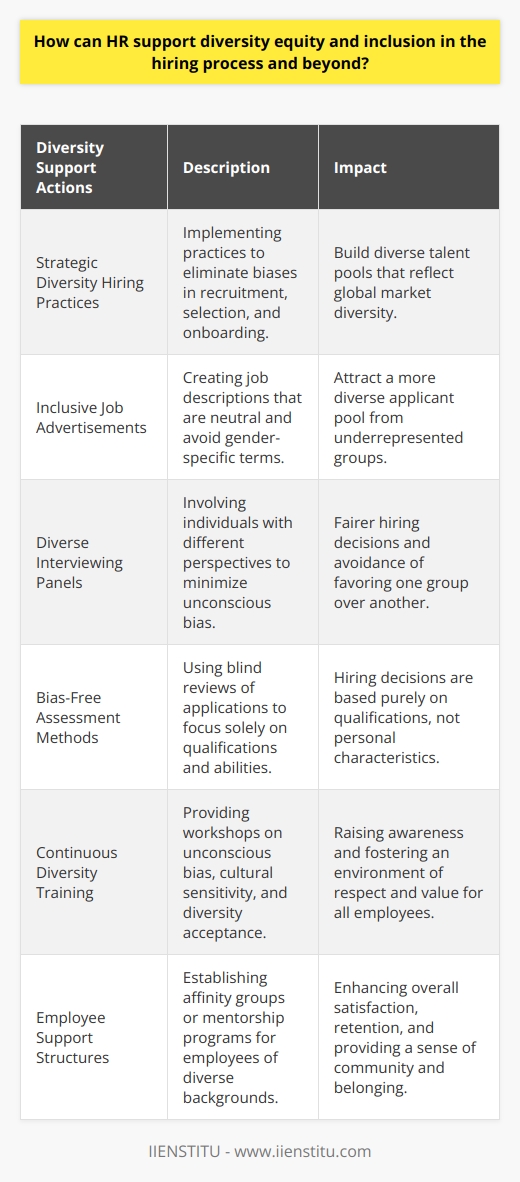
How can HR support diversity equity and inclusion in the hiring process and beyond?
HR and Strategic Diversity Hiring
One key way Human Resources (HR) can support diversity, equity, and inclusion in the hiring process is by implementing strategic diversity hiring. This refers to a set of hiring practices aimed at eliminating biases in recruitment, selection, and onboarding. By employing this method, organizations can increase the diversity of their talent pools, resulting in a workforce that more accurately reflects the diversity of the global market.
Creating Inclusive Job Adverts
Creating inclusive job adverts is another significant step HR can take towards promoting diversity and inclusion. Job descriptions should be neutral, avoiding gender-specific terms. Companies can also make sure they advertise in diverse media sources to reach underrepresented groups.
Diverse Interviewing Panels
Having diverse interviewing panels can help to minimize unconscious bias during the selection process. It ensures various perspectives during candidate assessment, resulting in fairer hiring decisions.
Bias-Free Assessment Methods
HR can use bias-free assessment methods such as blind reviews of applications. This method involves removing details like names from applications, which could influence hiring decisions based on race or gender. It preserves the main focus on the content of the application rather than personal details of applicants.
Continuous Training on Diversity
Beyond the hiring process, HR can foster a culture of diversity and inclusion by providing regular training sessions. This could involve workshops on unconscious bias, cultural sensitivity, and diversity acceptance. By doing so, HR helps to create a work environment where all employees feel respected and valued.
Employee Support Structures
Finally, HR should establish support structures for employees of diverse backgrounds. For example, setting up affinity groups or mentorship programs can provide additional support. It builds a sense of community and belonging, promoting overall satisfaction and retention.
To conclude, HR plays a crucial role in enhancing diversity, equity, and inclusion in the hiring process and beyond. They can achieve this by implementing strategic diversity hiring, creating inclusive job adverts, ensuring a diverse interviewing panel, using bias-free assessment methods, providing diversity training, and establishing employee support structures. This not only enriches the workforce but also contributes to the overall success of the organization.
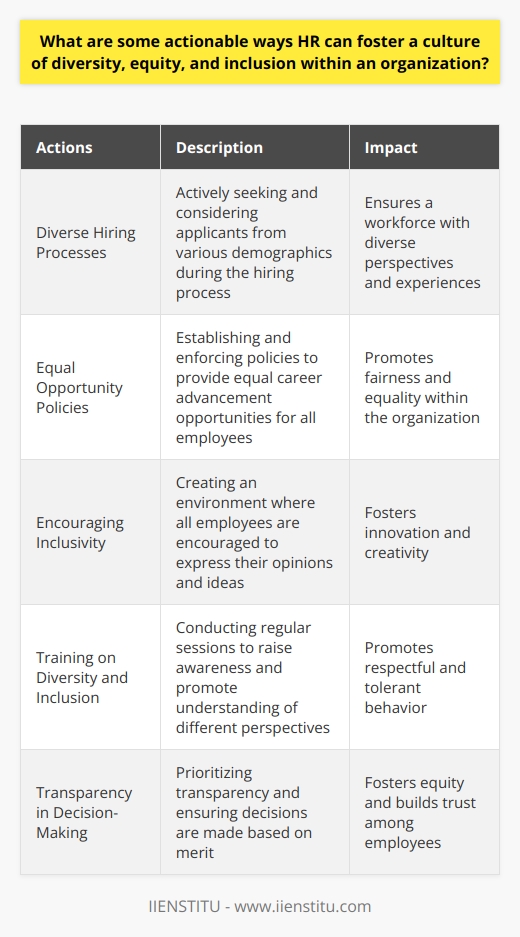
What are some actionable ways HR can foster a culture of diversity, equity, and inclusion within an organization?
Creating a Culture of Diversity
Human Resources (HR) can create a diverse, inclusive and equitable work culture through various ways. First, the hiring processes should reflect diversity. HR should consider applicants of various ethnicities, genders, age groups and backgrounds, enhancing the organization's diversity.
Promoting Equality in the Organization
Second, HR must establish equal opportunities policies. This means all employees should get an equal chance to advance in their career, regardless of race, religion, or gender. By doing so, HR fosters an atmosphere of equality and fairness.
Encouraging Inclusivity
The third approach is through inclusivity. HR should encourage employees to voice their opinions and ideas openly. This move builds an inclusive culture, where every voice counts, enhancing innovation and creativity.
Training on Diversity and Inclusion
Further, the role of training and workshops in supporting diversity and inclusion cannot be overlooked. HR should conduct regular training sessions to raise employees' awareness about the importance of diversity, equity, and inclusion. These learning interventions will help inculcate the principles of respect and tolerance among staff.
Transparency in Decision-Making
Lastly, HR should emphasize transparency. Decisions should not favor any group, and everyone should have access to all necessary information. Transparent practices ensure equity and build trust among employees, enhancing the overall culture of diversity and inclusion.
In conclusion, HR plays a crucial role in fostering an atmosphere of diversity, equity, and inclusion. By using the right strategies such as equal opportunity policies, promoting inclusivity, imparting training, and adopting transparent practices, HR can ensure a robust and diverse corporate culture.
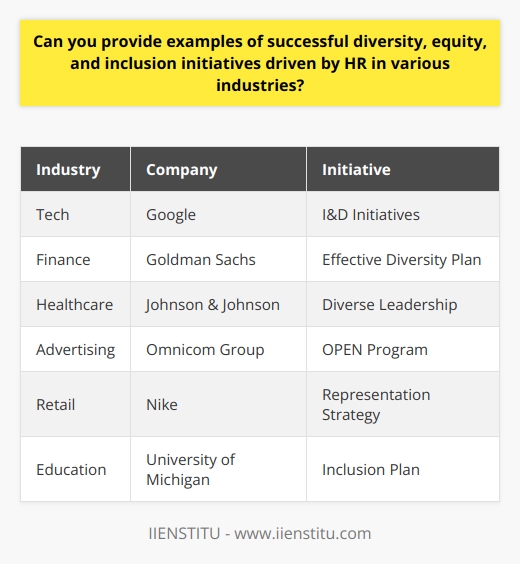
Can you provide examples of successful diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives driven by HR in various industries?
Tech Industry Example: Google’s I&D Initiatives
Multi-billion tech company, Google, stands out for its commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion. Through a diversity annual report, they publicly track and share their progress. Google also offers retention programs focused on maintaining a multicultural workforce.
Finance Sector Example: Goldman Sachs’ Effective Diversity Plan
Goldman Sachs promotes gender equality by ensuring at least 40% of their incoming analyst class are women. They are consistent in breaking the gender gap and allowing everyone to thrive regardless of their gender.
Healthcare Example: Johnson & Johnson’s Diverse Leadership
Johnson & Johnson actively supports diversity in leadership. They continue to work on achieving gender parity at the management board level. They also have a formal mentoring program to nurture minorities, women, and veterans.
Advertising Industry Example: The Omnicom Group’s OPEN Program
Advertising firm, Omnicom Group introduced the OPEN (Omnicom People Engagement Network) program. It includes several employee resource groups focused on different facets of diversity. OPEN ensures colleagues understand and respect specified sub-cultures and their impact on the business.
Retail Sector Example: Nike’s Representation Strategy
Nike is known for its commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion. They set clear diversity targets; for example, raising the number of women and racial/ethnic minorities in leadership roles. Nike continues to work towards their targets and publish progress reports.
Education Sector Example: The University of Michigan’s Inclusion Plan
The University of Michigan is actively making the campus more inclusive. Their strategic plan includes mandatory unconscious-bias training for staff and faculty. This initiative aims to create a more welcoming environment for all students.
These examples show successful diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives from various industries. Each of these strategies has a significant impact on the respective organizations' culture, morale, and ultimately, their bottom line.